Ghost work, characterized by invisible digital labor performed behind the scenes, contrasts sharply with job sharing, where multiple employees collaboratively split responsibilities for a single position. Ghost work powers many online platforms through tasks like data labeling and content moderation, while job sharing enhances work-life balance and productivity by distributing workload among colleagues. Explore the evolving employment landscape to understand how these models impact the future of work.
Why it is important
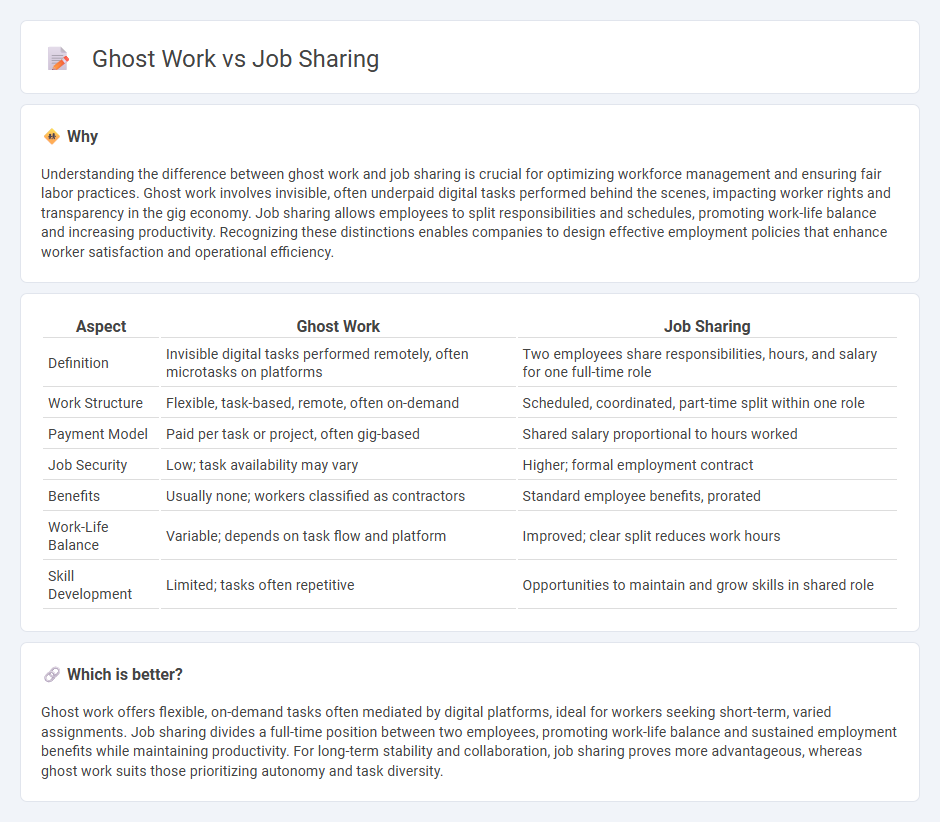
Understanding the difference between ghost work and job sharing is crucial for optimizing workforce management and ensuring fair labor practices. Ghost work involves invisible, often underpaid digital tasks performed behind the scenes, impacting worker rights and transparency in the gig economy. Job sharing allows employees to split responsibilities and schedules, promoting work-life balance and increasing productivity. Recognizing these distinctions enables companies to design effective employment policies that enhance worker satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Job Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invisible digital tasks performed remotely, often microtasks on platforms | Two employees share responsibilities, hours, and salary for one full-time role |
| Work Structure | Flexible, task-based, remote, often on-demand | Scheduled, coordinated, part-time split within one role |
| Payment Model | Paid per task or project, often gig-based | Shared salary proportional to hours worked |
| Job Security | Low; task availability may vary | Higher; formal employment contract |
| Benefits | Usually none; workers classified as contractors | Standard employee benefits, prorated |
| Work-Life Balance | Variable; depends on task flow and platform | Improved; clear split reduces work hours |
| Skill Development | Limited; tasks often repetitive | Opportunities to maintain and grow skills in shared role |
Which is better?
Ghost work offers flexible, on-demand tasks often mediated by digital platforms, ideal for workers seeking short-term, varied assignments. Job sharing divides a full-time position between two employees, promoting work-life balance and sustained employment benefits while maintaining productivity. For long-term stability and collaboration, job sharing proves more advantageous, whereas ghost work suits those prioritizing autonomy and task diversity.
Connection
Ghost work, which involves invisible or behind-the-scenes digital tasks, intersects with job sharing by distributing workload among multiple individuals, enhancing flexibility and efficiency in employment. This connection allows companies to break down complex projects into smaller tasks, assigned to a distributed workforce, leading to optimized resource utilization. The combination of ghost work and job sharing supports gig economy dynamics and promotes diverse, scalable employment models.
Key Terms
Task allocation
Job sharing distributes tasks between two employees who split responsibilities and work hours, ensuring balanced workload and enhanced collaboration. Ghost work involves assigning microtasks to remote workers via online platforms, often without recognition or direct employment status. Discover how task allocation varies significantly between these models and impacts workforce management.
Flexibility
Job sharing offers flexibility by allowing two or more employees to split responsibilities and hours within a single full-time position, enhancing work-life balance and productivity. Ghost work, often involving on-demand, task-based jobs, provides temporal and locational flexibility but may lack job security and benefits. Explore how these flexible work models impact employee satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Worker visibility
Job sharing enhances worker visibility by clearly defining shared responsibilities between employees, allowing both individuals to receive recognition and career advancement opportunities. In contrast, ghost work involves invisible labor, where workers complete tasks without acknowledgment or transparency, often obscuring their contributions in digital platforms. Explore how increasing worker visibility can transform labor practices and empower employees.
Source and External Links
The Benefits of Job Sharing for Employers and Employees - Job sharing is an employment arrangement where two or more employees share the responsibilities and duties of a single full-time job by dividing work hours and tasks, enabling part-time work while covering the full position collectively.
What is job sharing? - Job sharing is a flexible working form allowing two employees to share one full-time role's duties and pay on a pro-rata basis, often splitting hours by days or shifts and requiring strong communication and compatibility for success.
Job sharing - Job sharing involves two or more people working part-time on one full-time position, sharing workload, pay, holidays, and responsibilities jointly while reducing individual work hours and income proportionally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com