Talent hoarding occurs when managers retain skilled employees within their teams to maintain expertise and control, potentially limiting organizational flexibility and growth. Job rotation systematically moves employees across different roles and departments to enhance skill diversity, boost engagement, and foster a more adaptable workforce. Discover how balancing talent hoarding and job rotation can optimize employee development and organizational performance.
Why it is important
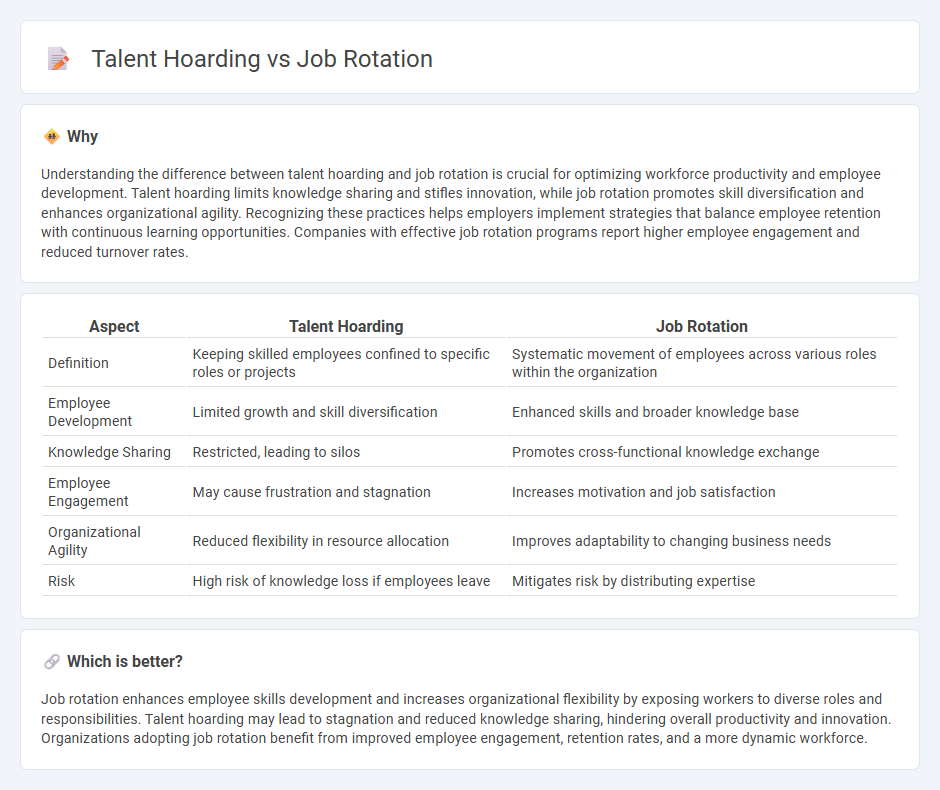
Understanding the difference between talent hoarding and job rotation is crucial for optimizing workforce productivity and employee development. Talent hoarding limits knowledge sharing and stifles innovation, while job rotation promotes skill diversification and enhances organizational agility. Recognizing these practices helps employers implement strategies that balance employee retention with continuous learning opportunities. Companies with effective job rotation programs report higher employee engagement and reduced turnover rates.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Talent Hoarding | Job Rotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Keeping skilled employees confined to specific roles or projects | Systematic movement of employees across various roles within the organization |
| Employee Development | Limited growth and skill diversification | Enhanced skills and broader knowledge base |
| Knowledge Sharing | Restricted, leading to silos | Promotes cross-functional knowledge exchange |
| Employee Engagement | May cause frustration and stagnation | Increases motivation and job satisfaction |
| Organizational Agility | Reduced flexibility in resource allocation | Improves adaptability to changing business needs |
| Risk | High risk of knowledge loss if employees leave | Mitigates risk by distributing expertise |
Which is better?
Job rotation enhances employee skills development and increases organizational flexibility by exposing workers to diverse roles and responsibilities. Talent hoarding may lead to stagnation and reduced knowledge sharing, hindering overall productivity and innovation. Organizations adopting job rotation benefit from improved employee engagement, retention rates, and a more dynamic workforce.
Connection
Talent hoarding occurs when employees or managers retain skilled individuals within a team to maintain control over critical knowledge and resources, limiting opportunities for others. Job rotation mitigates talent hoarding by systematically moving employees across roles, promoting skill diversification and knowledge transfer throughout the organization. This dynamic enhances workforce flexibility, innovation, and succession planning, fostering overall organizational resilience.
Key Terms
Skill Development
Job rotation enhances skill development by exposing employees to diverse roles, fostering adaptability and comprehensive expertise within the organization. Talent hoarding limits growth opportunities, restricting employees' skillsets and hindering overall organizational agility. Explore strategic approaches to maximize workforce capabilities and drive continuous learning.
Workforce Flexibility
Job rotation enhances workforce flexibility by enabling employees to acquire diverse skills, promoting adaptability and reducing skill silos within organizations. Talent hoarding restricts career development and stifles organizational agility by limiting knowledge sharing and employee mobility. Explore strategies to balance job rotation and talent retention for optimizing workforce flexibility.
Internal Mobility
Job rotation enhances internal mobility by exposing employees to diverse roles, which broadens skill sets and fosters adaptability within the organization. Talent hoarding, however, restricts this growth by limiting knowledge sharing and career progression opportunities, resulting in stagnation and decreased employee engagement. Explore strategies to balance job rotation and talent management to maximize workforce potential and retention.
Source and External Links
Job rotation - Wikipedia - Job rotation is the lateral transfer of employees between jobs in an organization without a change in their hierarchical rank or salary grade, used to enhance skills, motivation, career development, and manage fatigue, differing from promotion and specialization.
Job rotation | EBSCO Research Starters - Job rotation is a human resources strategy that moves employees between jobs to cultivate broad skills, reduce monotony and burnout, and improve workforce flexibility and productivity.
What is Job Rotation: Types, Training Methods, Benefits - Job rotation involves laterally moving employees to different positions, departments, or locations to develop skills and includes types such as horizontal (same level roles) and vertical (different hierarchical levels) rotations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com