Digital nomad visas offer remote workers flexible, short-term residency in foreign countries, allowing them to work legally while traveling without the need for traditional employment sponsorship. Green cards provide permanent residency in the United States, granting holders the right to live and work indefinitely with a pathway to citizenship. Explore the benefits and eligibility requirements of both options to determine the best fit for your global career ambitions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital nomad visas and green cards is crucial for employment because digital nomad visas offer temporary remote work permissions without permanent residency rights, while green cards provide lawful permanent resident status enabling full work authorization and benefits. Digital nomad visas typically cater to foreign employees working remotely for foreign companies, limiting access to local employment markets and social services. Green card holders can access a broader range of employment opportunities, participate in social security programs, and pursue permanent residency or citizenship. Clarifying these distinctions ensures compliance with immigration laws and optimizes long-term career planning.
Comparison Table
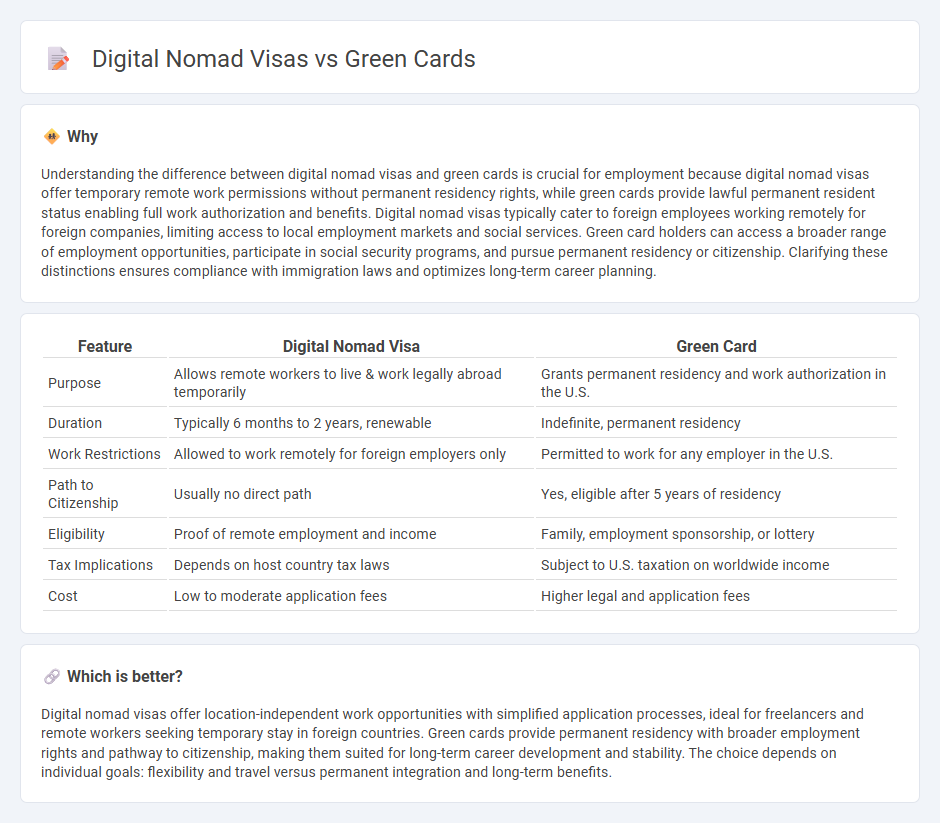
| Feature | Digital Nomad Visa | Green Card |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Allows remote workers to live & work legally abroad temporarily | Grants permanent residency and work authorization in the U.S. |
| Duration | Typically 6 months to 2 years, renewable | Indefinite, permanent residency |
| Work Restrictions | Allowed to work remotely for foreign employers only | Permitted to work for any employer in the U.S. |
| Path to Citizenship | Usually no direct path | Yes, eligible after 5 years of residency |
| Eligibility | Proof of remote employment and income | Family, employment sponsorship, or lottery |
| Tax Implications | Depends on host country tax laws | Subject to U.S. taxation on worldwide income |
| Cost | Low to moderate application fees | Higher legal and application fees |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer location-independent work opportunities with simplified application processes, ideal for freelancers and remote workers seeking temporary stay in foreign countries. Green cards provide permanent residency with broader employment rights and pathway to citizenship, making them suited for long-term career development and stability. The choice depends on individual goals: flexibility and travel versus permanent integration and long-term benefits.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and green cards both facilitate extended legal work and residency for individuals in foreign countries, enabling remote employment without traditional work permits. These permits support the global shift toward flexible employment by allowing professionals to contribute economically while residing abroad temporarily or permanently. The integration of digital nomad visas with immigration pathways like green cards reflects evolving labor mobility policies addressing the rise of remote work and international talent acquisition.
Key Terms
Permanent Residency
Green cards provide permanent residency status in the United States, allowing holders to live and work indefinitely with a path to citizenship. Digital nomad visas offer temporary residence for remote workers, typically lasting from six months to a few years without conferring permanent residency rights. Explore the detailed differences between green cards and digital nomad visas to determine which option best suits your long-term residency goals.
Remote Work Authorization
Green cards grant permanent residency and unrestricted remote work authorization across the United States, enabling holders to live and work without employer sponsorship. Digital nomad visas offer temporary remote work permits, typically ranging from six months to two years, allowing foreign nationals to legally work remotely while residing in a specific country. Explore detailed comparisons of eligibility, benefits, and application processes to choose the best remote work authorization option for your lifestyle.
Tax Residency
Green cards grant permanent residency in the U.S., establishing clear tax residency with worldwide income taxation and obligations such as filing annual tax returns. Digital nomad visas offer temporary legal stay in various countries, where tax residency rules vary based on duration of stay and local regulations, often allowing avoidance of full tax residency status. Explore detailed comparisons of tax implications and residency requirements to choose the best option for your financial planning.
Source and External Links
Green card - A green card, officially a permanent resident card, is a U.S. identity document proving permanent residency, allowing holders to live and work in the United States and apply for citizenship after meeting certain requirements.
Green Card - The USCIS website explains eligibility categories, application processes, and procedures to apply for a Green Card to live and work permanently in the U.S., including details on adjustment of status and card replacement.
Get a Green Card - Green Card holders are authorized permanent residents who can obtain the card through family or employer sponsorship, humanitarian programs, or individual filings granted by USCIS as proof of permanent resident status.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com