Gig platforms offer flexible work opportunities, allowing individuals to choose projects and set their schedules, which contrasts with the structured hours and stability of full-time employment. Full-time jobs typically provide consistent income, benefits, and long-term career growth, whereas gig work often lacks these securities but offers autonomy and variety. Explore the differences in job security, income stability, and work-life balance to determine the best fit for your career goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between gig platforms and full-time employment is crucial for managing financial stability, benefits eligibility, and career growth opportunities. Gig platforms offer flexibility and short-term engagements without traditional employee benefits like health insurance or retirement plans. Full-time employment provides steady income, job security, and access to comprehensive benefits, impacting long-term financial planning. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals make informed decisions aligning with their lifestyle and professional goals.
Comparison Table
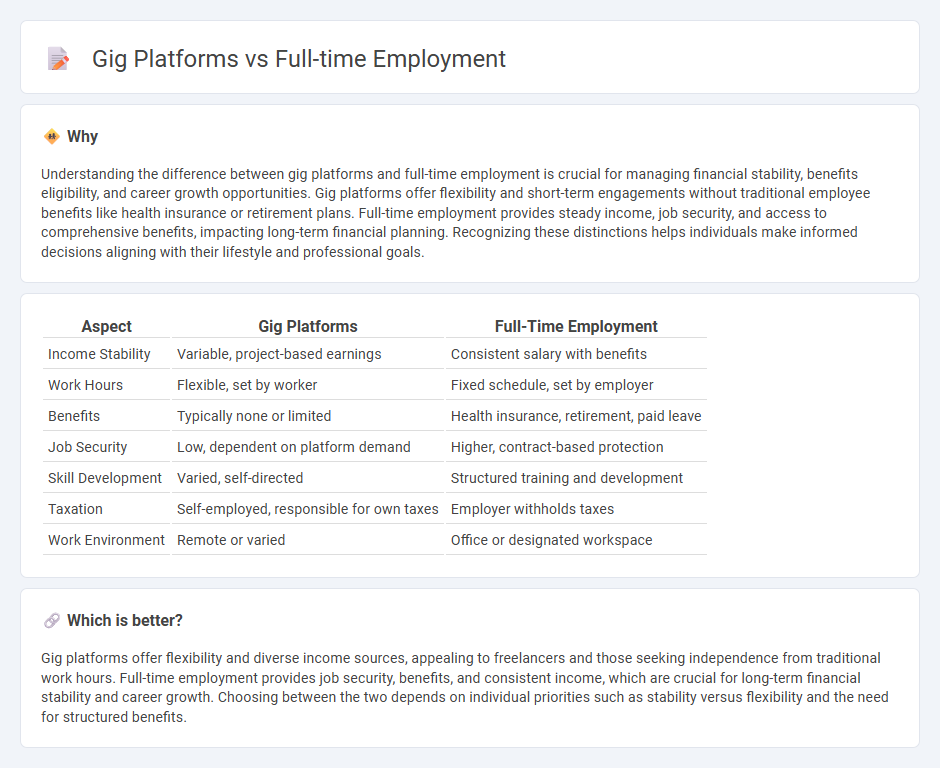
| Aspect | Gig Platforms | Full-Time Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Income Stability | Variable, project-based earnings | Consistent salary with benefits |
| Work Hours | Flexible, set by worker | Fixed schedule, set by employer |
| Benefits | Typically none or limited | Health insurance, retirement, paid leave |
| Job Security | Low, dependent on platform demand | Higher, contract-based protection |
| Skill Development | Varied, self-directed | Structured training and development |
| Taxation | Self-employed, responsible for own taxes | Employer withholds taxes |
| Work Environment | Remote or varied | Office or designated workspace |
Which is better?
Gig platforms offer flexibility and diverse income sources, appealing to freelancers and those seeking independence from traditional work hours. Full-time employment provides job security, benefits, and consistent income, which are crucial for long-term financial stability and career growth. Choosing between the two depends on individual priorities such as stability versus flexibility and the need for structured benefits.
Connection
Gig platforms complement full-time employment by offering flexible job opportunities that allow workers to supplement their income or develop new skills outside traditional roles. These platforms often provide on-demand tasks that can fill gaps between full-time commitments, enhancing workforce adaptability and economic resilience. Integration of gig work with permanent employment creates a hybrid labor model that addresses diverse worker preferences and market demands.
Key Terms
Job Security
Full-time employment offers consistent income, comprehensive benefits, and legal protections that enhance job security for workers. Gig platforms provide flexibility but often lack guaranteed wages, benefits, and long-term stability, leading to higher financial uncertainty. Discover detailed insights and strategies for balancing job security within these evolving work models.
Flexibility
Full-time employment offers structured hours and consistent income, but often limits flexibility in work location and schedule. Gig platforms provide increased autonomy, allowing workers to choose tasks and set their own hours, accommodating personal and lifestyle needs. Explore the advantages of flexibility in both models to determine which fits your career goals best.
Benefits
Full-time employment typically offers comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security, providing workers with financial stability and longer-term support. Gig platforms often lack these traditional benefits, instead offering flexibility and control over work schedules, but frequently leaving workers responsible for their own health coverage and retirement savings. Explore the key differences in employee benefits to determine which work arrangement best suits your needs.
Source and External Links
Full-time employment | EBSCO Research Starters - In the U.S., full-time employment is typically defined as working at least 30 hours per week, with the Affordable Care Act (ACA) using this threshold for health benefit requirements, but employers may set their own higher standards for internal purposes.
Part-Time vs Full-Time: How Many Hours & How to Classify? - According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, full-time employment is usually at least 35 hours per week, but the definition can vary by organization, and it's essential for employers to specify their own guidelines for benefits and pay.
Identifying full-time employees | Internal Revenue Service - For ACA compliance, the IRS defines a full-time employee as someone employed on average at least 30 hours per week (130 hours per month), using either a monthly measurement or a look-back measurement method.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com