Quiet quitting involves employees disengaging from extra work without formally leaving their jobs, reflecting a boundary between effort and personal life. Resenteeism occurs when employees attend work despite poor health or low motivation, often leading to decreased productivity and increased errors. Explore the implications of these workplace behaviors to better understand modern employment dynamics.
Why it is important
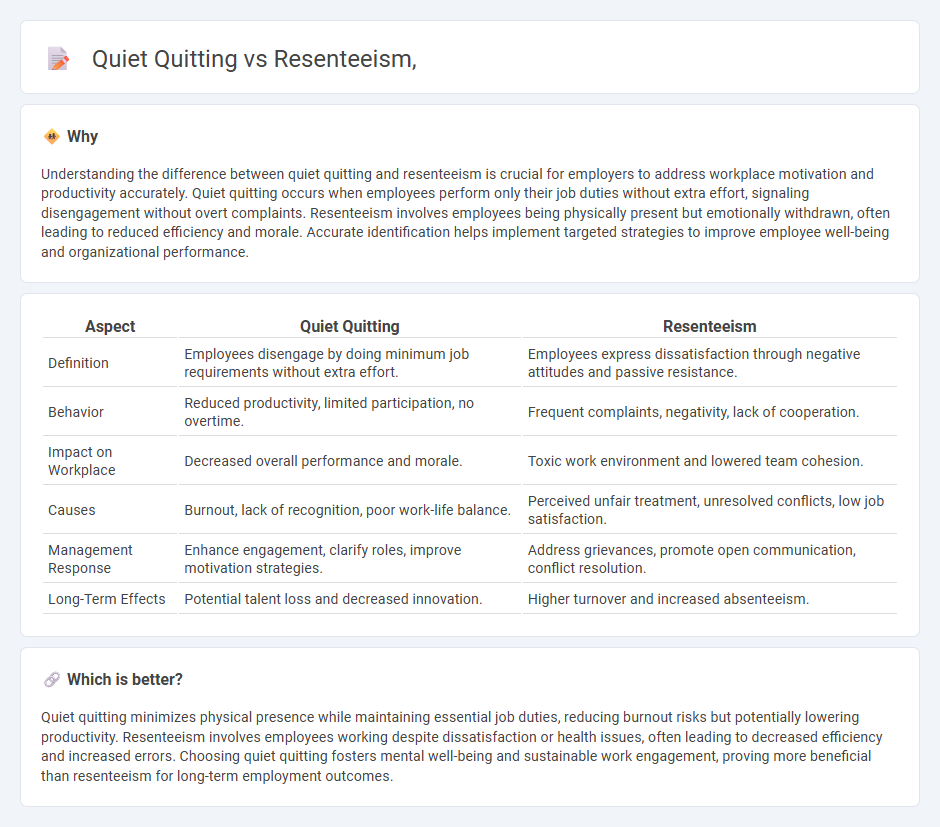
Understanding the difference between quiet quitting and resenteeism is crucial for employers to address workplace motivation and productivity accurately. Quiet quitting occurs when employees perform only their job duties without extra effort, signaling disengagement without overt complaints. Resenteeism involves employees being physically present but emotionally withdrawn, often leading to reduced efficiency and morale. Accurate identification helps implement targeted strategies to improve employee well-being and organizational performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Quitting | Resenteeism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees disengage by doing minimum job requirements without extra effort. | Employees express dissatisfaction through negative attitudes and passive resistance. |
| Behavior | Reduced productivity, limited participation, no overtime. | Frequent complaints, negativity, lack of cooperation. |
| Impact on Workplace | Decreased overall performance and morale. | Toxic work environment and lowered team cohesion. |
| Causes | Burnout, lack of recognition, poor work-life balance. | Perceived unfair treatment, unresolved conflicts, low job satisfaction. |
| Management Response | Enhance engagement, clarify roles, improve motivation strategies. | Address grievances, promote open communication, conflict resolution. |
| Long-Term Effects | Potential talent loss and decreased innovation. | Higher turnover and increased absenteeism. |
Which is better?
Quiet quitting minimizes physical presence while maintaining essential job duties, reducing burnout risks but potentially lowering productivity. Resenteeism involves employees working despite dissatisfaction or health issues, often leading to decreased efficiency and increased errors. Choosing quiet quitting fosters mental well-being and sustainable work engagement, proving more beneficial than resenteeism for long-term employment outcomes.
Connection
Quiet quitting and presenteeism are connected through employee disengagement and reduced productivity, where quiet quitting manifests as doing only minimum work while still physically present. Both behaviors reflect a lack of motivation and satisfaction, leading to ineffective work performance and potential burnout. Addressing workplace culture and employee well-being is crucial to mitigating these issues and improving overall organizational efficiency.
Key Terms
Disengagement
Resenteeism and quiet quitting both reflect employee disengagement but manifest differently; presenteeism involves employees physically present but mentally withdrawn, while quiet quitting entails doing the bare minimum without formal resignation. These behaviors signal underlying dissatisfaction and reduced productivity, impacting organizational performance and employee morale. Explore effective strategies to recognize and address disengagement for a healthier workplace environment.
Job dissatisfaction
Job dissatisfaction often drives both presenteeism and quiet quitting, where employees either show up physically but remain disengaged or reduce effort to the bare minimum. Presenteeism impacts productivity due to hidden disengagement despite physical attendance, while quiet quitting signals deeper dissatisfaction through withdrawal from extra-role activities. Explore further to understand how addressing job dissatisfaction can mitigate these workforce challenges.
Presenteeism
Presenteeism occurs when employees are physically present at work but perform below their full capacity due to illness, stress, or disengagement, leading to reduced productivity and increased organizational costs. Unlike quiet quitting, where employees intentionally limit their efforts to meet job requirements without extra involvement, presenteeism hides under the surface of attendance metrics and often goes unnoticed by management. Explore how addressing presenteeism can enhance workforce well-being and operational efficiency in your organization.
Source and External Links
Resenteeism - Wikipedia - Resenteeism is a workplace phenomenon where individuals remain in unfulfilling jobs out of fear or lack of alternatives, leading to resentment, disengagement, and negative mental health impacts; it rose after the COVID-19 pandemic and is linked to poor workplace culture and diminished employee engagement.
Resenteeism: Can You Spot the Signs in Your Workplace? - AIHR - Resenteeism occurs when employees stay in their jobs despite dissatisfaction due to financial constraints, lack of alternatives, or workplace inflexibility, resulting in mental withdrawal, reduced productivity, and potential toxicity in work environments that HR can address by fostering trust and open communication.
What is Resenteeism and How Does it Impact Workplace Productivity? - Shiftbase - Resenteeism describes employees who physically attend work but are mentally disengaged and resentful, doing the bare minimum and not feeling valued; it differs from absenteeism and presenteeism by involving physical presence yet emotional and cognitive withdrawal.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com