An ethical supply chain prioritizes fair labor practices, transparency, and adherence to human rights standards throughout the production process. A sustainable supply chain focuses on minimizing environmental impact by reducing waste, lowering carbon emissions, and promoting resource efficiency. Explore our insights to understand how integrating both approaches drives responsible business growth.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between an ethical supply chain and a sustainable supply chain is crucial for consulting professionals to design strategies that align with a client's core values and regulatory requirements. Ethical supply chains focus on human rights, fair labor practices, and transparency, while sustainable supply chains emphasize environmental impact, resource efficiency, and long-term ecological balance. Consultants must tailor recommendations based on these distinctions to mitigate risks, enhance brand reputation, and ensure compliance with industry standards. Accurate knowledge enables the development of comprehensive solutions that address both social responsibility and environmental sustainability effectively.
Comparison Table
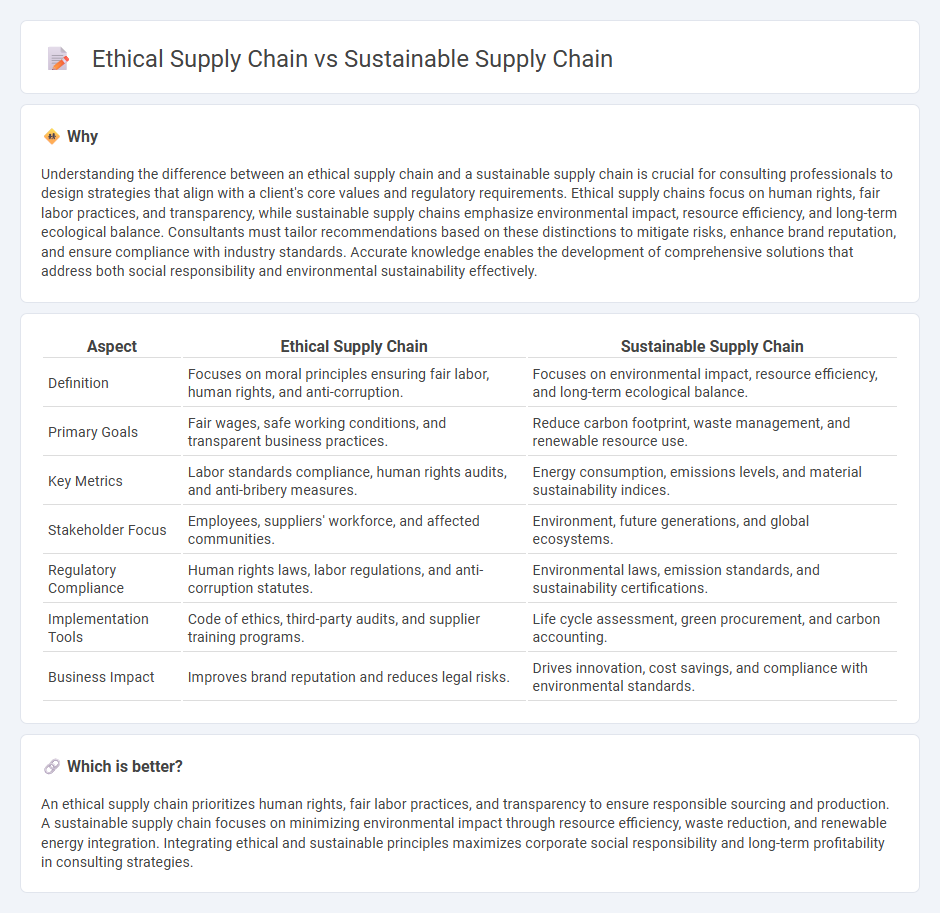
| Aspect | Ethical Supply Chain | Sustainable Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on moral principles ensuring fair labor, human rights, and anti-corruption. | Focuses on environmental impact, resource efficiency, and long-term ecological balance. |
| Primary Goals | Fair wages, safe working conditions, and transparent business practices. | Reduce carbon footprint, waste management, and renewable resource use. |
| Key Metrics | Labor standards compliance, human rights audits, and anti-bribery measures. | Energy consumption, emissions levels, and material sustainability indices. |
| Stakeholder Focus | Employees, suppliers' workforce, and affected communities. | Environment, future generations, and global ecosystems. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Human rights laws, labor regulations, and anti-corruption statutes. | Environmental laws, emission standards, and sustainability certifications. |
| Implementation Tools | Code of ethics, third-party audits, and supplier training programs. | Life cycle assessment, green procurement, and carbon accounting. |
| Business Impact | Improves brand reputation and reduces legal risks. | Drives innovation, cost savings, and compliance with environmental standards. |
Which is better?
An ethical supply chain prioritizes human rights, fair labor practices, and transparency to ensure responsible sourcing and production. A sustainable supply chain focuses on minimizing environmental impact through resource efficiency, waste reduction, and renewable energy integration. Integrating ethical and sustainable principles maximizes corporate social responsibility and long-term profitability in consulting strategies.
Connection
Ethical supply chain practices ensure fair labor conditions, transparency, and responsible sourcing while sustainable supply chains focus on minimizing environmental impact through resource efficiency and waste reduction. Both concepts intersect by promoting corporate social responsibility and long-term viability in procurement and production processes. Integrating ethical and sustainable supply chain strategies enhances brand reputation, compliance with regulations, and stakeholder trust.
Key Terms
Environmental Impact
A sustainable supply chain prioritizes reducing environmental footprints through waste minimization, energy efficiency, and resource conservation, ensuring long-term ecological balance. An ethical supply chain emphasizes fair labor practices and human rights while also addressing environmental responsibilities to prevent exploitation and degradation. Discover how integrating both approaches can create a resilient and responsible supply network.
Labor Standards
Sustainable supply chains prioritize environmental impact reduction and resource efficiency, while ethical supply chains emphasize fair labor practices, human rights, and worker well-being. Labor standards in ethical supply chains include fair wages, safe working conditions, and the prohibition of child or forced labor. Discover more about how these approaches shape responsible business operations and impact global industries.
Supplier Transparency
Supplier transparency in a sustainable supply chain emphasizes reducing environmental impact through clear visibility into sourcing, energy use, and waste management practices, ensuring eco-friendly operations. Ethical supply chains prioritize transparency related to labor rights, fair wages, and working conditions, promoting human rights and social responsibility within the supplier network. Discover how understanding these transparency aspects can enhance your supply chain strategy.
Source and External Links
What Is Sustainable Supply Chain Management? - IBM - Sustainable supply chain management integrates environmental, social, and financial considerations into sourcing, production, and distribution, focusing on reducing emissions, ethical labor practices, and cost/risk management through technology and supplier collaboration.
What Is Supply Chain Sustainability and Why Is It Important? - NetSuite - Supply chain sustainability addresses the environmental and human impacts across multiple supplier tiers, emphasizing the need for visibility and due diligence to prevent harmful practices and uphold sustainability throughout the supply network.
Supply chain sustainability: what is it and why is it important? - Sedex - A sustainable supply chain uses environmentally and socially responsible practices at every stage, including protecting workers' rights and reducing environmental harm, highlighting the need to address both ecological and social factors for true sustainability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com