Regenerative business models focus on restoring and rejuvenating environmental and social systems through circular practices and sustainable innovation, driving long-term resilience and positive impact. Social enterprises prioritize addressing social issues by integrating mission-driven goals with business strategies to create measurable community benefits and economic value. Explore how these approaches redefine success and inspire transformative change in the business landscape.
Why it is important
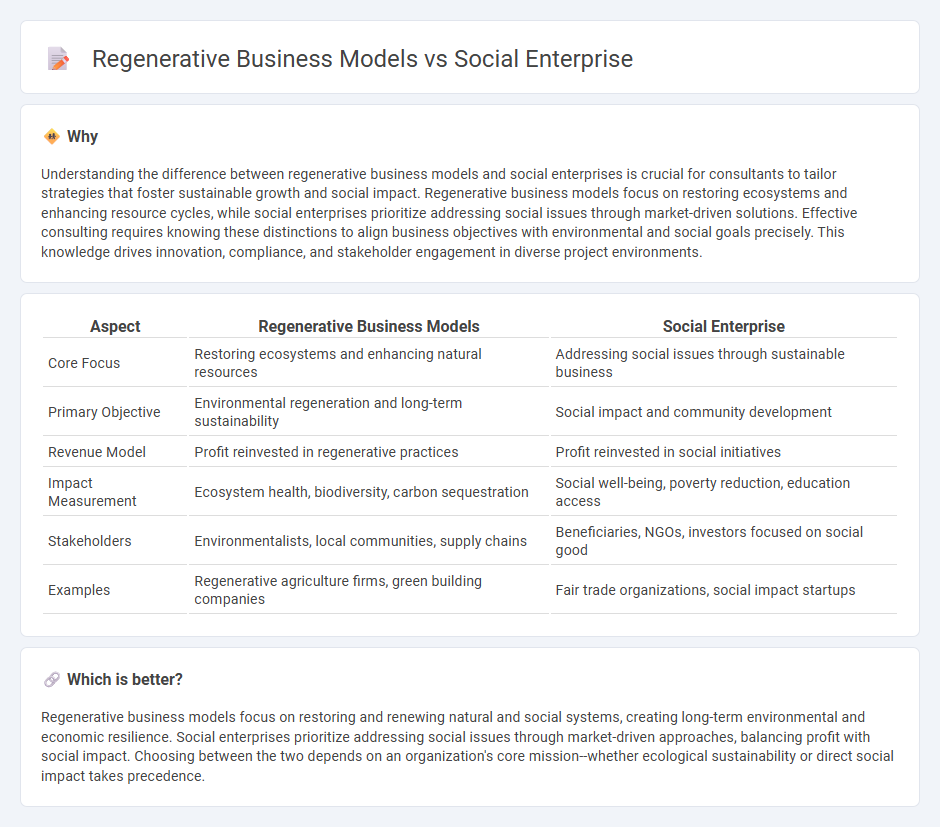
Understanding the difference between regenerative business models and social enterprises is crucial for consultants to tailor strategies that foster sustainable growth and social impact. Regenerative business models focus on restoring ecosystems and enhancing resource cycles, while social enterprises prioritize addressing social issues through market-driven solutions. Effective consulting requires knowing these distinctions to align business objectives with environmental and social goals precisely. This knowledge drives innovation, compliance, and stakeholder engagement in diverse project environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Regenerative Business Models | Social Enterprise |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Restoring ecosystems and enhancing natural resources | Addressing social issues through sustainable business |
| Primary Objective | Environmental regeneration and long-term sustainability | Social impact and community development |
| Revenue Model | Profit reinvested in regenerative practices | Profit reinvested in social initiatives |
| Impact Measurement | Ecosystem health, biodiversity, carbon sequestration | Social well-being, poverty reduction, education access |
| Stakeholders | Environmentalists, local communities, supply chains | Beneficiaries, NGOs, investors focused on social good |
| Examples | Regenerative agriculture firms, green building companies | Fair trade organizations, social impact startups |
Which is better?
Regenerative business models focus on restoring and renewing natural and social systems, creating long-term environmental and economic resilience. Social enterprises prioritize addressing social issues through market-driven approaches, balancing profit with social impact. Choosing between the two depends on an organization's core mission--whether ecological sustainability or direct social impact takes precedence.
Connection
Regenerative business models prioritize restoring natural and social systems, aligning closely with social enterprises that aim to create positive community impact alongside financial returns. Both approaches integrate sustainability principles with innovative solutions to address environmental degradation and social inequality. This interconnected focus enhances long-term value creation by fostering economic resilience and social well-being.
Key Terms
Triple Bottom Line
Social enterprises prioritize people, planet, and profit equally within the Triple Bottom Line framework, aiming for sustainable community impact. Regenerative business models go further by renewing natural ecosystems and enhancing social equity alongside economic viability, creating positive feedback loops that restore and improve resources over time. Explore deeper insights into how these models redefine success and drive systemic change.
Circular Economy
Social enterprises prioritize addressing social issues through sustainable business practices, often measuring impact in terms of community well-being and social equity. Regenerative business models emphasize restoring and enhancing natural ecosystems by integrating circular economy principles such as resource recovery, waste minimization, and product lifecycle extension. Discover how embracing circular economy strategies can transform business impact and drive sustainability at scale.
Impact Measurement
Social enterprises primarily measure impact through social and environmental performance metrics, emphasizing community well-being and equity. Regenerative business models extend this by incorporating systems thinking and ecological health indicators to restore and enhance natural and social capital. Explore how innovative impact measurement tools can transform your approach to sustainable business outcomes.
Source and External Links
Social enterprise - Wikipedia - A social enterprise is an organization applying commercial strategies to maximize improvements in financial, social, and environmental well-being, aiming to generate social impact alongside profits and operate sustainably without relying solely on philanthropy.
What is a Social Enterprise? - Definition & Examples - A social enterprise is a business that prioritizes social or environmental goals over profits, operating with entrepreneurial approaches to provide sustainable solutions to social problems and reinvesting profits back into their social mission.
14 Social Enterprises & Examples: How They Impact the World - Social enterprises use business strategies to intentionally tackle social and environmental issues by reinvesting profits to benefit communities, such as through fair trade or eco-friendly businesses, supporting marginalized groups, and creating employment opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com