Diagnostic mapping offers a detailed visualization of organizational processes and pain points, enabling targeted interventions. SWOT analysis systematically evaluates internal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to guide strategic decision-making. Explore deeper insights into how these complementary tools enhance consulting outcomes.
Why it is important
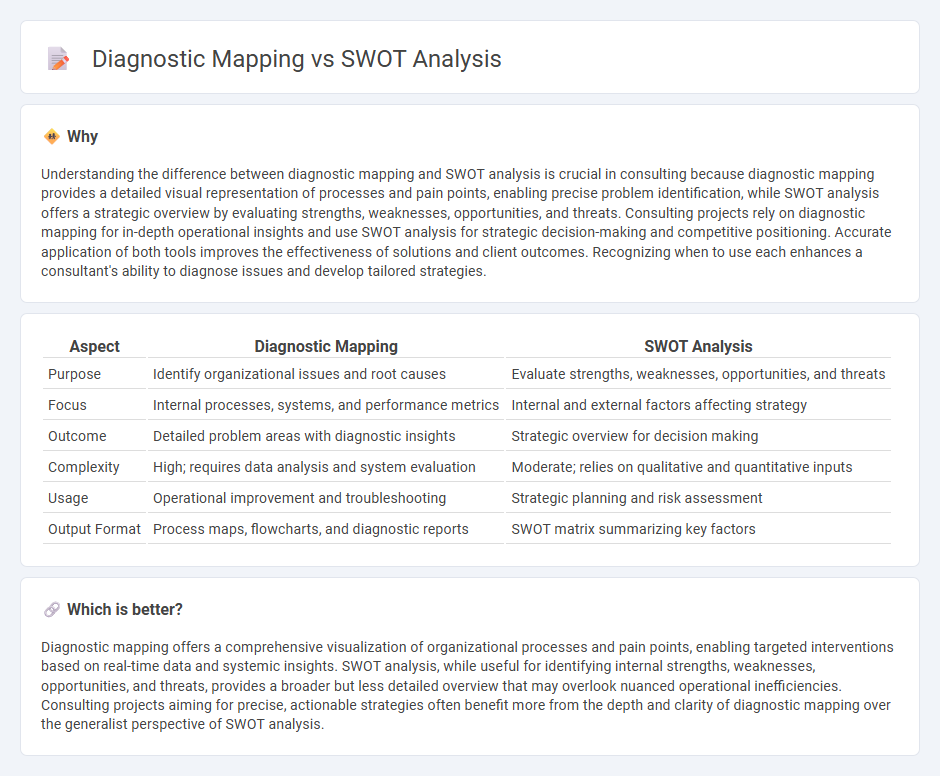
Understanding the difference between diagnostic mapping and SWOT analysis is crucial in consulting because diagnostic mapping provides a detailed visual representation of processes and pain points, enabling precise problem identification, while SWOT analysis offers a strategic overview by evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Consulting projects rely on diagnostic mapping for in-depth operational insights and use SWOT analysis for strategic decision-making and competitive positioning. Accurate application of both tools improves the effectiveness of solutions and client outcomes. Recognizing when to use each enhances a consultant's ability to diagnose issues and develop tailored strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Diagnostic Mapping | SWOT Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify organizational issues and root causes | Evaluate strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats |
| Focus | Internal processes, systems, and performance metrics | Internal and external factors affecting strategy |
| Outcome | Detailed problem areas with diagnostic insights | Strategic overview for decision making |
| Complexity | High; requires data analysis and system evaluation | Moderate; relies on qualitative and quantitative inputs |
| Usage | Operational improvement and troubleshooting | Strategic planning and risk assessment |
| Output Format | Process maps, flowcharts, and diagnostic reports | SWOT matrix summarizing key factors |
Which is better?
Diagnostic mapping offers a comprehensive visualization of organizational processes and pain points, enabling targeted interventions based on real-time data and systemic insights. SWOT analysis, while useful for identifying internal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, provides a broader but less detailed overview that may overlook nuanced operational inefficiencies. Consulting projects aiming for precise, actionable strategies often benefit more from the depth and clarity of diagnostic mapping over the generalist perspective of SWOT analysis.
Connection
Diagnostic mapping identifies organizational strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats by visualizing internal processes and external factors, serving as a foundation for a comprehensive SWOT analysis. SWOT analysis refines insights from diagnostic mapping to develop strategic recommendations tailored to business objectives. Together, they enable consultants to pinpoint critical areas for improvement and growth, enhancing decision-making and competitive advantage.
Key Terms
Strengths vs. Root Causes
SWOT analysis emphasizes identifying organizational Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to provide a broad overview of internal and external factors influencing performance. Diagnostic mapping delves deeper into Root Causes, systematically uncovering underlying issues impacting processes and outcomes through detailed analysis techniques. Explore further to understand how these approaches complement strategic planning and problem-solving.
Weaknesses vs. Process Flows
SWOT analysis emphasizes identifying internal Weaknesses such as resource constraints, skill gaps, and organizational inefficiencies, offering a broad strategic perspective. Diagnostic mapping focuses on visualizing detailed Process Flows to pinpoint bottlenecks, redundancies, and operational risks within workflows, enabling targeted process improvements. Explore how combining these tools enhances comprehensive organizational assessments and strategic decision-making.
Opportunities/Threats vs. Systemic Issues
SWOT analysis emphasizes identifying external Opportunities and Threats that impact organizational strategy, while diagnostic mapping concentrates on uncovering systemic issues within processes and structures. SWOT provides a high-level overview useful for strategic planning, whereas diagnostic mapping offers detailed insights to address root causes of operational challenges. Explore the distinct advantages of each method to optimize your organizational assessment approach.
Source and External Links
SWOT Analysis: Examples and Templates [2025] - SWOT analysis is a technique to identify internal strengths and weaknesses, plus external opportunities and threats, to help with strategic business or project decisions.
SWOT analysis - SWOT is a decision-making tool used across organizations to link internal factors with external ones and formulate strategies such as aggressive, defensive, or conversion strategies.
What is SWOT? - SWOT Analysis - Research Guides - CUNY - SWOT organizes internal and external information to assess strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, helping companies strategize and evaluate possible changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com