Digital twin strategy leverages virtual replicas of physical assets to optimize performance through real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency in manufacturing environments. Smart manufacturing integrates IoT, automation, and AI-driven analytics to create adaptive, data-driven production systems that improve quality, reduce downtime, and boost productivity. Explore how these innovative approaches can transform your manufacturing processes for competitive advantage.
Why it is important
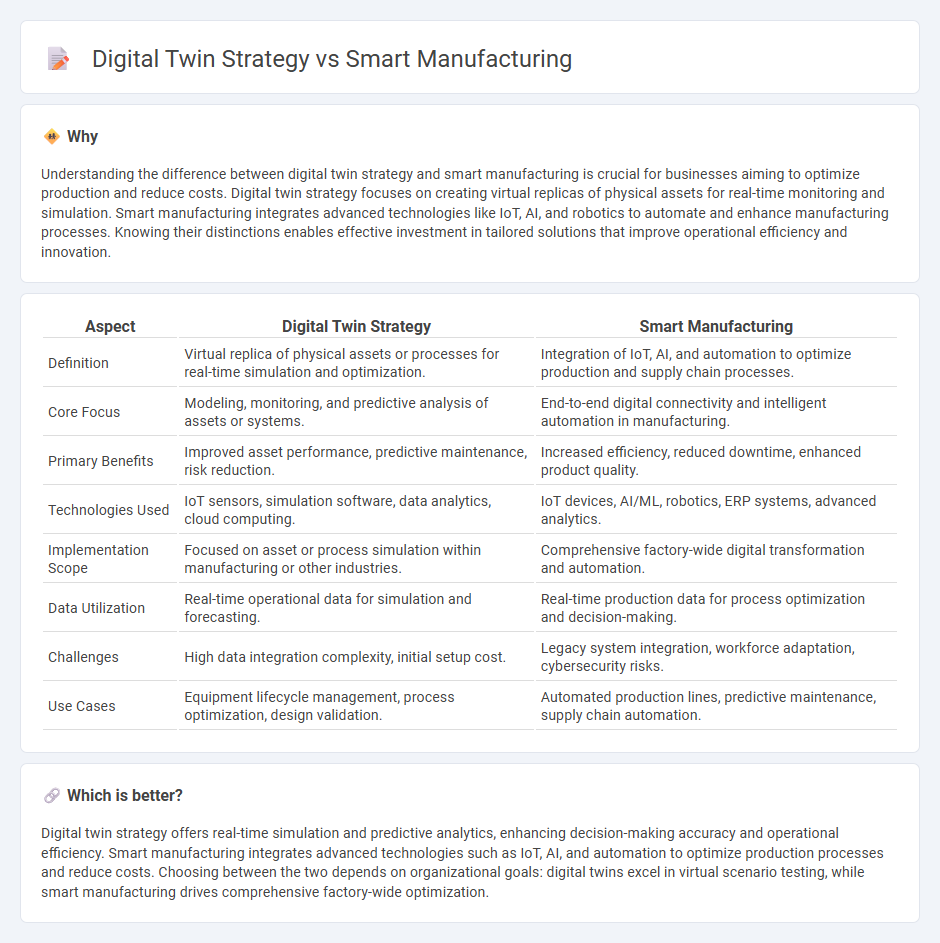
Understanding the difference between digital twin strategy and smart manufacturing is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize production and reduce costs. Digital twin strategy focuses on creating virtual replicas of physical assets for real-time monitoring and simulation. Smart manufacturing integrates advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics to automate and enhance manufacturing processes. Knowing their distinctions enables effective investment in tailored solutions that improve operational efficiency and innovation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Twin Strategy | Smart Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replica of physical assets or processes for real-time simulation and optimization. | Integration of IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production and supply chain processes. |
| Core Focus | Modeling, monitoring, and predictive analysis of assets or systems. | End-to-end digital connectivity and intelligent automation in manufacturing. |
| Primary Benefits | Improved asset performance, predictive maintenance, risk reduction. | Increased efficiency, reduced downtime, enhanced product quality. |
| Technologies Used | IoT sensors, simulation software, data analytics, cloud computing. | IoT devices, AI/ML, robotics, ERP systems, advanced analytics. |
| Implementation Scope | Focused on asset or process simulation within manufacturing or other industries. | Comprehensive factory-wide digital transformation and automation. |
| Data Utilization | Real-time operational data for simulation and forecasting. | Real-time production data for process optimization and decision-making. |
| Challenges | High data integration complexity, initial setup cost. | Legacy system integration, workforce adaptation, cybersecurity risks. |
| Use Cases | Equipment lifecycle management, process optimization, design validation. | Automated production lines, predictive maintenance, supply chain automation. |
Which is better?
Digital twin strategy offers real-time simulation and predictive analytics, enhancing decision-making accuracy and operational efficiency. Smart manufacturing integrates advanced technologies such as IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production processes and reduce costs. Choosing between the two depends on organizational goals: digital twins excel in virtual scenario testing, while smart manufacturing drives comprehensive factory-wide optimization.
Connection
Digital twin strategy enhances smart manufacturing by creating real-time virtual replicas of physical assets and processes, enabling predictive maintenance, optimized production, and reduced downtime. This integration allows manufacturers to simulate and analyze production scenarios, improving operational efficiency and product quality. Leveraging IoT sensors and advanced analytics, digital twins drive data-informed decisions that support continuous improvement in smart manufacturing environments.
Key Terms
Digital Thread
Smart manufacturing integrates IoT, AI, and automation to optimize production processes, whereas digital twin strategy emphasizes creating virtual replicas of physical assets to simulate and predict performance. Digital thread serves as the critical link that continuously connects data flow across the entire product lifecycle, enabling real-time insights and seamless collaboration. Discover more about how leveraging digital thread enhances both smart manufacturing and digital twin strategies.
Real-time Data Integration
Smart manufacturing leverages real-time data integration to optimize production efficiency, reduce downtime, and enhance decision-making through connected IoT devices and advanced analytics. Digital twin strategy simulates physical assets and processes with real-time data streams for predictive maintenance and process optimization, creating a virtual replica that mirrors operational conditions. Explore how integrating real-time data drives innovation and operational excellence in both frameworks.
Predictive Analytics
Smart manufacturing integrates real-time data from IoT sensors with advanced analytics to optimize production processes and reduce downtime. Digital twin strategies leverage virtual replicas of physical assets to simulate and predict operational performance, enabling more precise predictive analytics for maintenance and quality control. Explore the latest advancements in predictive analytics to enhance both smart manufacturing and digital twin implementations.
Source and External Links
What Is Smart Manufacturing? | Oracle - Smart manufacturing is the convergence of data science and artificial intelligence technologies to create highly connected, real-time data-driven manufacturing processes that boost efficiency, sustainability, and economic performance.
What Is Smart Manufacturing? - CESMII - Smart manufacturing is an information-driven, event-driven approach that integrates and continuously monitors resources and processes, enabling automation, predictive analytics, and real-time collaboration across the manufacturing ecosystem.
Smart manufacturing - Wikipedia - Smart manufacturing is a broad category that employs computer-integrated systems, high adaptability, and rapid design changes to optimize efficiency, reduce workplace hazards, and eliminate inefficiencies through advanced automation and AI.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com