Purpose-driven leadership inspires teams by aligning organizational goals with meaningful values, driving lasting engagement and innovation. Transactional leadership focuses on structured tasks, rewards, and performance metrics to achieve immediate results. Explore how choosing the right leadership style can transform your business outcomes.
Why it is important
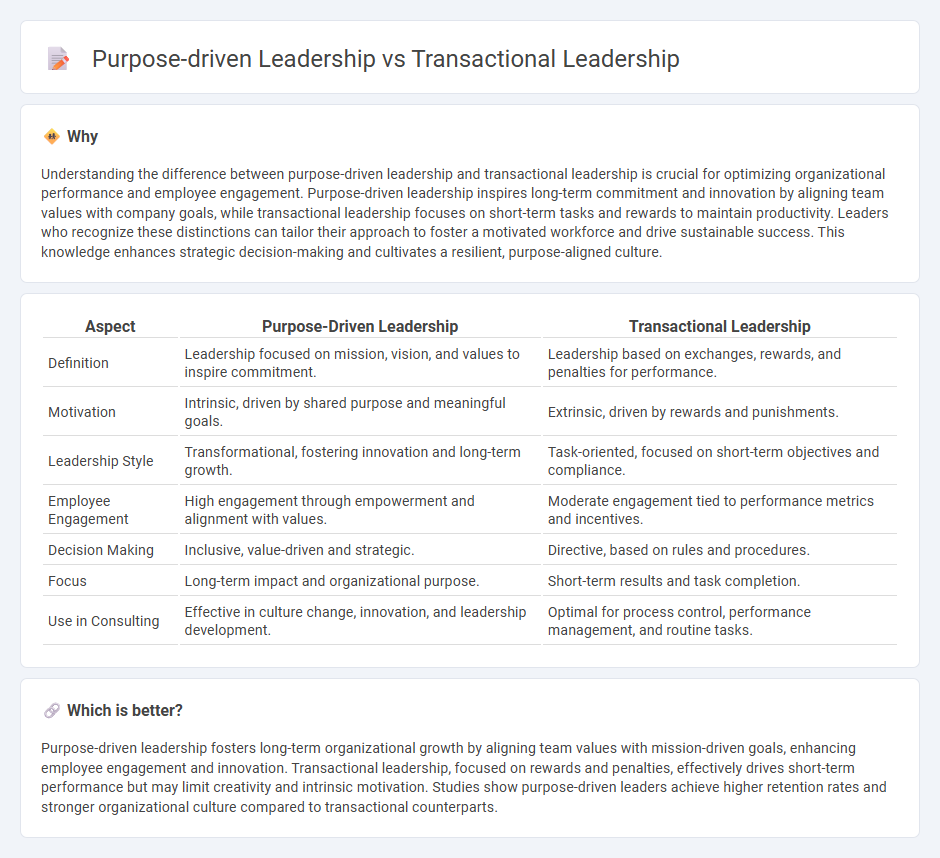
Understanding the difference between purpose-driven leadership and transactional leadership is crucial for optimizing organizational performance and employee engagement. Purpose-driven leadership inspires long-term commitment and innovation by aligning team values with company goals, while transactional leadership focuses on short-term tasks and rewards to maintain productivity. Leaders who recognize these distinctions can tailor their approach to foster a motivated workforce and drive sustainable success. This knowledge enhances strategic decision-making and cultivates a resilient, purpose-aligned culture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Purpose-Driven Leadership | Transactional Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leadership focused on mission, vision, and values to inspire commitment. | Leadership based on exchanges, rewards, and penalties for performance. |
| Motivation | Intrinsic, driven by shared purpose and meaningful goals. | Extrinsic, driven by rewards and punishments. |
| Leadership Style | Transformational, fostering innovation and long-term growth. | Task-oriented, focused on short-term objectives and compliance. |
| Employee Engagement | High engagement through empowerment and alignment with values. | Moderate engagement tied to performance metrics and incentives. |
| Decision Making | Inclusive, value-driven and strategic. | Directive, based on rules and procedures. |
| Focus | Long-term impact and organizational purpose. | Short-term results and task completion. |
| Use in Consulting | Effective in culture change, innovation, and leadership development. | Optimal for process control, performance management, and routine tasks. |
Which is better?
Purpose-driven leadership fosters long-term organizational growth by aligning team values with mission-driven goals, enhancing employee engagement and innovation. Transactional leadership, focused on rewards and penalties, effectively drives short-term performance but may limit creativity and intrinsic motivation. Studies show purpose-driven leaders achieve higher retention rates and stronger organizational culture compared to transactional counterparts.
Connection
Purpose-driven leadership focuses on inspiring and motivating employees by aligning organizational goals with a higher mission, fostering commitment and innovation. Transactional leadership centers on clear structures, rewards, and performance-based feedback to achieve specific tasks and outcomes efficiently. Both leadership styles complement each other by integrating motivation and goal-oriented management to drive sustained organizational success.
Key Terms
Decision-making approach
Transactional leadership centers on structured decision-making, emphasizing clear roles, rewards, and penalties to achieve specific organizational goals. Purpose-driven leadership adopts a values-based decision-making style, aligning choices with the broader mission and inspiring intrinsic motivation among team members. Explore how these leadership approaches impact organizational culture and performance for deeper insights.
Motivation source
Transactional leadership centers on motivation through rewards and penalties, emphasizing clear structures and performance-based outcomes. Purpose-driven leadership fosters intrinsic motivation by aligning individual values with a compelling organizational mission, inspiring deeper engagement and commitment. Explore how each leadership style uniquely impacts employee motivation and organizational success.
Organizational vision
Transactional leadership emphasizes clear roles, reward-based performance, and short-term goals to maintain organizational efficiency, while purpose-driven leadership centers on inspiring employees through a compelling vision aligned with core values and long-term impact. Purpose-driven leaders foster deeper engagement by connecting daily tasks to a meaningful mission that transcends mere transactions. Explore how integrating these leadership styles can enhance your organization's vision and drive sustainable success.
Source and External Links
Transactional leadership: Examples leaders should know - Transactional leadership is a practical style focused on a give-and-take relationship where leaders use contingent rewards, active management by exception, or passive management by exception to motivate and control team performance.
What is transactional leadership? - Definition from WhatIs. - Transactional leadership relies on rewards and punishments to achieve specific, measurable goals, working best in structured environments that value efficiency and clear expectations rather than change or flexibility.
Transactional leadership - Transactional leadership emphasizes short-term goals and performance through exchanges of rewards for effort, and corrective actions only when standards are not met, aiming to maintain the status quo in an organizational setting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com