Corporate venturing involves established companies investing in or collaborating with startups to foster innovation and access emerging technologies, whereas joint ventures are formal partnerships where two or more businesses create a new entity to pursue shared objectives and risks. Corporate venturing focuses on strategic investment and innovation pipelines, while joint ventures emphasize shared management, resources, and operational control. Discover how these approaches can drive growth and competitive advantage in your organization.
Why it is important
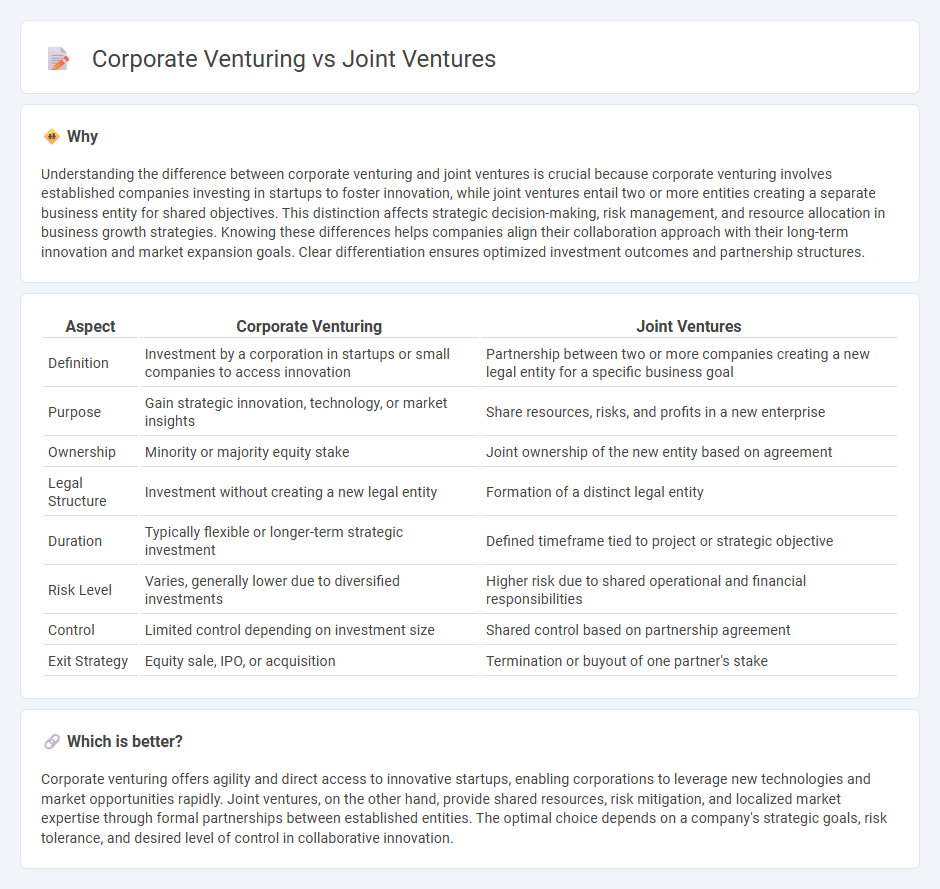
Understanding the difference between corporate venturing and joint ventures is crucial because corporate venturing involves established companies investing in startups to foster innovation, while joint ventures entail two or more entities creating a separate business entity for shared objectives. This distinction affects strategic decision-making, risk management, and resource allocation in business growth strategies. Knowing these differences helps companies align their collaboration approach with their long-term innovation and market expansion goals. Clear differentiation ensures optimized investment outcomes and partnership structures.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Corporate Venturing | Joint Ventures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment by a corporation in startups or small companies to access innovation | Partnership between two or more companies creating a new legal entity for a specific business goal |
| Purpose | Gain strategic innovation, technology, or market insights | Share resources, risks, and profits in a new enterprise |
| Ownership | Minority or majority equity stake | Joint ownership of the new entity based on agreement |
| Legal Structure | Investment without creating a new legal entity | Formation of a distinct legal entity |
| Duration | Typically flexible or longer-term strategic investment | Defined timeframe tied to project or strategic objective |
| Risk Level | Varies, generally lower due to diversified investments | Higher risk due to shared operational and financial responsibilities |
| Control | Limited control depending on investment size | Shared control based on partnership agreement |
| Exit Strategy | Equity sale, IPO, or acquisition | Termination or buyout of one partner's stake |
Which is better?
Corporate venturing offers agility and direct access to innovative startups, enabling corporations to leverage new technologies and market opportunities rapidly. Joint ventures, on the other hand, provide shared resources, risk mitigation, and localized market expertise through formal partnerships between established entities. The optimal choice depends on a company's strategic goals, risk tolerance, and desired level of control in collaborative innovation.
Connection
Corporate venturing and joint ventures are connected through their collaborative approach to innovation and growth, where corporate venturing involves investing in or partnering with startups to access new technologies, and joint ventures establish shared enterprises between companies to combine resources and expertise. Both strategies enable corporations to expand market reach, share risks, and accelerate product development by leveraging external capabilities. Utilizing corporate venturing alongside joint ventures enhances a company's competitive edge by fostering strategic alliances and facilitating access to emerging business opportunities.
Key Terms
Equity Sharing
Joint ventures involve two or more firms pooling resources to create a separate legal entity with shared equity ownership, facilitating long-term strategic collaboration and risk sharing. Corporate venturing typically refers to a company investing in or partnering with startups or emerging businesses, often without full equity control, to drive innovation and access new technologies. Explore the nuances of equity sharing and ownership structures in joint ventures versus corporate venturing to enhance your strategic partnership decisions.
Strategic Alignment
Joint ventures foster strategic alignment by combining complementary resources and expertise from partnering companies, enabling shared goals and risk distribution. Corporate venturing aligns strategic objectives through investments or partnerships with startups, promoting innovation and market expansion within the corporate framework. Explore how aligning strategies in joint ventures and corporate venturing can drive growth and competitive advantage.
Governance Structure
Joint ventures typically involve the creation of a separate legal entity jointly owned by participating firms, with governance structures defined by shared equity stakes and formal agreements specifying decision-making processes. Corporate venturing often operates through internal corporate units or external partnerships without forming a new entity, emphasizing flexible governance models aligned with strategic objectives and rapid innovation cycles. Explore deeper insights into governance distinctions and their impact on strategic outcomes.
Source and External Links
Joint venture - Wikipedia - A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties with shared ownership, returns, risks, and governance, often formed to access new markets, share risks, or combine capabilities, and can be incorporated or unincorporated depending on industry practices.
Joint Venture (JV) - Top 10 Advantages - A JV is a commercial partnership where organizations pool resources to gain strategic advantages such as entering new markets, sharing financial burdens, and leveraging specialized expertise to enhance growth and productivity.
joint venture | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A joint venture is a collaboration between parties to develop a single enterprise or project for profit with shared contributions, joint control, and profit or loss sharing, distinguished legally from partnerships or corporations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com