Digital lean transformation streamlines business operations by integrating lean principles with advanced digital technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce waste. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks using software robots to boost productivity and accuracy. Explore how these approaches can revolutionize your organization's workflow and drive innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital lean transformation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is crucial because digital lean transformation focuses on optimizing end-to-end business processes through cultural and technological changes, while RPA automates repetitive tasks using software bots. Digital lean transformation drives long-term strategic improvements and operational efficiency, whereas RPA offers quick wins by automating specific manual activities. Consulting firms leverage this distinction to tailor strategies that align with clients' unique business goals, ensuring maximum ROI and sustainable growth. Clarity in these concepts helps organizations prioritize investments and manage change effectively.
Comparison Table
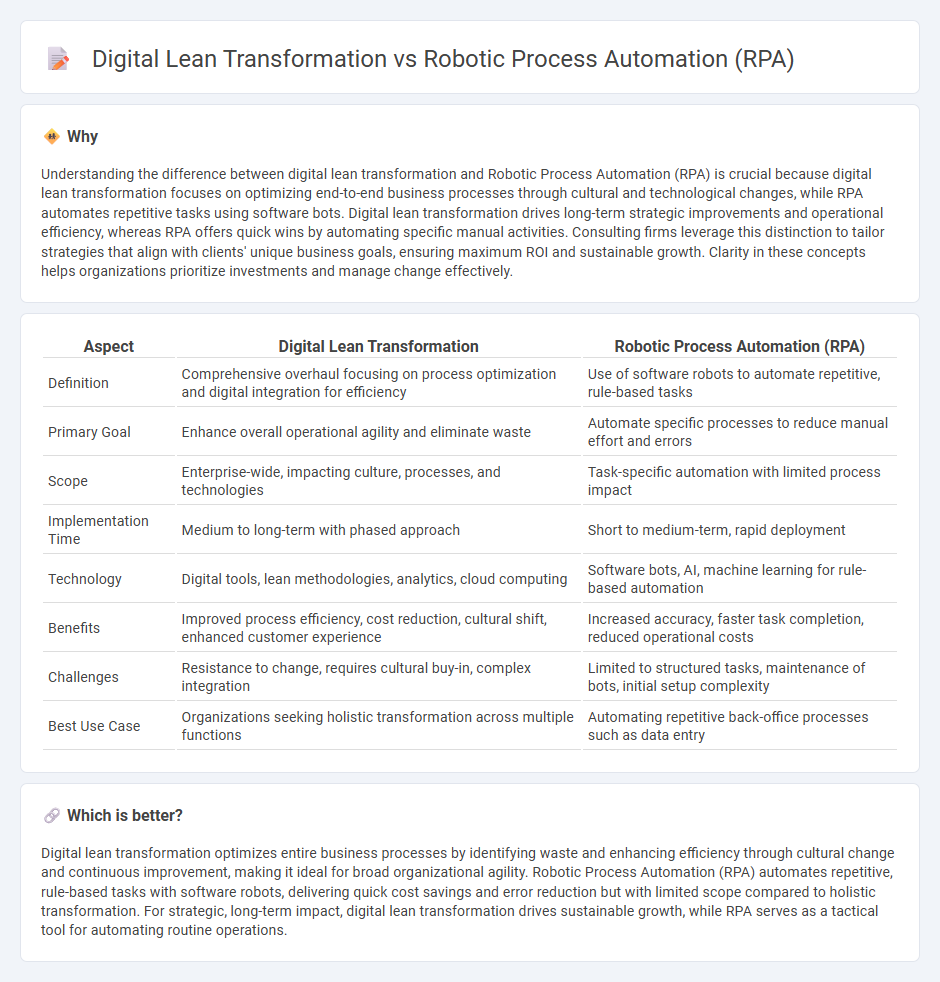
| Aspect | Digital Lean Transformation | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive overhaul focusing on process optimization and digital integration for efficiency | Use of software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks |
| Primary Goal | Enhance overall operational agility and eliminate waste | Automate specific processes to reduce manual effort and errors |
| Scope | Enterprise-wide, impacting culture, processes, and technologies | Task-specific automation with limited process impact |
| Implementation Time | Medium to long-term with phased approach | Short to medium-term, rapid deployment |
| Technology | Digital tools, lean methodologies, analytics, cloud computing | Software bots, AI, machine learning for rule-based automation |
| Benefits | Improved process efficiency, cost reduction, cultural shift, enhanced customer experience | Increased accuracy, faster task completion, reduced operational costs |
| Challenges | Resistance to change, requires cultural buy-in, complex integration | Limited to structured tasks, maintenance of bots, initial setup complexity |
| Best Use Case | Organizations seeking holistic transformation across multiple functions | Automating repetitive back-office processes such as data entry |
Which is better?
Digital lean transformation optimizes entire business processes by identifying waste and enhancing efficiency through cultural change and continuous improvement, making it ideal for broad organizational agility. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks with software robots, delivering quick cost savings and error reduction but with limited scope compared to holistic transformation. For strategic, long-term impact, digital lean transformation drives sustainable growth, while RPA serves as a tactical tool for automating routine operations.
Connection
Digital lean transformation streamlines business processes by eliminating waste and enhancing operational efficiency, while Robotic Process Automation (RPA) automates repetitive, rule-based tasks to further accelerate workflow optimization. Integrating RPA into digital lean strategies amplifies productivity gains by enabling rapid process execution and reducing human error. This synergy drives sustainable growth, enhances customer experience, and supports agile decision-making within consulting frameworks.
Key Terms
Workflow Optimization
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks within workflows, significantly reducing human error and operational costs. Digital Lean Transformation focuses on streamlining end-to-end processes by identifying waste, enhancing value streams, and fostering continuous improvement using digital tools and methodologies. Explore deeper insights on how these approaches complement each other for superior workflow optimization.
Process Standardization
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances process standardization by automating repetitive tasks, reducing human error, and ensuring consistent execution across workflows. Digital lean transformation focuses on streamlining processes end-to-end, eliminating waste, and embedding continuous improvement within organizational culture. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand how each approach drives process standardization and operational excellence.
Technology Integration
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) leverages software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, enhancing efficiency and accuracy within existing technology frameworks. Digital lean transformation integrates multiple advanced technologies, including RPA, AI, IoT, and data analytics, to streamline entire business processes, reduce waste, and foster continuous improvement across organizations. Explore how these technology integration strategies can drive digital innovation and operational excellence in your enterprise.
Source and External Links
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? - IBM - RPA is a business process automation technology using software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based human tasks by emulating user interactions and integrating APIs, enhancing digital transformation with intelligent automation.
What is RPA Software? Robotic Process Automation Explained - RPA software uses bots to mimic human actions and perform repetitive processes, available in attended, unattended, and hybrid forms, aimed at saving time and improving accuracy in business workflows.
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)? | Laserfiche Blog - RPA enlists bots to perform repetitive tasks via user interfaces, bridging automation gaps by simulating human software interactions, boosting accuracy and freeing employees for higher-impact work.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com