Anticipatory governance focuses on proactive, strategic foresight to manage emerging risks and opportunities in public administration, enhancing adaptive capacity and resilience. E-government emphasizes digitizing public services and processes to improve accessibility, efficiency, and transparency for citizens and businesses. Explore how consulting can bridge these approaches to drive innovative governance solutions.
Why it is important
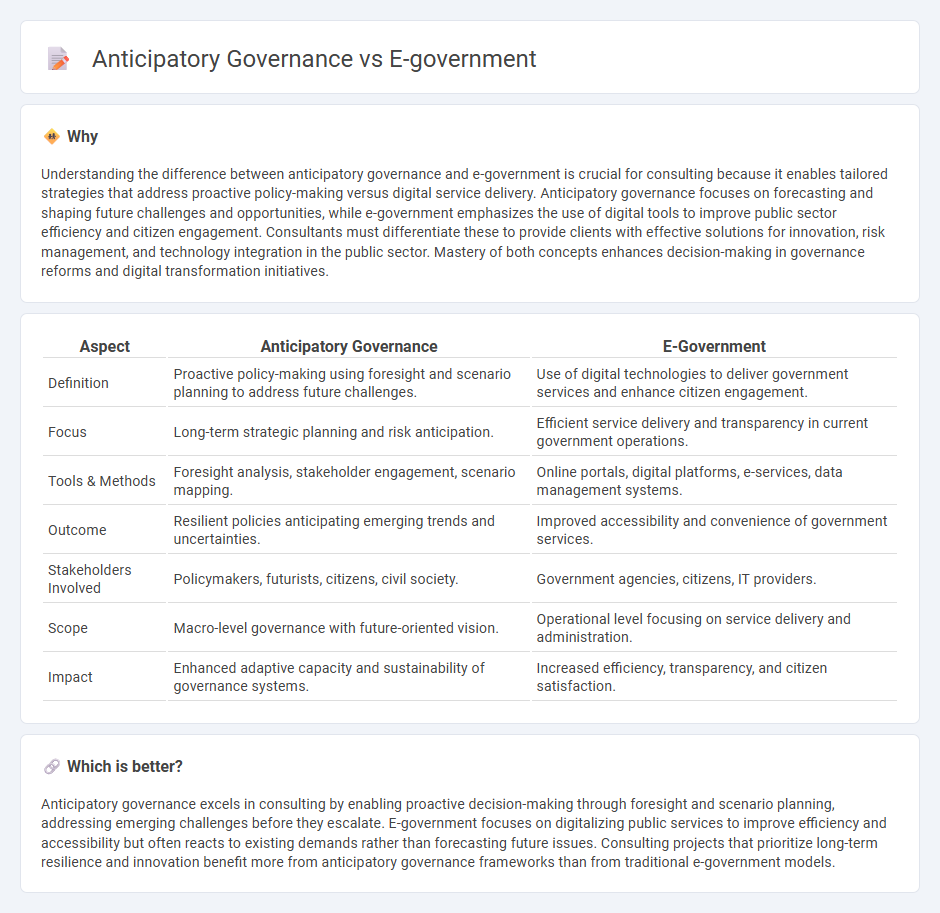
Understanding the difference between anticipatory governance and e-government is crucial for consulting because it enables tailored strategies that address proactive policy-making versus digital service delivery. Anticipatory governance focuses on forecasting and shaping future challenges and opportunities, while e-government emphasizes the use of digital tools to improve public sector efficiency and citizen engagement. Consultants must differentiate these to provide clients with effective solutions for innovation, risk management, and technology integration in the public sector. Mastery of both concepts enhances decision-making in governance reforms and digital transformation initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Anticipatory Governance | E-Government |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactive policy-making using foresight and scenario planning to address future challenges. | Use of digital technologies to deliver government services and enhance citizen engagement. |
| Focus | Long-term strategic planning and risk anticipation. | Efficient service delivery and transparency in current government operations. |
| Tools & Methods | Foresight analysis, stakeholder engagement, scenario mapping. | Online portals, digital platforms, e-services, data management systems. |
| Outcome | Resilient policies anticipating emerging trends and uncertainties. | Improved accessibility and convenience of government services. |
| Stakeholders Involved | Policymakers, futurists, citizens, civil society. | Government agencies, citizens, IT providers. |
| Scope | Macro-level governance with future-oriented vision. | Operational level focusing on service delivery and administration. |
| Impact | Enhanced adaptive capacity and sustainability of governance systems. | Increased efficiency, transparency, and citizen satisfaction. |
Which is better?
Anticipatory governance excels in consulting by enabling proactive decision-making through foresight and scenario planning, addressing emerging challenges before they escalate. E-government focuses on digitalizing public services to improve efficiency and accessibility but often reacts to existing demands rather than forecasting future issues. Consulting projects that prioritize long-term resilience and innovation benefit more from anticipatory governance frameworks than from traditional e-government models.
Connection
Anticipatory governance leverages data analytics and foresight tools to inform proactive policy-making, which is enhanced through e-government platforms that facilitate real-time citizen engagement and transparent service delivery. E-government's digital infrastructure supports anticipatory governance by enabling efficient data collection, scenario planning, and stakeholder collaboration across multiple public sectors. This integration accelerates decision-making processes, reduces bureaucratic delays, and improves public trust in governance systems.
Key Terms
Digital Public Services
E-government leverages digital platforms to streamline public service delivery, enhancing accessibility and efficiency for citizens. Anticipatory governance incorporates foresight and adaptive policies to proactively address emerging challenges in digital public services. Explore the evolving landscape of digital governance to understand how these approaches shape future-ready service frameworks.
Predictive Policy-Making
E-government leverages digital technologies to streamline public services and enhance transparency, while anticipatory governance emphasizes forward-looking strategies and predictive policy-making to address future challenges. Predictive policy-making employs data analytics, machine learning, and scenario planning to forecast potential outcomes and inform proactive decision-making in public administration. Explore how integrating e-government platforms with anticipatory governance can revolutionize policy effectiveness and civic engagement.
Stakeholder Engagement
E-government primarily emphasizes digital platforms to streamline interactions between government and citizens, enhancing transparency and service efficiency. Anticipatory governance integrates proactive stakeholder engagement, encouraging collaboration among diverse groups to address future challenges and co-create solutions. Explore the dynamics of stakeholder participation in these governance models to understand their impact on policy development and public trust.
Source and External Links
E-Government (E-Gov) | Home - USDA - E-Government is the use of web-based Internet applications and information technology by the government to enhance access to and delivery of services and information to the public, agencies, and government entities.
About e-Government - E-Government applies information and communication technologies (ICTs) to government functions and procedures to increase efficiency, transparency, and citizen participation.
Twenty years of making government more accessible through the E-Government Act - The E-Government Act of 2002 established structures for federal agencies to deliver better public services using technology and the internet, including creating the Office of E-Government and supporting cross-agency digital initiatives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com