Circular supply chains prioritize resource regeneration by designing products for reuse, recycling, and minimal waste, enhancing sustainability in commerce. Value chains focus on maximizing efficiency and profitability through interlinked activities that add value at each stage, from production to delivery. Explore the differences between circular supply chains and value chains to optimize your business strategy for sustainability and efficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between circular supply chain and value chain is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and sustainability in commerce. The circular supply chain focuses on reducing waste through recycling and reusing materials, while the value chain emphasizes maximizing product value from raw materials to end consumer. This knowledge enables businesses to implement environmentally friendly practices without compromising profitability. Companies like Patagonia and IKEA successfully leverage circular supply chains to enhance brand reputation and reduce costs.
Comparison Table
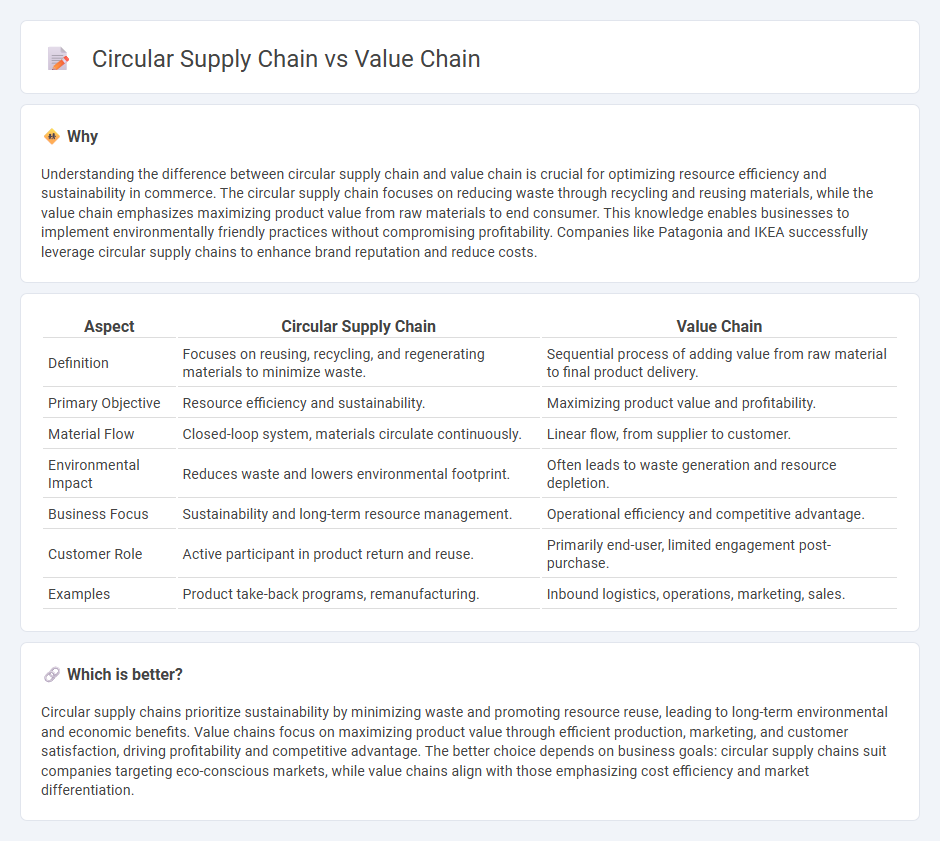
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Value Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on reusing, recycling, and regenerating materials to minimize waste. | Sequential process of adding value from raw material to final product delivery. |
| Primary Objective | Resource efficiency and sustainability. | Maximizing product value and profitability. |
| Material Flow | Closed-loop system, materials circulate continuously. | Linear flow, from supplier to customer. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste and lowers environmental footprint. | Often leads to waste generation and resource depletion. |
| Business Focus | Sustainability and long-term resource management. | Operational efficiency and competitive advantage. |
| Customer Role | Active participant in product return and reuse. | Primarily end-user, limited engagement post-purchase. |
| Examples | Product take-back programs, remanufacturing. | Inbound logistics, operations, marketing, sales. |
Which is better?
Circular supply chains prioritize sustainability by minimizing waste and promoting resource reuse, leading to long-term environmental and economic benefits. Value chains focus on maximizing product value through efficient production, marketing, and customer satisfaction, driving profitability and competitive advantage. The better choice depends on business goals: circular supply chains suit companies targeting eco-conscious markets, while value chains align with those emphasizing cost efficiency and market differentiation.
Connection
The circular supply chain integrates sustainability by promoting resource reuse and waste reduction, directly enhancing the efficiency and resilience of the value chain. Both concepts focus on maximizing product lifecycle value, with the circular supply chain enabling continuous material flow that supports value chain activities such as production, distribution, and consumption. This synergy creates a closed-loop system that drives economic performance while minimizing environmental impact, aligning commerce strategies with sustainable development goals.
Key Terms
Resource Efficiency
A value chain traditionally emphasizes the linear flow of materials from raw inputs to finished products, often resulting in resource depletion and waste generation. In contrast, a circular supply chain prioritizes resource efficiency by designing processes that reuse, refurbish, and recycle materials to minimize environmental impact and reduce costs. Explore the advantages of adopting circular supply chains to enhance sustainability and operational efficiency.
Waste Management
A value chain primarily emphasizes linear processes that move raw materials through production to disposal, often generating significant waste by discarding by-products. Circular supply chains prioritize waste management by designing closed-loop systems that recycle, reuse, and recover materials, minimizing environmental impact and promoting resource efficiency. Explore more about how integrating circular principles transforms waste management within modern supply chains.
Source and External Links
What is a value chain? Definitions and characteristics - The value chain describes the full range of activities required to bring a product or service from conception through production, delivery, and disposal, emphasizing the value created at each step for end-users and other stakeholders.
What is a value chain and why is it important? - A value chain outlines all business activities involved in creating and delivering a product or service, from acquiring materials to reaching the customer, distinguishing primary activities like operations and logistics from support activities like procurement and technology.
The Value Chain - Institute For Strategy And Competitiveness - The value chain is a strategic tool for analyzing a company's activities to identify sources of competitive advantage, focusing on how each activity adds value and is connected to others in a broader value system.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com