Green logistics focuses on reducing environmental impact by optimizing transportation, warehousing, and packaging to minimize carbon emissions and resource consumption. Cold chain logistics ensures the integrity and safety of temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods through controlled temperature management during storage and distribution. Explore the key differences and benefits of green logistics versus cold chain logistics to enhance sustainable and efficient supply chain operations.
Why it is important
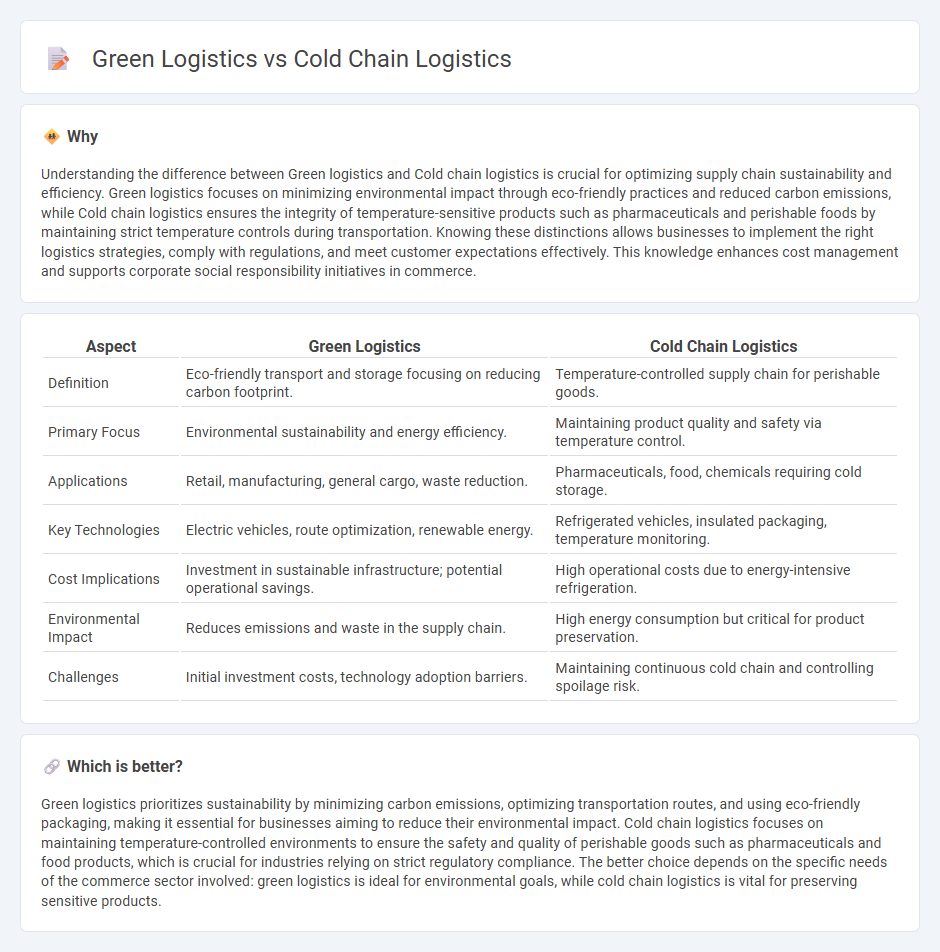
Understanding the difference between Green logistics and Cold chain logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain sustainability and efficiency. Green logistics focuses on minimizing environmental impact through eco-friendly practices and reduced carbon emissions, while Cold chain logistics ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods by maintaining strict temperature controls during transportation. Knowing these distinctions allows businesses to implement the right logistics strategies, comply with regulations, and meet customer expectations effectively. This knowledge enhances cost management and supports corporate social responsibility initiatives in commerce.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Logistics | Cold Chain Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Eco-friendly transport and storage focusing on reducing carbon footprint. | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. |
| Primary Focus | Environmental sustainability and energy efficiency. | Maintaining product quality and safety via temperature control. |
| Applications | Retail, manufacturing, general cargo, waste reduction. | Pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals requiring cold storage. |
| Key Technologies | Electric vehicles, route optimization, renewable energy. | Refrigerated vehicles, insulated packaging, temperature monitoring. |
| Cost Implications | Investment in sustainable infrastructure; potential operational savings. | High operational costs due to energy-intensive refrigeration. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces emissions and waste in the supply chain. | High energy consumption but critical for product preservation. |
| Challenges | Initial investment costs, technology adoption barriers. | Maintaining continuous cold chain and controlling spoilage risk. |
Which is better?
Green logistics prioritizes sustainability by minimizing carbon emissions, optimizing transportation routes, and using eco-friendly packaging, making it essential for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact. Cold chain logistics focuses on maintaining temperature-controlled environments to ensure the safety and quality of perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals and food products, which is crucial for industries relying on strict regulatory compliance. The better choice depends on the specific needs of the commerce sector involved: green logistics is ideal for environmental goals, while cold chain logistics is vital for preserving sensitive products.
Connection
Green logistics integrates sustainable practices in transportation and warehousing, directly impacting cold chain logistics by reducing carbon emissions and energy consumption during temperature-sensitive goods' handling. Cold chain logistics relies on eco-friendly refrigeration technologies and optimized route planning to maintain product integrity while minimizing environmental footprint. This synergy promotes efficient sustainability in supply chains for perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals and fresh food.
Key Terms
Temperature Control
Cold chain logistics emphasizes the stringent temperature control necessary for preserving perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, food products, and chemicals, utilizing refrigerated transport and storage solutions to maintain specific thermal conditions. Green logistics prioritizes sustainable practices that reduce environmental impact by optimizing energy use, employing eco-friendly packaging, and implementing carbon footprint reduction methods. Explore how integrating temperature control strategies within green logistics can enhance both product integrity and environmental responsibility.
Carbon Footprint
Cold chain logistics involves temperature-controlled transportation and storage to preserve perishable goods, often relying on energy-intensive refrigeration systems that contribute significantly to carbon emissions. Green logistics emphasizes minimizing environmental impact by optimizing routes, using renewable energy, and integrating sustainable packaging to reduce the overall carbon footprint of supply chains. Explore innovative strategies to balance cold chain requirements with eco-friendly practices for lower emissions.
Refrigerated Transport
Cold chain logistics specializes in maintaining temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and perishable food items within controlled environments during storage and transportation. Green logistics emphasizes sustainable practices by reducing carbon emissions, optimizing energy use, and employing eco-friendly materials in refrigerated transport systems. Explore detailed strategies and innovations enhancing refrigerated transport efficiency and sustainability.
Source and External Links
Cold Chain Logistics: Definition, Industries, and Elements - Cold chain logistics involves the handling, storage, and transport of perishable goods under controlled temperatures, utilizing packaging, storage, transport, and monitoring to maintain product quality and safety throughout the supply chain.
Cold Chain Logistics: The Ultimate Guide for 2025 - It is the complex process ensuring temperature-sensitive products like food and pharmaceuticals are kept within required temperature ranges from production to delivery, involving specialized equipment, skilled personnel, and effective management throughout.
Cold Chain Logistics: A Comprehensive Guide - Cold chain logistics specializes in temperature-controlled storage and transport of sensitive goods to preserve product quality, assure regulatory compliance, and guarantee public health and safety by preventing spoilage and contamination.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com