Dark stores operate as localized fulfillment centers focused exclusively on online order processing, optimizing inventory management and reducing delivery times compared to traditional retail stores, which cater directly to in-person shoppers with physical product displays and customer interactions. This shift toward dark stores is transforming the commerce landscape, emphasizing efficiency, speed, and convenience in urban retail logistics. Explore the differences between dark stores and traditional retail stores to understand their evolving roles in modern commerce.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark stores and traditional retail stores is crucial for optimizing inventory management and improving delivery efficiency in commerce. Dark stores operate solely as fulfillment centers for online orders without customer foot traffic, reducing overhead costs and enabling faster shipping. Traditional retail stores focus on in-person customer experiences and immediate product availability, which impacts merchandising and sales strategies differently. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses tailor their operations to meet market demands and enhance customer satisfaction effectively.
Comparison Table
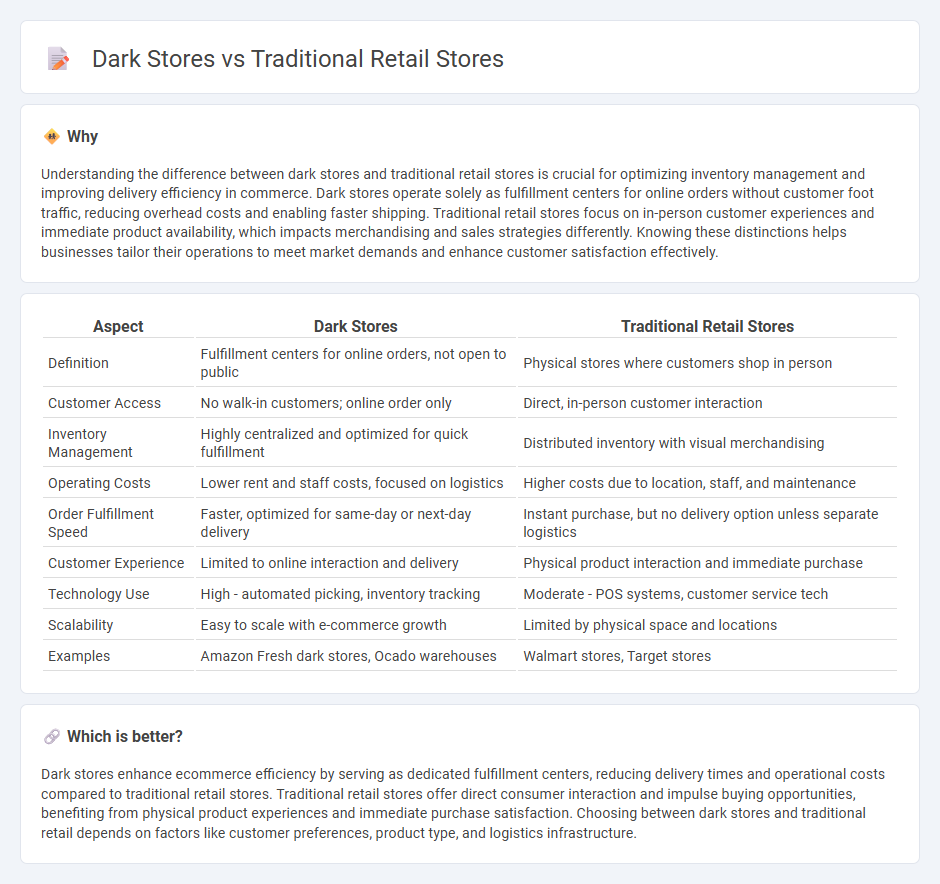
| Aspect | Dark Stores | Traditional Retail Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fulfillment centers for online orders, not open to public | Physical stores where customers shop in person |
| Customer Access | No walk-in customers; online order only | Direct, in-person customer interaction |
| Inventory Management | Highly centralized and optimized for quick fulfillment | Distributed inventory with visual merchandising |
| Operating Costs | Lower rent and staff costs, focused on logistics | Higher costs due to location, staff, and maintenance |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Faster, optimized for same-day or next-day delivery | Instant purchase, but no delivery option unless separate logistics |
| Customer Experience | Limited to online interaction and delivery | Physical product interaction and immediate purchase |
| Technology Use | High - automated picking, inventory tracking | Moderate - POS systems, customer service tech |
| Scalability | Easy to scale with e-commerce growth | Limited by physical space and locations |
| Examples | Amazon Fresh dark stores, Ocado warehouses | Walmart stores, Target stores |
Which is better?
Dark stores enhance ecommerce efficiency by serving as dedicated fulfillment centers, reducing delivery times and operational costs compared to traditional retail stores. Traditional retail stores offer direct consumer interaction and impulse buying opportunities, benefiting from physical product experiences and immediate purchase satisfaction. Choosing between dark stores and traditional retail depends on factors like customer preferences, product type, and logistics infrastructure.
Connection
Dark stores serve as fulfillment centers for online orders, enabling traditional retail stores to enhance their omnichannel capabilities by offering faster delivery and click-and-collect services. These specialized facilities optimize inventory management and reduce last-mile delivery costs, bridging the gap between digital commerce and physical retail presence. Retailers integrate dark stores into their supply chain to improve customer experience and drive sales across both online and offline channels.
Key Terms
Physical Footprint
Traditional retail stores maintain a large physical footprint with aisles designed for in-person browsing and customer experience, often occupying high-traffic urban locations. Dark stores, in contrast, are optimized for online order fulfillment with minimal customer access, allowing for efficient storage and rapid dispatch within compact spaces. Explore how these differing physical footprints impact operational strategy and consumer convenience.
Inventory Fulfillment
Traditional retail stores rely on in-store inventory fulfillment, where products are stocked for direct customer purchase, often leading to limited variety due to shelf space constraints. Dark stores operate exclusively as fulfillment centers for online orders, optimizing inventory management by holding larger quantities and broader assortments without the need for customer-facing displays. Explore more to understand how these models impact supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Customer Experience
Traditional retail stores offer tactile product interactions and immediate purchase satisfaction, enhancing the sensory customer experience. Dark stores, optimized for online order fulfillment, prioritize speed and accuracy, minimizing wait times and improving delivery reliability. Explore how each model transforms shopping expectations and customer engagement.
Source and External Links
Grab and Go Autonomous Stores vs. Traditional Retail - AiFi - Traditional retail stores offer personalized customer service, tangible immediate shopping experiences, and human interaction, but face challenges such as long lines, limited hours, and high labor costs.
Retail vs. E-commerce: What's the Difference? | Indeed.com - Traditional retail stores provide direct customer interaction, the ability for customers to test products before purchase, and minimal shipping costs, which can foster repeat business and customer loyalty.
The Fall of Traditional Retail Commerce | Nexcess - Traditional retail evolved from mom-and-pop shops to department stores, malls, and big-box stores, but faces decline due to ecommerce growth, illustrated by the bankruptcy of prominent brick-and-mortar retailers like Bed Bath & Beyond.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com