Green logistics emphasizes sustainable practices such as reducing carbon emissions, utilizing renewable energy, and optimizing supply chain efficiency to minimize environmental impact. Traditional logistics primarily focuses on cost reduction and speed, often relying on fossil fuels and conventional transportation modes with less regard for ecological consequences. Explore how integrating green logistics strategies can transform commerce while promoting environmental responsibility.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Green logistics and Traditional logistics is crucial for promoting sustainable business practices and minimizing environmental impact. Green logistics focuses on reducing carbon emissions, optimizing resource usage, and decreasing waste throughout the supply chain. Traditional logistics prioritizes cost-effectiveness and speed, often at the expense of ecological concerns. Businesses adopting green logistics gain competitive advantage by meeting regulatory requirements and appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
Comparison Table
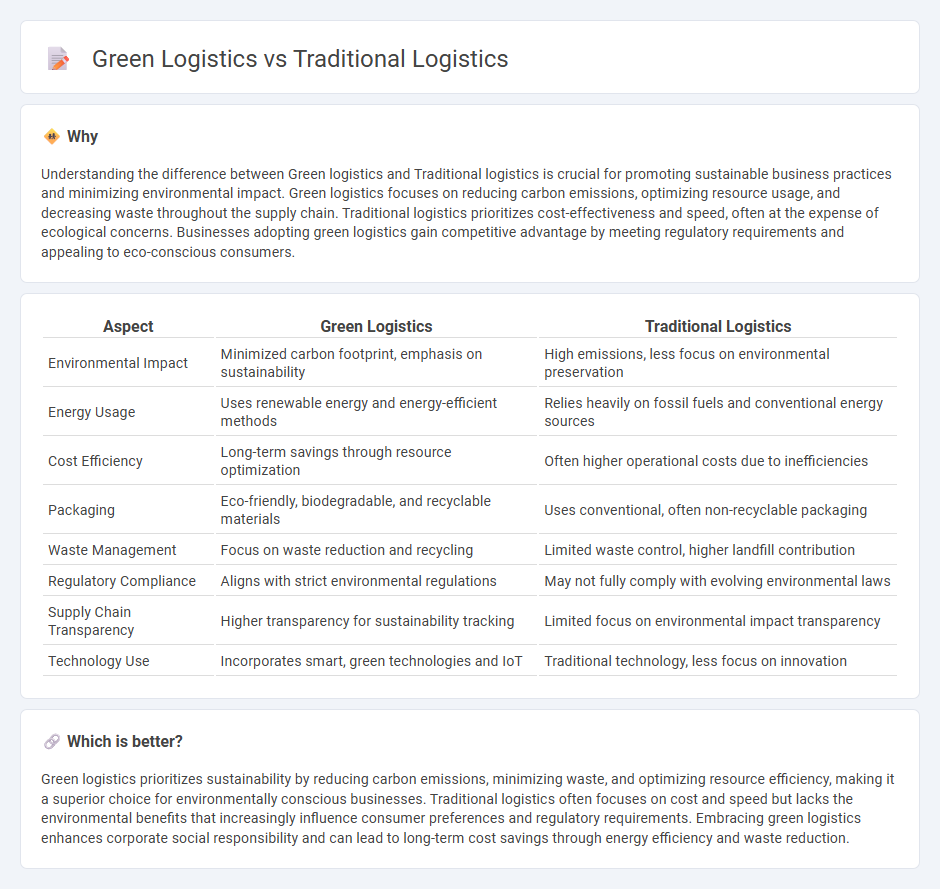
| Aspect | Green Logistics | Traditional Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Minimized carbon footprint, emphasis on sustainability | High emissions, less focus on environmental preservation |
| Energy Usage | Uses renewable energy and energy-efficient methods | Relies heavily on fossil fuels and conventional energy sources |
| Cost Efficiency | Long-term savings through resource optimization | Often higher operational costs due to inefficiencies |
| Packaging | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, and recyclable materials | Uses conventional, often non-recyclable packaging |
| Waste Management | Focus on waste reduction and recycling | Limited waste control, higher landfill contribution |
| Regulatory Compliance | Aligns with strict environmental regulations | May not fully comply with evolving environmental laws |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Higher transparency for sustainability tracking | Limited focus on environmental impact transparency |
| Technology Use | Incorporates smart, green technologies and IoT | Traditional technology, less focus on innovation |
Which is better?
Green logistics prioritizes sustainability by reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and optimizing resource efficiency, making it a superior choice for environmentally conscious businesses. Traditional logistics often focuses on cost and speed but lacks the environmental benefits that increasingly influence consumer preferences and regulatory requirements. Embracing green logistics enhances corporate social responsibility and can lead to long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and waste reduction.
Connection
Green logistics integrates sustainable practices such as carbon footprint reduction and eco-friendly packaging within traditional logistics frameworks that focus on inventory management and transportation efficiency. Both approaches collaborate to optimize supply chain operations by balancing cost-effectiveness with environmental responsibility. This synergy enhances overall commodity flow while minimizing ecological impact in commerce.
Key Terms
Carbon emissions
Traditional logistics heavily relies on fossil fuel-based transportation methods, leading to significant carbon emissions and environmental degradation. Green logistics emphasizes sustainable practices such as using electric vehicles, optimizing routes, and adopting renewable energy sources to minimize the carbon footprint. Explore how green logistics solutions can transform supply chains for a more sustainable future.
Supply chain optimization
Traditional logistics emphasizes cost reduction, inventory management, and transportation efficiency to optimize the supply chain. Green logistics integrates environmental sustainability by minimizing carbon emissions, using renewable energy sources, and adopting eco-friendly packaging and transportation methods. Explore how green logistics transforms supply chain optimization for sustainable business growth.
Environmental regulations
Traditional logistics primarily emphasizes cost-efficiency and delivery speed, often neglecting environmental impact, whereas green logistics integrates stringent environmental regulations to minimize carbon emissions and waste. Compliance with international standards such as ISO 14001 and the EU Emission Trading System plays a critical role in green logistics strategies, promoting sustainable transportation and resource management. Explore how adopting green logistics can align your supply chain with evolving environmental regulations and drive sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
Difference Between Traditional Logistics and E-Commerce Logistics - Traditional logistics serves domestic manufacturers and industries with long-cycle, fixed orders, focused on large volumes and stable demands, primarily using air and sea freight, but lacks flexibility and personalized services compared to newer models.
Traditional Methods to Modern Logistics - Traditional logistics originated from ancient military supply chains and evolved through the Industrial Revolution, involving manual, basic transport methods before modern technological advances transformed supply chain efficiency.
Reverse and Traditional Logistics: What The Differences? - Traditional logistics refers to the flow of goods from suppliers through distribution channels to customers, focusing on forward movement, unlike reverse logistics which manages returns and returns processing starting from customers back to suppliers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com