Recommerce involves the process of reselling used or returned products through online platforms and retail outlets, promoting sustainability and reducing waste by extending product lifecycles. Reverse logistics focuses on the management of returned goods, recycling, and disposal to optimize supply chain efficiency and recover value from returned items. Explore the distinctions and benefits of recommerce and reverse logistics to enhance your business's sustainability strategy.
Why it is important
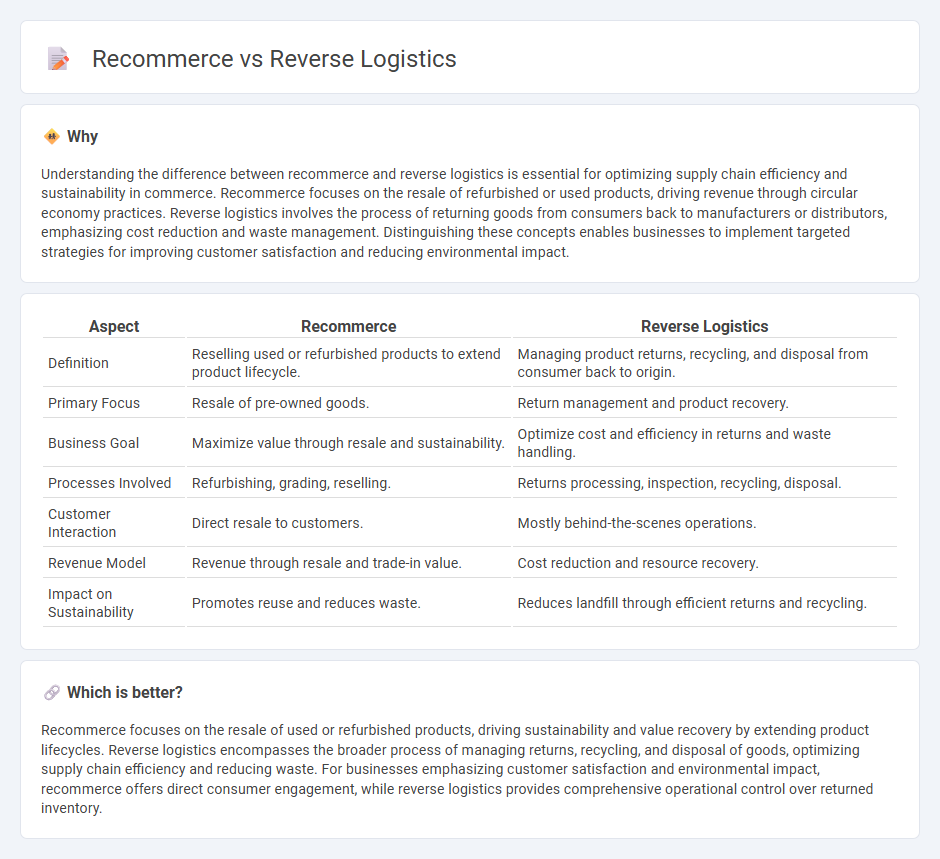
Understanding the difference between recommerce and reverse logistics is essential for optimizing supply chain efficiency and sustainability in commerce. Recommerce focuses on the resale of refurbished or used products, driving revenue through circular economy practices. Reverse logistics involves the process of returning goods from consumers back to manufacturers or distributors, emphasizing cost reduction and waste management. Distinguishing these concepts enables businesses to implement targeted strategies for improving customer satisfaction and reducing environmental impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Recommerce | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reselling used or refurbished products to extend product lifecycle. | Managing product returns, recycling, and disposal from consumer back to origin. |
| Primary Focus | Resale of pre-owned goods. | Return management and product recovery. |
| Business Goal | Maximize value through resale and sustainability. | Optimize cost and efficiency in returns and waste handling. |
| Processes Involved | Refurbishing, grading, reselling. | Returns processing, inspection, recycling, disposal. |
| Customer Interaction | Direct resale to customers. | Mostly behind-the-scenes operations. |
| Revenue Model | Revenue through resale and trade-in value. | Cost reduction and resource recovery. |
| Impact on Sustainability | Promotes reuse and reduces waste. | Reduces landfill through efficient returns and recycling. |
Which is better?
Recommerce focuses on the resale of used or refurbished products, driving sustainability and value recovery by extending product lifecycles. Reverse logistics encompasses the broader process of managing returns, recycling, and disposal of goods, optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing waste. For businesses emphasizing customer satisfaction and environmental impact, recommerce offers direct consumer engagement, while reverse logistics provides comprehensive operational control over returned inventory.
Connection
Recommerce relies heavily on reverse logistics to efficiently manage the return, refurbishment, and resale of used products, reducing waste and extending product life cycles. Reverse logistics streamlines the flow of goods from consumers back to sellers or manufacturers, enabling effective inventory management and cost savings in recommerce operations. The integration of reverse logistics in recommerce supports sustainability goals by minimizing landfill impact and promoting circular economy practices.
Key Terms
Product Returns
Reverse logistics encompasses the process of managing product returns, refurbishing, and recycling, aimed at minimizing waste and recovering value. Recommerce specifically targets reselling returned or used products after inspection and refurbishment, capitalizing on sustainability and cost-efficiency. Explore the key differences and benefits of reverse logistics and recommerce in handling product returns to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Resale Market
Reverse logistics encompasses the process of returning products from consumers to businesses for reuse, refurbishment, or disposal, while recommerce specifically targets the resale market by refurbishing and reselling used goods. The resale market benefits from recommerce by extending product life cycles, reducing waste, and capitalizing on consumer demand for affordable, sustainable options. Discover how businesses leverage these strategies to optimize value recovery and environmental impact in the resale market.
Refurbishment
Reverse logistics involves the process of returning products from the consumer back to the manufacturer or distributor for reuse, refurbishment, or recycling, optimizing supply chain efficiency and minimizing waste. Recommerce specifically centers on refurbishing returned or used products to resell them, extending product life cycles and reducing environmental impact. Explore how these strategies enhance sustainability and profitability in modern retail and manufacturing sectors.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of moving goods from their final destination back to the manufacturer for return, repair, remanufacture, recycling, or disposal, incorporating lean principles to enhance supply chain efficiency and support sustainability goals.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics involves managing the flow of returned goods and optimizing the process through clear policies, supplier collaboration, data analysis, centralized return centers, and automation to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
What Is Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management? - Flowspace - Reverse logistics refers to handling the movement of products from customers back to manufacturers, focusing on returns management, remanufacturing, refurbishment, and reducing waste while enhancing customer experience and brand loyalty.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com