Circular supply chain focuses on designing products and processes to maximize resource efficiency by reusing, refurbishing, and recycling materials throughout the product lifecycle. Reverse logistics involves the strategic planning and management of product returns, repairs, recycling, and disposal to recover value or ensure proper sustainability. Explore the key differences and benefits of circular supply chains and reverse logistics to enhance your business sustainability practices.
Why it is important
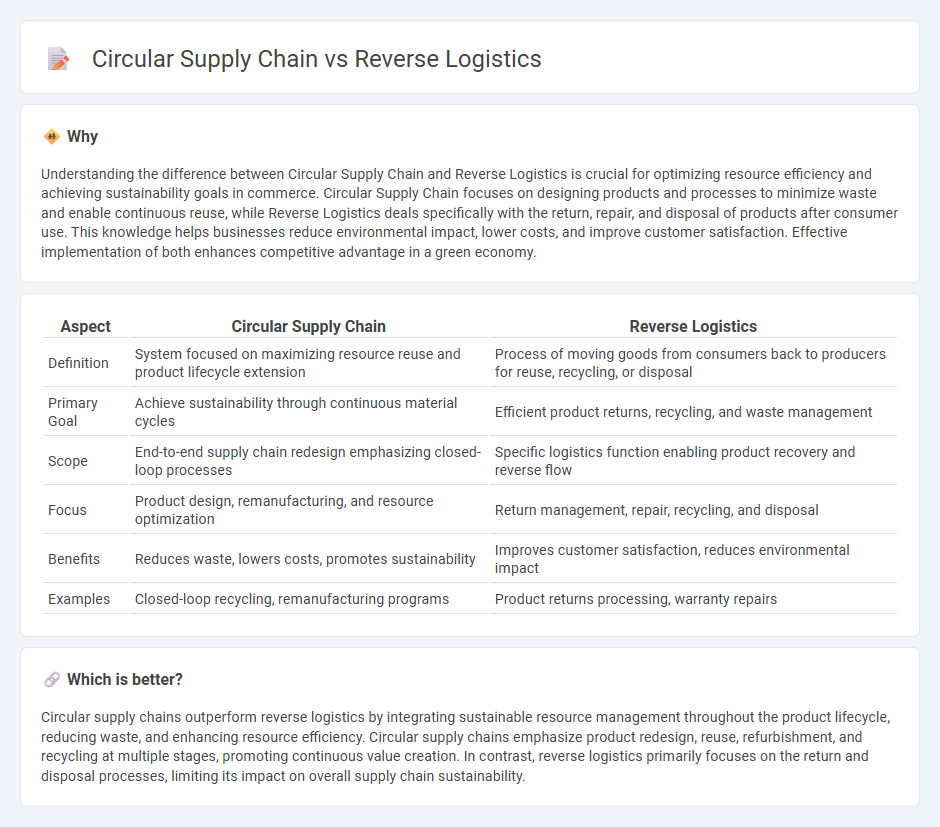
Understanding the difference between Circular Supply Chain and Reverse Logistics is crucial for optimizing resource efficiency and achieving sustainability goals in commerce. Circular Supply Chain focuses on designing products and processes to minimize waste and enable continuous reuse, while Reverse Logistics deals specifically with the return, repair, and disposal of products after consumer use. This knowledge helps businesses reduce environmental impact, lower costs, and improve customer satisfaction. Effective implementation of both enhances competitive advantage in a green economy.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System focused on maximizing resource reuse and product lifecycle extension | Process of moving goods from consumers back to producers for reuse, recycling, or disposal |
| Primary Goal | Achieve sustainability through continuous material cycles | Efficient product returns, recycling, and waste management |
| Scope | End-to-end supply chain redesign emphasizing closed-loop processes | Specific logistics function enabling product recovery and reverse flow |
| Focus | Product design, remanufacturing, and resource optimization | Return management, repair, recycling, and disposal |
| Benefits | Reduces waste, lowers costs, promotes sustainability | Improves customer satisfaction, reduces environmental impact |
| Examples | Closed-loop recycling, remanufacturing programs | Product returns processing, warranty repairs |
Which is better?
Circular supply chains outperform reverse logistics by integrating sustainable resource management throughout the product lifecycle, reducing waste, and enhancing resource efficiency. Circular supply chains emphasize product redesign, reuse, refurbishment, and recycling at multiple stages, promoting continuous value creation. In contrast, reverse logistics primarily focuses on the return and disposal processes, limiting its impact on overall supply chain sustainability.
Connection
Circular supply chain integrates reverse logistics by focusing on the return, refurbishment, and recycling of products to minimize waste and enhance sustainability within commerce. Reverse logistics facilitates the movement of goods from consumers back to manufacturers for reuse or proper disposal, enabling the circular flow of materials. Together, they reduce environmental impact and promote resource efficiency across supply chain operations.
Key Terms
Returns management
Reverse logistics centers on managing product returns efficiently by processing returned items for resale, refurbishment, or recycling, minimizing waste and recovering value. Circular supply chains extend this concept by designing products and systems that enable continuous reuse and regeneration of materials, aiming for zero waste and closed-loop operations. Explore deeper insights into how these models transform returns management and sustainability in supply chains.
Resource recovery
Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient return, recycling, and disposal of products to recover value and reduce waste. Circular supply chains integrate resource recovery by designing closed-loop systems that maintain product lifecycle through reuse, refurbishment, and remanufacturing. Explore more to understand how these strategies drive sustainability and operational efficiency.
Closed-loop system
Reverse logistics involves the process of moving goods from the end consumer back to the manufacturer for reuse, remanufacturing, or disposal, emphasizing efficient returns management and waste reduction. Circular supply chains expand on this concept by integrating closed-loop systems that continuously cycle materials through production, consumption, and recovery stages, promoting resource sustainability and minimizing environmental impact. Explore more about how closed-loop systems revolutionize supply chain resilience and sustainability.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of planning, controlling, and implementing the cost-effective flow of goods from the customer back to the manufacturer for returns, repair, recycling, or remanufacturing, serving as a strategic part of supply chain efficiency and sustainability.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics moves goods from customers back to sellers or manufacturers and can be optimized through strategies like clear return policies, supplier collaboration, data utilization, centralized return centers, and automation.
What Is Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management? - Flowspace - Reverse logistics involves managing returns, refurbishing products, recycling materials, and is essential for enhancing customer experience, reducing waste, and recapturing product value in the supply chain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com