Circular supply chains emphasize sustainability by reusing, refurbishing, and recycling materials to minimize waste and environmental impact, whereas digital supply chains leverage advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain to enhance transparency, efficiency, and real-time decision-making. Both models drive innovation in commerce, promoting resilience and adaptability in global markets. Explore how these supply chain strategies redefine business operations and customer value.
Why it is important
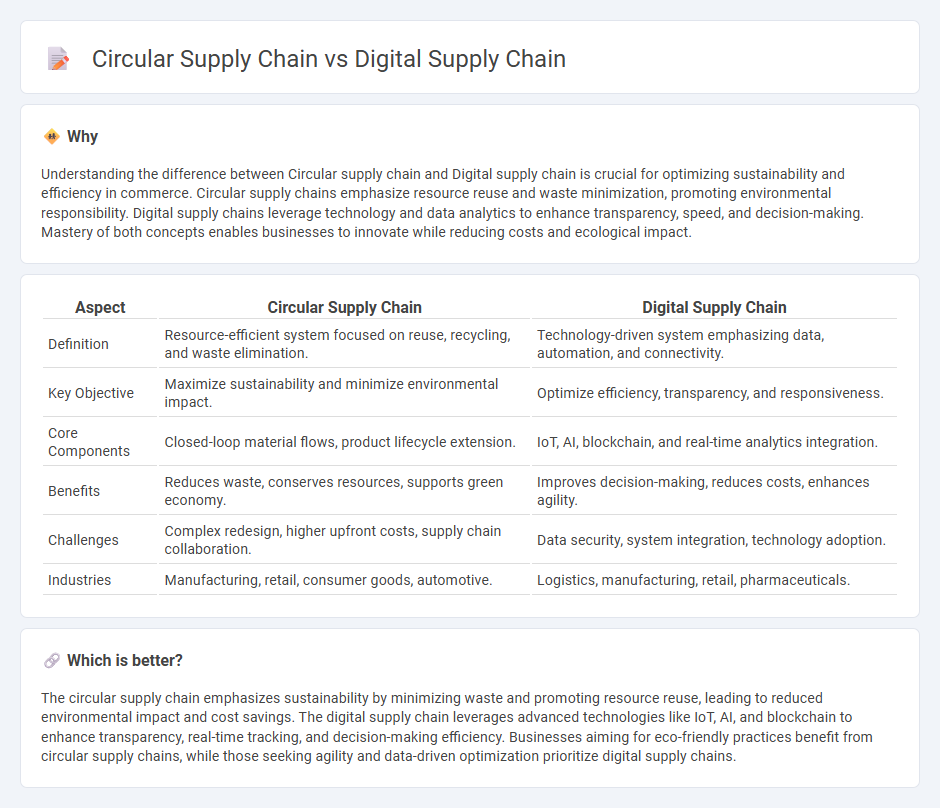
Understanding the difference between Circular supply chain and Digital supply chain is crucial for optimizing sustainability and efficiency in commerce. Circular supply chains emphasize resource reuse and waste minimization, promoting environmental responsibility. Digital supply chains leverage technology and data analytics to enhance transparency, speed, and decision-making. Mastery of both concepts enables businesses to innovate while reducing costs and ecological impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Supply Chain | Digital Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Resource-efficient system focused on reuse, recycling, and waste elimination. | Technology-driven system emphasizing data, automation, and connectivity. |
| Key Objective | Maximize sustainability and minimize environmental impact. | Optimize efficiency, transparency, and responsiveness. |
| Core Components | Closed-loop material flows, product lifecycle extension. | IoT, AI, blockchain, and real-time analytics integration. |
| Benefits | Reduces waste, conserves resources, supports green economy. | Improves decision-making, reduces costs, enhances agility. |
| Challenges | Complex redesign, higher upfront costs, supply chain collaboration. | Data security, system integration, technology adoption. |
| Industries | Manufacturing, retail, consumer goods, automotive. | Logistics, manufacturing, retail, pharmaceuticals. |
Which is better?
The circular supply chain emphasizes sustainability by minimizing waste and promoting resource reuse, leading to reduced environmental impact and cost savings. The digital supply chain leverages advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain to enhance transparency, real-time tracking, and decision-making efficiency. Businesses aiming for eco-friendly practices benefit from circular supply chains, while those seeking agility and data-driven optimization prioritize digital supply chains.
Connection
Circular supply chains focus on resource recovery and waste reduction through recycling, reuse, and remanufacturing, while digital supply chains leverage technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain for real-time tracking and data analytics. Integrating digital tools enhances the circular supply chain by improving transparency, optimizing inventory management, and enabling predictive maintenance to reduce material waste. This connection drives sustainable commerce by aligning operational efficiency with environmental responsibility.
Key Terms
Traceability
Digital supply chains leverage advanced technologies like IoT, blockchain, and AI to enhance traceability by providing real-time data and end-to-end visibility of products throughout the supply process. Circular supply chains prioritize resource regeneration and reuse, employing traceability systems to track material flows and ensure sustainable sourcing, waste reduction, and product lifecycle management. Explore how integrating digital traceability tools can optimize circular supply chain transparency and sustainability efforts.
Resource Recovery
Digital supply chains leverage advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain to enhance transparency, efficiency, and real-time data analytics across the supply network. Circular supply chains prioritize resource recovery by designing processes that minimize waste, enable product reuse, and facilitate material recycling to create a closed-loop system. Explore how these approaches integrate to optimize sustainability and resource utilization in modern supply chains.
Real-time Data Integration
Real-time data integration in digital supply chains enhances visibility and responsiveness by leveraging IoT sensors, AI analytics, and cloud computing to monitor inventory, track shipments, and predict demand with precision. Circular supply chains utilize real-time data to optimize resource recovery, manage reverse logistics efficiently, and facilitate product lifecycle tracking, promoting sustainability through closed-loop systems. Explore how advanced data integration transforms supply chain resilience and environmental impact.
Source and External Links
Digital Supply Chain Management: 7 Essential Elements - A digital supply chain leverages technologies like AI, IoT, and cloud computing to automate and integrate operations, enabling real-time data flow, end-to-end transparency, and more efficient, responsive decision-making across procurement, production, and distribution.
Digital Supply Chain Explained | NetSuite - Unlike traditional linear supply chains, digital supply chains provide near real-time visibility into supplier performance and customer needs, integrating internal and external data for two-way collaboration, greater resilience, and customer-centric fulfillment of speed, personalization, and choice.
Digital Supply Chains: Definition, Benefits, and Careers | Coursera - Digital supply chains use digital technologies and data analytics to capture, monitor, and analyze big data from every stage, empowering businesses to optimize performance, guide decision-making, and quickly adapt to changing market conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com