Ghost commerce operates through invisible, backend e-commerce platforms that streamline supply chain and logistics without traditional storefronts, leveraging data analytics and automation for efficiency. Retail arbitrage involves purchasing discounted products from retail stores and reselling them at higher prices on online marketplaces, capitalizing on price discrepancies and market demand shifts. Explore the differences and benefits of ghost commerce versus retail arbitrage to optimize your selling strategy.
Why it is important
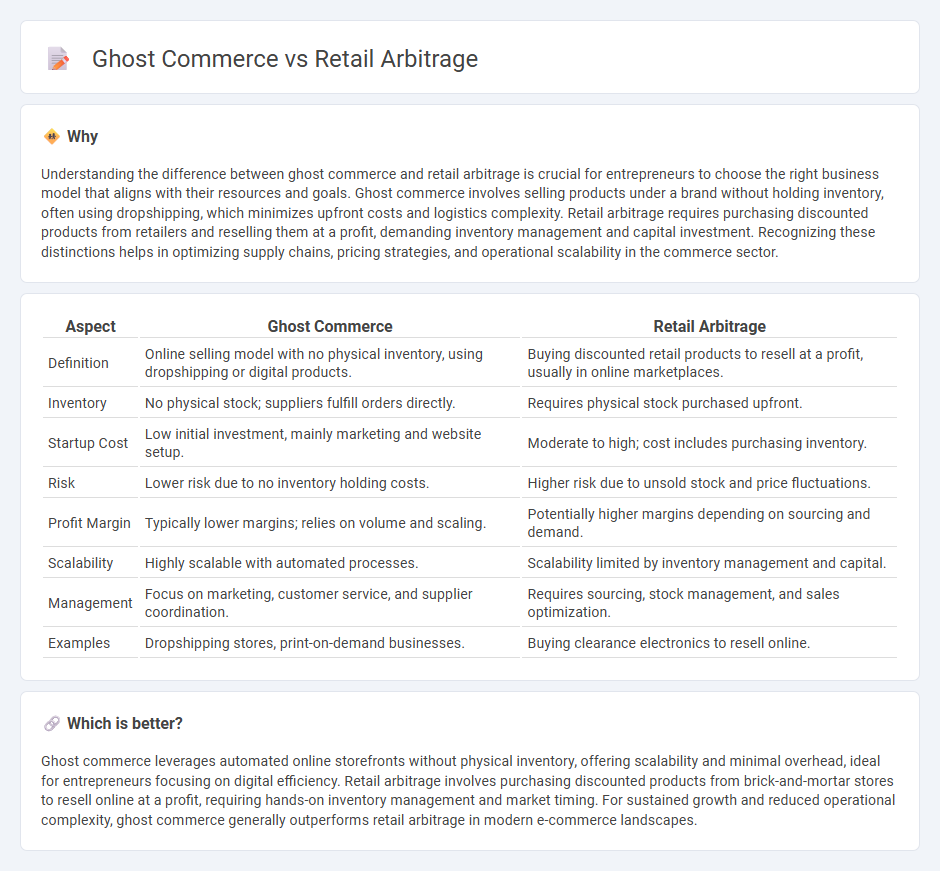
Understanding the difference between ghost commerce and retail arbitrage is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right business model that aligns with their resources and goals. Ghost commerce involves selling products under a brand without holding inventory, often using dropshipping, which minimizes upfront costs and logistics complexity. Retail arbitrage requires purchasing discounted products from retailers and reselling them at a profit, demanding inventory management and capital investment. Recognizing these distinctions helps in optimizing supply chains, pricing strategies, and operational scalability in the commerce sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Commerce | Retail Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Online selling model with no physical inventory, using dropshipping or digital products. | Buying discounted retail products to resell at a profit, usually in online marketplaces. |
| Inventory | No physical stock; suppliers fulfill orders directly. | Requires physical stock purchased upfront. |
| Startup Cost | Low initial investment, mainly marketing and website setup. | Moderate to high; cost includes purchasing inventory. |
| Risk | Lower risk due to no inventory holding costs. | Higher risk due to unsold stock and price fluctuations. |
| Profit Margin | Typically lower margins; relies on volume and scaling. | Potentially higher margins depending on sourcing and demand. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with automated processes. | Scalability limited by inventory management and capital. |
| Management | Focus on marketing, customer service, and supplier coordination. | Requires sourcing, stock management, and sales optimization. |
| Examples | Dropshipping stores, print-on-demand businesses. | Buying clearance electronics to resell online. |
Which is better?
Ghost commerce leverages automated online storefronts without physical inventory, offering scalability and minimal overhead, ideal for entrepreneurs focusing on digital efficiency. Retail arbitrage involves purchasing discounted products from brick-and-mortar stores to resell online at a profit, requiring hands-on inventory management and market timing. For sustained growth and reduced operational complexity, ghost commerce generally outperforms retail arbitrage in modern e-commerce landscapes.
Connection
Ghost commerce and retail arbitrage intersect through the strategy of leveraging low-overhead, virtual storefronts to capitalize on pricing discrepancies across markets. Retail arbitrage involves sourcing discounted products from physical or online retailers and reselling them for profit, often facilitated by ghost commerce's digital platforms that minimize traditional inventory and location costs. This synergy allows entrepreneurs to scale operations efficiently by integrating real-time market analysis tools and automated sales channels.
Key Terms
Inventory sourcing
Retail arbitrage relies on purchasing discounted or clearance products from physical or online stores to resell at a profit, emphasizing timely and opportunistic inventory sourcing. Ghost commerce focuses on leveraging private label or white-label products sourced directly from manufacturers or wholesalers, enabling scalable and brand-controlled inventory management. Explore deeper insights into optimizing inventory sourcing strategies for both retail arbitrage and ghost commerce models.
Order fulfillment
Retail arbitrage involves sourcing products from retail stores at discounted prices and reselling them online, requiring efficient order fulfillment processes to manage inventory and shipping logistics. Ghost commerce eliminates physical inventory by leveraging dropshipping or digital products, streamlining order fulfillment through direct supplier shipping or instant digital delivery. Discover how optimizing order fulfillment can elevate your retail arbitrage or ghost commerce business strategies.
Branding
Retail arbitrage involves purchasing products from retail stores at discounted prices and reselling them online, often resulting in minimal brand identity due to reliance on existing products. Ghost commerce, by contrast, emphasizes building private label brands and creating unique product offerings, enhancing long-term brand value and customer loyalty. Explore more to understand how branding strategies differ and impact success in each model.
Source and External Links
A Complete Guide on Amazon Retail Arbitrage - SellerApp - Retail arbitrage is a business model where individuals buy products at a lower price from retail stores and resell them on platforms like Amazon or Walmart for a profit by leveraging price differences between markets.
Smash Retail Arbitrage on Amazon (2025 Guide) - Repricer Express - Retail arbitrage involves buying products from a retailer and reselling them on other platforms such as Amazon for profit; it is legal if products are purchased legally and not counterfeit, and scanning apps help assess profitability.
Amazon Retail Arbitrage: How to Resell Products on Amazon in 2024 - Retail arbitrage taps into price differences between markets by buying low at retailers and reselling on Amazon, operating under the first-sale doctrine, and differs from wholesale, private label, dropshipping, and handmade business models.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com