Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing upfront costs and risks for e-commerce entrepreneurs. Manufacturing involves producing goods in-house or through third-party factories, offering greater control over product quality and customization but requiring higher investment and operational management. Explore these business models in depth to determine the best fit for your commercial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dropshipping and manufacturing is crucial for optimizing inventory management, cost efficiency, and supply chain control in commerce. Dropshipping eliminates the need for upfront inventory investment, allowing businesses to sell products without holding stock, while manufacturing involves producing goods, ensuring quality control and customization. Selecting the appropriate model impacts profit margins, customer satisfaction, and operational scalability. Accurate knowledge enables entrepreneurs to tailor strategies for competitive advantage and sustainable growth.
Comparison Table
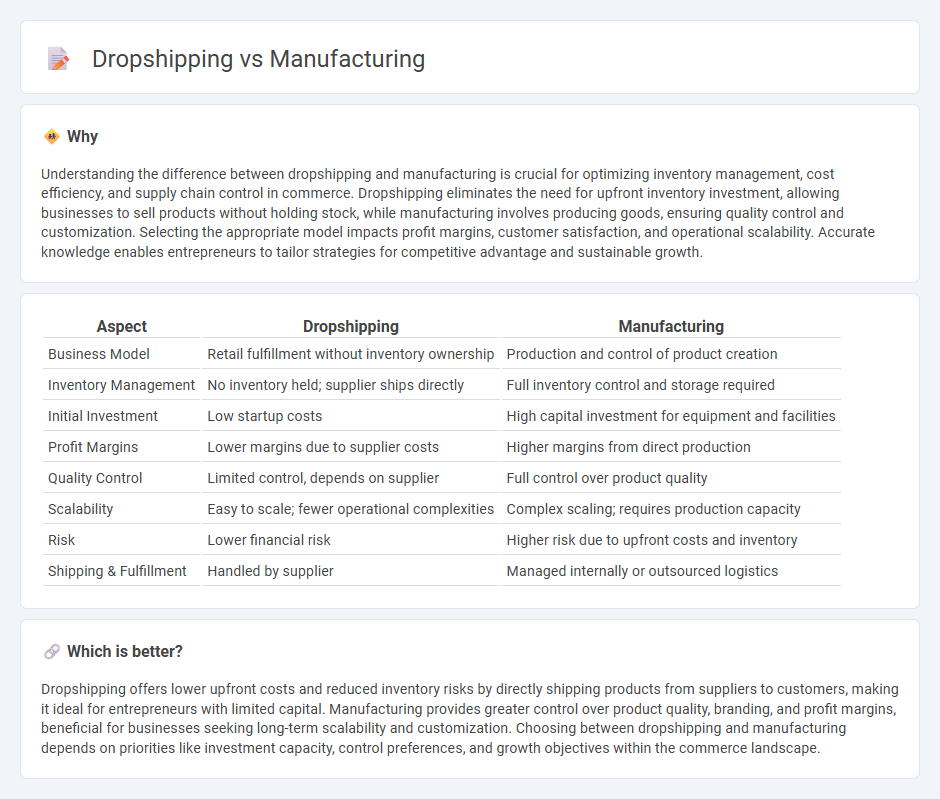
| Aspect | Dropshipping | Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Retail fulfillment without inventory ownership | Production and control of product creation |
| Inventory Management | No inventory held; supplier ships directly | Full inventory control and storage required |
| Initial Investment | Low startup costs | High capital investment for equipment and facilities |
| Profit Margins | Lower margins due to supplier costs | Higher margins from direct production |
| Quality Control | Limited control, depends on supplier | Full control over product quality |
| Scalability | Easy to scale; fewer operational complexities | Complex scaling; requires production capacity |
| Risk | Lower financial risk | Higher risk due to upfront costs and inventory |
| Shipping & Fulfillment | Handled by supplier | Managed internally or outsourced logistics |
Which is better?
Dropshipping offers lower upfront costs and reduced inventory risks by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, making it ideal for entrepreneurs with limited capital. Manufacturing provides greater control over product quality, branding, and profit margins, beneficial for businesses seeking long-term scalability and customization. Choosing between dropshipping and manufacturing depends on priorities like investment capacity, control preferences, and growth objectives within the commerce landscape.
Connection
Dropshipping and manufacturing are interconnected through their roles in the supply chain, where manufacturers produce goods that dropshippers sell without holding inventory. Dropshipping relies on manufacturers to directly ship products to customers, streamlining the order fulfillment process and reducing overhead costs. Efficient communication and reliable production cycles between manufacturers and dropshippers ensure timely delivery and product quality, essential for customer satisfaction in e-commerce commerce models.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Manufacturing requires maintaining in-house inventory, which demands storage space, quality control, and continuous stock level monitoring to prevent overproduction or shortages. Dropshipping eliminates the need for physical inventory by relying on suppliers to ship products directly to customers, reducing upfront investment and risks associated with unsold stock. Explore detailed strategies to optimize inventory management in both models for efficient supply chain operations.
Fulfillment
Manufacturing offers control over product quality and inventory management, ensuring faster fulfillment times and customization capabilities. Dropshipping eliminates inventory risks but depends heavily on suppliers for order processing, often resulting in longer shipping durations and less oversight. Explore the advantages and challenges of each model to optimize your fulfillment strategy.
Upfront Costs
Manufacturing requires significant upfront costs, including expenses for raw materials, production equipment, labor, and quality control, often amounting to thousands or even millions of dollars depending on scale. Dropshipping minimizes initial investment by allowing retailers to sell products without holding inventory or managing fulfillment, instead relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which model aligns best with your business goals and budget.
Source and External Links
Manufacturing - Wikipedia - Manufacturing is the creation of goods using equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processes, transforming raw materials into finished products on a large scale in the secondary sector of the economy.
The ultimate guide to what is manufacturing - Katana Cloud Inventory - Manufacturing involves converting raw materials and components into finished products through labor, tools, and machinery, and can be mass production or custom-made items using processes like batch or continuous manufacturing.
Manufacturing | NIST - The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) supports innovative manufacturing methods to help American industries produce reliable and safe products, ensuring economic and national security.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com