Recommerce focuses on the resale of pre-owned goods, emphasizing sustainability and cost savings by extending product lifecycle through platforms like ThredUp and Depop. Q-commerce, or quick commerce, prioritizes ultra-fast delivery, often within an hour, catering to immediate consumer demands via services such as DoorDash and Gopuff. Explore how recommerce and Q-commerce shape the future of retail and consumer behavior.
Why it is important
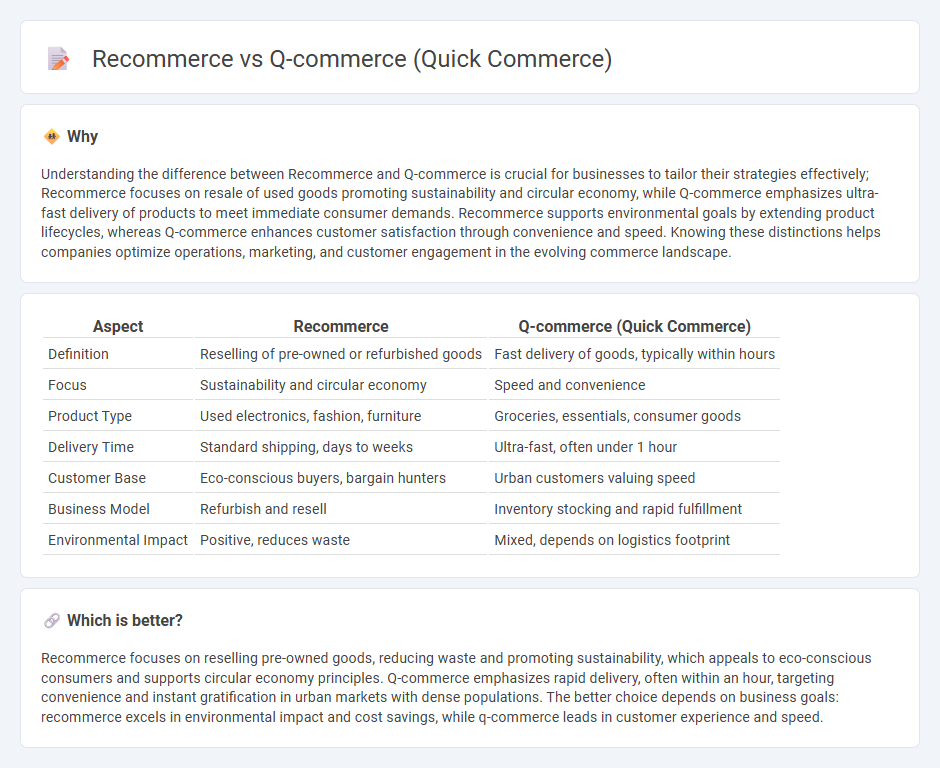
Understanding the difference between Recommerce and Q-commerce is crucial for businesses to tailor their strategies effectively; Recommerce focuses on resale of used goods promoting sustainability and circular economy, while Q-commerce emphasizes ultra-fast delivery of products to meet immediate consumer demands. Recommerce supports environmental goals by extending product lifecycles, whereas Q-commerce enhances customer satisfaction through convenience and speed. Knowing these distinctions helps companies optimize operations, marketing, and customer engagement in the evolving commerce landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Recommerce | Q-commerce (Quick Commerce) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reselling of pre-owned or refurbished goods | Fast delivery of goods, typically within hours |
| Focus | Sustainability and circular economy | Speed and convenience |
| Product Type | Used electronics, fashion, furniture | Groceries, essentials, consumer goods |
| Delivery Time | Standard shipping, days to weeks | Ultra-fast, often under 1 hour |
| Customer Base | Eco-conscious buyers, bargain hunters | Urban customers valuing speed |
| Business Model | Refurbish and resell | Inventory stocking and rapid fulfillment |
| Environmental Impact | Positive, reduces waste | Mixed, depends on logistics footprint |
Which is better?
Recommerce focuses on reselling pre-owned goods, reducing waste and promoting sustainability, which appeals to eco-conscious consumers and supports circular economy principles. Q-commerce emphasizes rapid delivery, often within an hour, targeting convenience and instant gratification in urban markets with dense populations. The better choice depends on business goals: recommerce excels in environmental impact and cost savings, while q-commerce leads in customer experience and speed.
Connection
Recommerce leverages quick commerce (Q-commerce) by enabling rapid resale and redistribution of pre-owned goods through fast delivery networks, enhancing sustainability in retail. Q-commerce platforms utilize real-time inventory management and localized logistics, which support recommerce activities by reducing transaction times and improving customer access to secondhand products. This synergy between recommerce and Q-commerce drives efficiency in circular economy models and meets increasing consumer demand for instant, eco-friendly shopping options.
Key Terms
Speed of Delivery (Q-commerce)
Q-commerce emphasizes ultra-fast delivery times, often within 30 minutes, to satisfy consumer demand for immediate gratification in urban settings. Recommerce prioritizes sustainability by facilitating the resale and recycling of products, focusing on environmental impact rather than speed. Explore how these distinct business models address evolving consumer preferences and operational challenges.
Secondhand/Resale (Recommerce)
Recommerce, centered on secondhand and resale markets, emphasizes sustainability and reducing waste by extending product lifecycles through platforms that facilitate buying and selling used goods. Unlike Q-commerce, which aims for ultra-fast delivery of new products primarily in urban areas, recommerce thrives on consumer demand for affordable, eco-friendly alternatives and leverages trust-building features like authentication and quality guarantees. Explore the evolving dynamics and benefits of recommerce to understand its growing impact on modern retail ecosystems.
Inventory Management
Q-commerce relies on real-time inventory management systems to ensure rapid order fulfillment by tracking stock levels dynamically across multiple micro-fulfillment centers. Recommerce prioritizes inventory accuracy for returned, refurbished, or second-hand goods, integrating reverse logistics to refurbish and restock items efficiently. Explore detailed strategies and technologies that optimize inventory management in both models.
Source and External Links
The Rise of Q-Commerce: Optimizing Payment Acceptance - Q-commerce, or quick commerce, focuses on ultra-fast delivery of goods typically within 10 to 30 minutes, emphasizing speed, convenience, hyperlocal fulfillment through dark stores, and optimized payment methods for small-value orders.
What Is Quick Commerce? Fast, Convenient Shopping Explained - Q-commerce provides rapid delivery (usually under 30 minutes) powered by local fulfillment centers, catering to customer convenience and expanding beyond groceries to diverse product categories like electronics and beauty products.
A Quick Guide to the Q-Commerce Business Model - Deonde - Q-commerce is a business model offering lightning-fast deliveries through strategically located warehouses and a network of delivery partners, enabling customers to conveniently order a wide range of products via seamless mobile or web apps.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com