Drop culture revolutionizes commerce by offering limited-edition products directly to consumers through online platforms, creating scarcity and exclusivity that drive demand. Traditional retail relies on physical stores and consistent inventory, focusing on accessibility and broad product availability. Explore more to understand how these models shape consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Why it is important
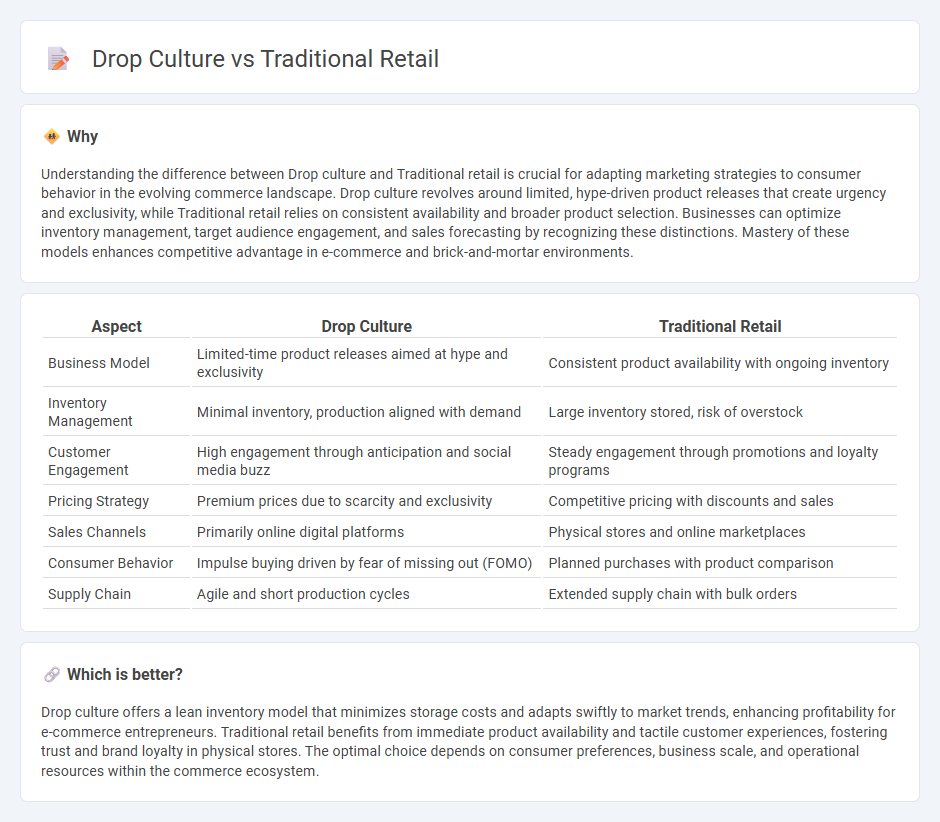
Understanding the difference between Drop culture and Traditional retail is crucial for adapting marketing strategies to consumer behavior in the evolving commerce landscape. Drop culture revolves around limited, hype-driven product releases that create urgency and exclusivity, while Traditional retail relies on consistent availability and broader product selection. Businesses can optimize inventory management, target audience engagement, and sales forecasting by recognizing these distinctions. Mastery of these models enhances competitive advantage in e-commerce and brick-and-mortar environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Drop Culture | Traditional Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Limited-time product releases aimed at hype and exclusivity | Consistent product availability with ongoing inventory |
| Inventory Management | Minimal inventory, production aligned with demand | Large inventory stored, risk of overstock |
| Customer Engagement | High engagement through anticipation and social media buzz | Steady engagement through promotions and loyalty programs |
| Pricing Strategy | Premium prices due to scarcity and exclusivity | Competitive pricing with discounts and sales |
| Sales Channels | Primarily online digital platforms | Physical stores and online marketplaces |
| Consumer Behavior | Impulse buying driven by fear of missing out (FOMO) | Planned purchases with product comparison |
| Supply Chain | Agile and short production cycles | Extended supply chain with bulk orders |
Which is better?
Drop culture offers a lean inventory model that minimizes storage costs and adapts swiftly to market trends, enhancing profitability for e-commerce entrepreneurs. Traditional retail benefits from immediate product availability and tactile customer experiences, fostering trust and brand loyalty in physical stores. The optimal choice depends on consumer preferences, business scale, and operational resources within the commerce ecosystem.
Connection
Drop culture revolutionizes traditional retail by creating limited-time product releases that generate hype and exclusivity, driving consumer urgency and demand. Traditional retail adapts by incorporating drops into launch strategies, blending physical and online shopping experiences to capture broader audiences. The synergy between drop culture and traditional retail enhances brand engagement, boosts sales, and fosters loyal communities.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Traditional retail relies on large inventory batches and steady restocking schedules, often resulting in overstock or stockouts due to demand fluctuations. Drop culture employs limited releases and just-in-time inventory strategies to create scarcity and hype, enhancing demand forecasting and reducing excess stock. Explore how innovative inventory management transforms retail efficiency and consumer experience.
Scarcity Marketing
Scarcity marketing leverages limited availability to drive consumer demand, with traditional retail often using fixed inventory and seasonal sales, while drop culture employs rapid, limited-time releases to create hype and exclusivity. Drop culture's strategy thrives on social media buzz and instant consumer engagement, making products appear more desirable through artificial scarcity and timed scarcity. Explore how these contrasting approaches impact consumer behavior and brand loyalty in today's competitive market.
Customer Experience
Traditional retail offers a consistent shopping environment with established in-store customer service, whereas Drop culture emphasizes limited-time, exclusive product releases that drive excitement and urgency. Drop culture leverages scarcity and hype to create a unique customer experience, often through digital platforms and social media engagement, contrasting with the predictable inventory and browsing experience of traditional retail. Explore the evolving dynamics between these models to understand how customer expectations are reshaping purchasing behavior.
Source and External Links
Direct to Customer vs. Traditional Retail Business Model - Traditional retail is a long-established model where products pass through wholesalers, distributors, and retailers before reaching customers, featuring physical stores, inventory management, and less direct customer interaction compared to DTC models.
Retail vs. E-commerce: What's the Difference? | Indeed.com - Traditional retail involves selling goods in physical locations, enabling direct personal interaction, immediate product access without shipping costs, and fostering customer loyalty through in-person service.
The Fall of Traditional Retail Commerce | Nexcess - Traditional retail evolved from 19th-century mom-and-pop shops through department stores, shopping malls, and big-box stores, but has since faced decline due to digital and economic changes favoring e-commerce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com