Distributed ledger marketplaces offer decentralized, transparent transaction records shared across multiple participants, enhancing trust and reducing fraud. Private ledger marketplaces restrict access to authorized entities, ensuring greater privacy and control over data with faster transaction processing. Explore further to understand which ledger type best suits your commerce needs.
Why it is important
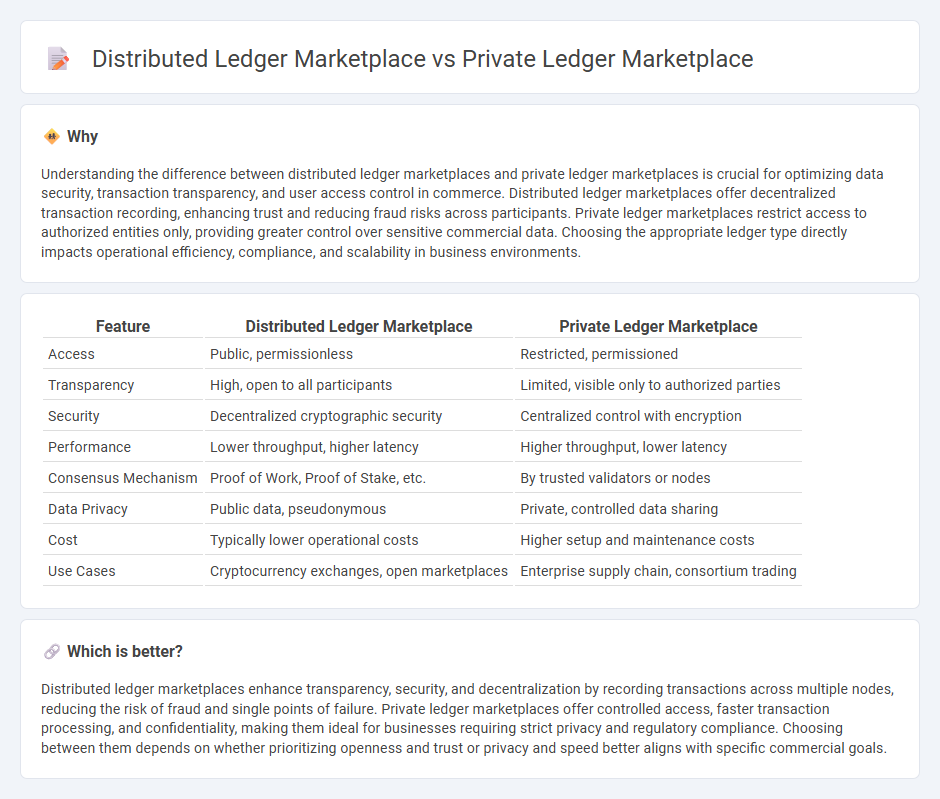
Understanding the difference between distributed ledger marketplaces and private ledger marketplaces is crucial for optimizing data security, transaction transparency, and user access control in commerce. Distributed ledger marketplaces offer decentralized transaction recording, enhancing trust and reducing fraud risks across participants. Private ledger marketplaces restrict access to authorized entities only, providing greater control over sensitive commercial data. Choosing the appropriate ledger type directly impacts operational efficiency, compliance, and scalability in business environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Marketplace | Private Ledger Marketplace |
|---|---|---|
| Access | Public, permissionless | Restricted, permissioned |
| Transparency | High, open to all participants | Limited, visible only to authorized parties |
| Security | Decentralized cryptographic security | Centralized control with encryption |
| Performance | Lower throughput, higher latency | Higher throughput, lower latency |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, etc. | By trusted validators or nodes |
| Data Privacy | Public data, pseudonymous | Private, controlled data sharing |
| Cost | Typically lower operational costs | Higher setup and maintenance costs |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency exchanges, open marketplaces | Enterprise supply chain, consortium trading |
Which is better?
Distributed ledger marketplaces enhance transparency, security, and decentralization by recording transactions across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of fraud and single points of failure. Private ledger marketplaces offer controlled access, faster transaction processing, and confidentiality, making them ideal for businesses requiring strict privacy and regulatory compliance. Choosing between them depends on whether prioritizing openness and trust or privacy and speed better aligns with specific commercial goals.
Connection
Distributed ledger marketplaces and private ledger marketplaces are interconnected through their shared use of blockchain technology to enhance transaction transparency and security. Distributed ledgers promote decentralized data management across multiple participants, while private ledgers restrict access to a predefined group, ensuring confidentiality within commerce ecosystems. This connection allows businesses to choose tailored solutions for supply chain management, digital assets trading, and secure record-keeping based on their specific privacy and scalability needs.
Key Terms
Centralization
Private ledger marketplaces operate on centralized networks where access and transaction validation are restricted to known participants, ensuring enhanced control and privacy but limiting decentralization. Distributed ledger marketplaces employ decentralized consensus mechanisms across multiple nodes to increase transparency, security, and fault tolerance while reducing reliance on a single authority. Explore deeper insights into how centralization impacts security, scalability, and trust models in these ledger systems.
Transparency
Private ledger marketplaces restrict access to a select group of participants, enhancing control but limiting transparency to external parties. Distributed ledger marketplaces operate on a decentralized network, where all transactions are visible to authorized participants, promoting greater transparency and trust. Explore the key differences and implications for your business by learning more about these ledger types.
Intermediaries
Private ledger marketplaces rely on centralized intermediaries to validate transactions and maintain controlled access, enhancing security and privacy within a closed network. Distributed ledger marketplaces eliminate traditional intermediaries by using consensus algorithms across decentralized nodes, promoting transparency and reducing single points of failure. Explore how the role of intermediaries shapes efficiency and trust in these contrasting marketplace models.
Source and External Links
Private Ledger - Faisal Khan - Private ledgers are permissioned digital ledgers with restricted access designed to offer greater control, faster transaction speeds, and enhanced privacy for enterprises, typically managed by a governing body or consortium to secure data sharing within a trusted network.
LedgerFunding: Working Capital Financing Marketplace - LedgerFunding operates a private, secure marketplace using enterprise blockchain technology to connect buyers, suppliers, and financiers, enhancing transparency, data integrity, and efficiency in working capital financing.
Ledger - Ledger provides an open financial platform and marketplace specializing in reinsurance deals and risk-capital connections, combining transparency and standardized processes to improve efficiency and clarity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com