Dark patterns manipulate users into taking actions that benefit businesses at the expense of user experience, often through deceptive or misleading interfaces. Persuasive design, rooted in psychology, ethically encourages desired behaviors by enhancing usability and aligning with user goals. Explore the distinctions between these tactics to better understand how commerce interfaces influence consumer decisions.
Why it is important
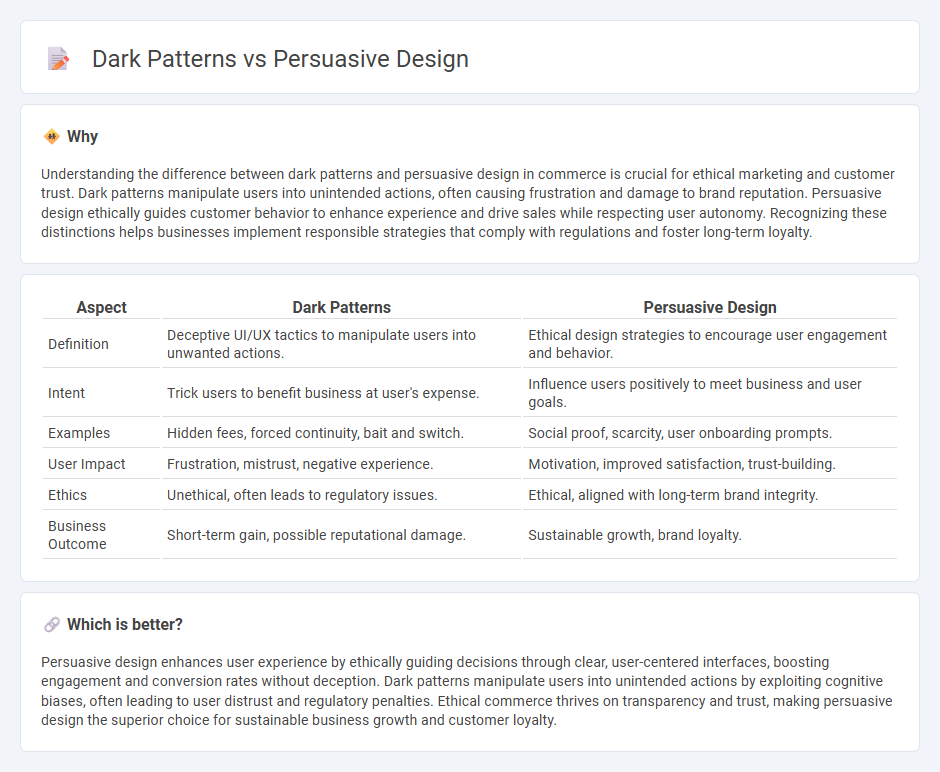
Understanding the difference between dark patterns and persuasive design in commerce is crucial for ethical marketing and customer trust. Dark patterns manipulate users into unintended actions, often causing frustration and damage to brand reputation. Persuasive design ethically guides customer behavior to enhance experience and drive sales while respecting user autonomy. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses implement responsible strategies that comply with regulations and foster long-term loyalty.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Patterns | Persuasive Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deceptive UI/UX tactics to manipulate users into unwanted actions. | Ethical design strategies to encourage user engagement and behavior. |
| Intent | Trick users to benefit business at user's expense. | Influence users positively to meet business and user goals. |
| Examples | Hidden fees, forced continuity, bait and switch. | Social proof, scarcity, user onboarding prompts. |
| User Impact | Frustration, mistrust, negative experience. | Motivation, improved satisfaction, trust-building. |
| Ethics | Unethical, often leads to regulatory issues. | Ethical, aligned with long-term brand integrity. |
| Business Outcome | Short-term gain, possible reputational damage. | Sustainable growth, brand loyalty. |
Which is better?
Persuasive design enhances user experience by ethically guiding decisions through clear, user-centered interfaces, boosting engagement and conversion rates without deception. Dark patterns manipulate users into unintended actions by exploiting cognitive biases, often leading to user distrust and regulatory penalties. Ethical commerce thrives on transparency and trust, making persuasive design the superior choice for sustainable business growth and customer loyalty.
Connection
Dark patterns exploit cognitive biases through persuasive design techniques to manipulate user behavior in commerce, often leading to unintended purchases or subscription traps. These design strategies optimize conversion rates by subtly guiding users toward actions that benefit sellers, sometimes at the expense of transparency and user autonomy. Understanding this connection is crucial for creating ethical e-commerce experiences that balance persuasive elements with consumer trust.
Key Terms
User Experience (UX)
Persuasive design leverages psychological principles to guide users toward beneficial actions, enhancing overall User Experience (UX) by making interactions intuitive and goal-oriented. Dark patterns manipulate user behavior through deceptive interfaces, often leading to frustration and mistrust, negatively impacting UX. Explore how ethical persuasive design can improve usability and foster lasting user trust.
Ethical Design
Persuasive design leverages psychological principles to motivate user actions ethically, enhancing user experience and satisfaction without manipulation. In contrast, dark patterns exploit cognitive biases to deceive users into unintended decisions, often prioritizing business gains over user well-being. Explore how ethical design frameworks create trust and transparency by aligning user goals with business objectives for responsible digital interactions.
Manipulation
Persuasive design employs psychological principles to encourage user engagement and facilitate decision-making, enhancing user experience by presenting choices transparently. Dark patterns exploit cognitive biases through deceptive tactics, manipulating users into actions they might not otherwise take, often undermining trust and autonomy. Explore deeper insights into how ethical design strategies can balance engagement without manipulation.
Source and External Links
Persuasive design: crafting interfaces that motivate and engage - Persuasive design is an approach that guides users toward specific behaviors or decisions by applying psychological principles like social proof, scarcity, reciprocity, commitment, authority, and framing to motivate and engage users effectively.
Persuasive Design: Understanding Psychology of Human Behavior - This design practice uses behavioral insights such as triggers, conditioning, and positive reinforcement to shape user habits and increase engagement by understanding and motivating user behavior through psychology and sociology.
Pixels of Influence: Breaking Down Persuasive Design Principles - Six common persuasive design principles are framing, reciprocity, scarcity, social proof, authority, and salience, which UX designers use to make user experiences more convincing and to encourage decision-making and action.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com