Headless commerce separates the frontend presentation layer from backend commerce functionalities, enabling flexible and customizable customer experiences across multiple channels. Microservices-based commerce breaks down the backend into independent, modular services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled separately for enhanced agility and resilience. Explore the differences and benefits of headless and microservices architectures to optimize your e-commerce strategy.
Why it is important
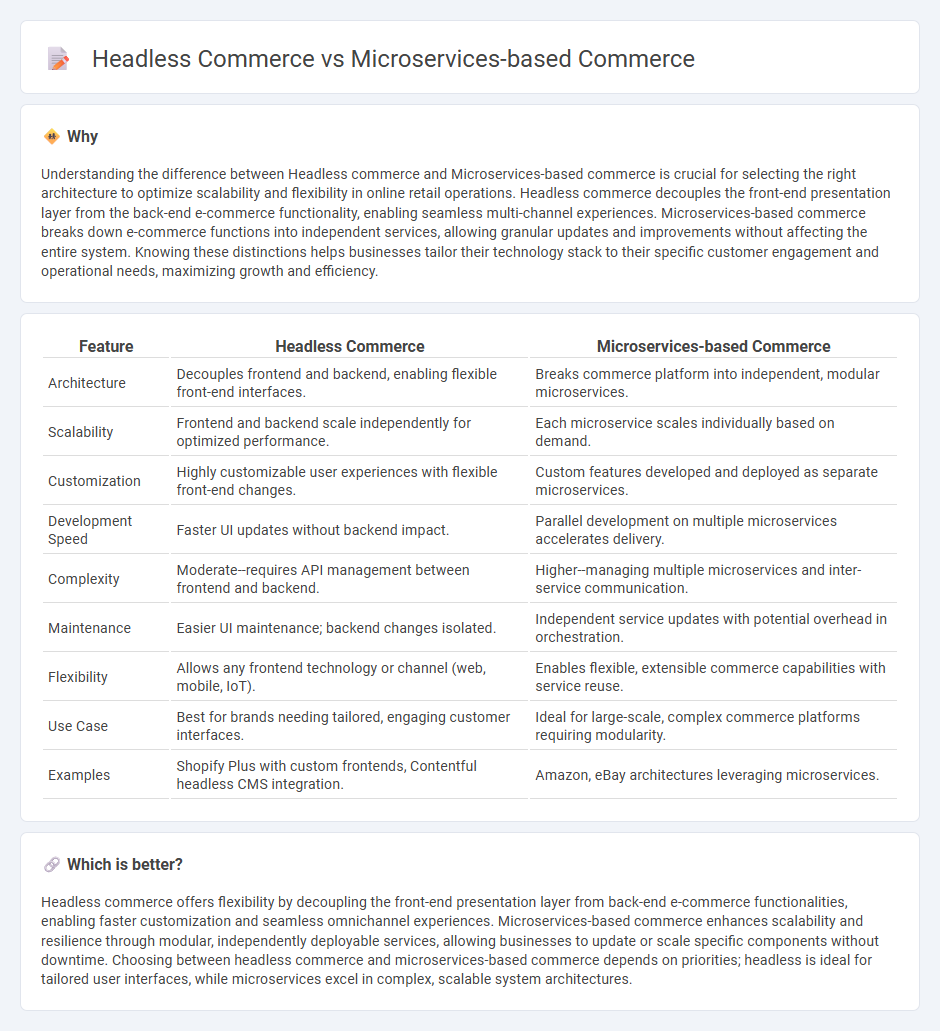
Understanding the difference between Headless commerce and Microservices-based commerce is crucial for selecting the right architecture to optimize scalability and flexibility in online retail operations. Headless commerce decouples the front-end presentation layer from the back-end e-commerce functionality, enabling seamless multi-channel experiences. Microservices-based commerce breaks down e-commerce functions into independent services, allowing granular updates and improvements without affecting the entire system. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses tailor their technology stack to their specific customer engagement and operational needs, maximizing growth and efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Headless Commerce | Microservices-based Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Decouples frontend and backend, enabling flexible front-end interfaces. | Breaks commerce platform into independent, modular microservices. |
| Scalability | Frontend and backend scale independently for optimized performance. | Each microservice scales individually based on demand. |
| Customization | Highly customizable user experiences with flexible front-end changes. | Custom features developed and deployed as separate microservices. |
| Development Speed | Faster UI updates without backend impact. | Parallel development on multiple microservices accelerates delivery. |
| Complexity | Moderate--requires API management between frontend and backend. | Higher--managing multiple microservices and inter-service communication. |
| Maintenance | Easier UI maintenance; backend changes isolated. | Independent service updates with potential overhead in orchestration. |
| Flexibility | Allows any frontend technology or channel (web, mobile, IoT). | Enables flexible, extensible commerce capabilities with service reuse. |
| Use Case | Best for brands needing tailored, engaging customer interfaces. | Ideal for large-scale, complex commerce platforms requiring modularity. |
| Examples | Shopify Plus with custom frontends, Contentful headless CMS integration. | Amazon, eBay architectures leveraging microservices. |
Which is better?
Headless commerce offers flexibility by decoupling the front-end presentation layer from back-end e-commerce functionalities, enabling faster customization and seamless omnichannel experiences. Microservices-based commerce enhances scalability and resilience through modular, independently deployable services, allowing businesses to update or scale specific components without downtime. Choosing between headless commerce and microservices-based commerce depends on priorities; headless is ideal for tailored user interfaces, while microservices excel in complex, scalable system architectures.
Connection
Headless commerce and microservices-based commerce are connected through their shared focus on flexibility and scalability in e-commerce architecture. Headless commerce decouples the front-end presentation layer from the back-end commerce logic, enabling seamless integration across multiple channels, while microservices-based commerce breaks down e-commerce functionalities into independent, modular services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. Together, these approaches enhance customization, improve system resilience, and accelerate time-to-market for e-commerce solutions.
Key Terms
Service Decomposition
Microservices-based commerce breaks down e-commerce functionality into independently deployable services, enabling granular control over inventory, payment, and user management. Headless commerce separates the front-end presentation layer from back-end commerce engines, allowing for flexible and customizable customer experiences across channels. Explore the nuanced differences in service decomposition to optimize your e-commerce architecture.
API-First
Microservices-based commerce leverages independently deployable services allowing granular control and scalability, enhancing modular development and flexibility. Headless commerce prioritizes decoupled front-end and back-end via API-first architecture, facilitating seamless omnichannel experiences and rapid front-end innovation. Explore the nuances of API-first strategies to optimize your digital commerce infrastructure.
Presentation Layer Decoupling
Microservices-based commerce structures e-commerce applications as independently deployable services focusing on specific business capabilities, providing granular control over each layer, including the presentation layer. Headless commerce separates the frontend presentation layer from the backend commerce logic via APIs, enabling flexible and customizable user interfaces independent of backend constraints. Explore the detailed distinctions to understand how presentation layer decoupling drives scalability and innovation in modern commerce architectures.
Source and External Links
What is eCommerce Microservices Architecture - Kibo Commerce - Microservices-based commerce uses independent, modular services operating separately to replace monolithic eCommerce systems, enabling scalability, agility, reduced downtime, and seamless omnichannel experiences with easier customization and future-proofing.
Microservices-Based Architecture in Ecommerce for Modular Solutions - Microservices architecture breaks ecommerce into separate components connected via APIs, allowing faster development, independent lifecycle management, cost optimization, improved resilience, and gradual migration from legacy systems.
Microservices - MACH(r) architecture - Commercetools - Microservices in commerce enable independently deployable, loosely coupled components aligned with business domains, improving speed, flexibility, modularity, scalability, team productivity, and delivering faster feature releases and reliable customer experiences.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com