Green logistics focuses on reducing environmental impact by optimizing transportation routes, utilizing eco-friendly packaging, and implementing sustainable supply chain practices. Freight forwarding specializes in managing the shipment of goods across international borders, ensuring efficient customs clearance and timely delivery. Explore more about how green logistics and freight forwarding intersect to create sustainable commerce solutions.
Why it is important
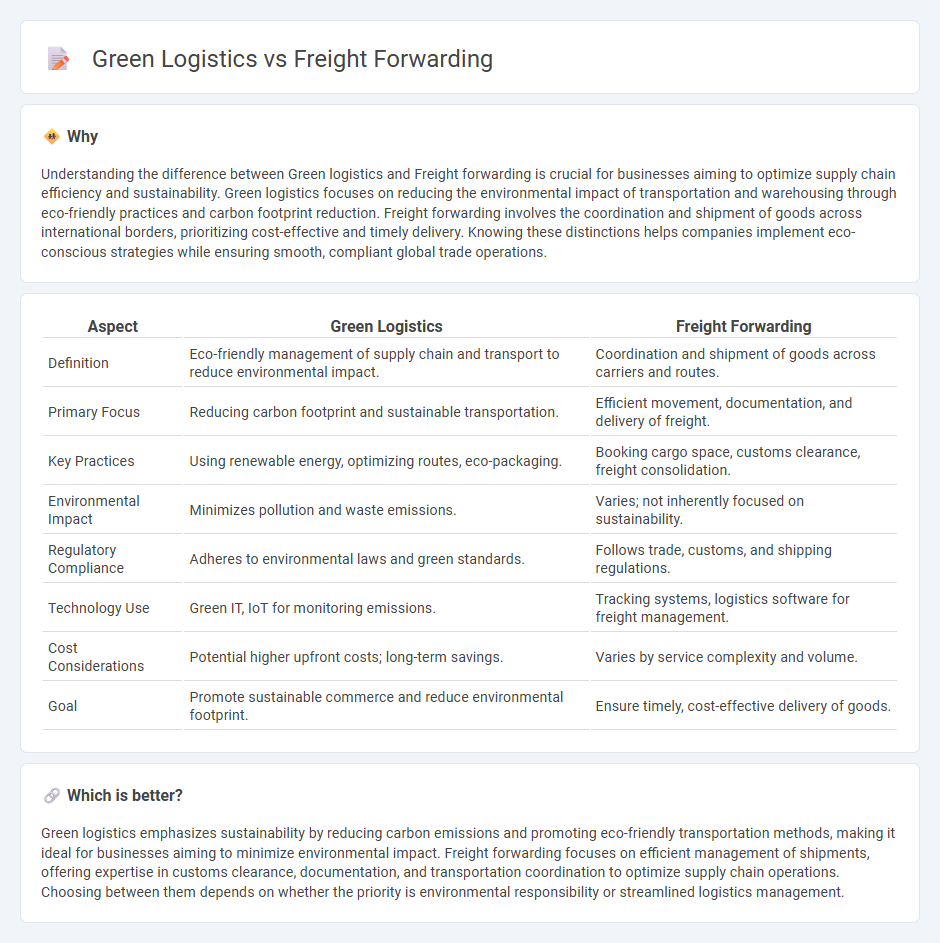
Understanding the difference between Green logistics and Freight forwarding is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize supply chain efficiency and sustainability. Green logistics focuses on reducing the environmental impact of transportation and warehousing through eco-friendly practices and carbon footprint reduction. Freight forwarding involves the coordination and shipment of goods across international borders, prioritizing cost-effective and timely delivery. Knowing these distinctions helps companies implement eco-conscious strategies while ensuring smooth, compliant global trade operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Logistics | Freight Forwarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Eco-friendly management of supply chain and transport to reduce environmental impact. | Coordination and shipment of goods across carriers and routes. |
| Primary Focus | Reducing carbon footprint and sustainable transportation. | Efficient movement, documentation, and delivery of freight. |
| Key Practices | Using renewable energy, optimizing routes, eco-packaging. | Booking cargo space, customs clearance, freight consolidation. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes pollution and waste emissions. | Varies; not inherently focused on sustainability. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adheres to environmental laws and green standards. | Follows trade, customs, and shipping regulations. |
| Technology Use | Green IT, IoT for monitoring emissions. | Tracking systems, logistics software for freight management. |
| Cost Considerations | Potential higher upfront costs; long-term savings. | Varies by service complexity and volume. |
| Goal | Promote sustainable commerce and reduce environmental footprint. | Ensure timely, cost-effective delivery of goods. |
Which is better?
Green logistics emphasizes sustainability by reducing carbon emissions and promoting eco-friendly transportation methods, making it ideal for businesses aiming to minimize environmental impact. Freight forwarding focuses on efficient management of shipments, offering expertise in customs clearance, documentation, and transportation coordination to optimize supply chain operations. Choosing between them depends on whether the priority is environmental responsibility or streamlined logistics management.
Connection
Green logistics and freight forwarding are interconnected through sustainable supply chain practices that minimize environmental impact while optimizing transportation efficiency. Freight forwarding integrates green logistics by selecting eco-friendly shipping routes, utilizing fuel-efficient vehicles, and implementing carbon footprint reduction strategies. These practices promote cost savings, regulatory compliance, and corporate social responsibility in global commerce.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Management
Freight forwarding plays a crucial role in supply chain management by coordinating the efficient transportation and delivery of goods across multiple modes, ensuring cost-effectiveness and timely distribution. Green logistics prioritizes sustainable practices within the supply chain, reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and promoting eco-friendly transportation alternatives to support environmental responsibility. Explore how integrating green logistics strategies with freight forwarding can optimize supply chain performance and sustainability.
Carbon Emissions
Freight forwarding plays a crucial role in global supply chains but often contributes significantly to carbon emissions due to transportation methods like air and sea freight. Green logistics aims to minimize environmental impact by optimizing routes, using renewable energy, and adopting electric or low-emission vehicles to reduce the overall carbon footprint. Explore how innovative green logistics strategies can transform freight forwarding for a sustainable future.
Customs Clearance
Freight forwarding involves the coordination and shipment of goods through various transportation modes, ensuring timely delivery and efficient customs clearance by managing documentation and regulatory compliance. Green logistics emphasizes sustainable practices in freight forwarding, aiming to reduce carbon emissions and environmental impact throughout the customs clearance process by promoting eco-friendly methods and technologies. Explore more about how innovations in customs clearance are shaping the future of eco-conscious freight forwarding and green logistics.
Source and External Links
What is freight forwarding? | Clarksons - Freight forwarding is the strategic planning and coordination of the international movement of goods via multiple transport modes, with freight forwarders acting as logistics experts who plan shipments, handle customs clearance, and liaise with transport providers to ensure timely and safe delivery.
What Is Freight Forwarding? Definition, Benefits and Key Stages - Freight forwarding involves a series of steps including export haulage, export customs clearance, and origin handling, where freight forwarders arrange transportation, ensure legal compliance, inspect goods, and manage shipments of various items under specific regulations.
About Freight Forwarding - FIATA - Freight forwarding encompasses carriage, consolidation, storage, handling, packing, and distribution of goods internationally, including advisory services like customs clearance and insurance, aiming to deliver goods economically, on time, and in good condition across the supply chain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com