Recommerce focuses on the buying and selling of pre-owned goods, emphasizing sustainability and cost-efficiency, while e-commerce involves the online retail of new products through digital platforms. The growth of recommerce is driven by increasing consumer awareness of environmental impact combined with the convenience of digital marketplaces. Explore how these commerce models shape consumer behavior and market dynamics.
Why it is important
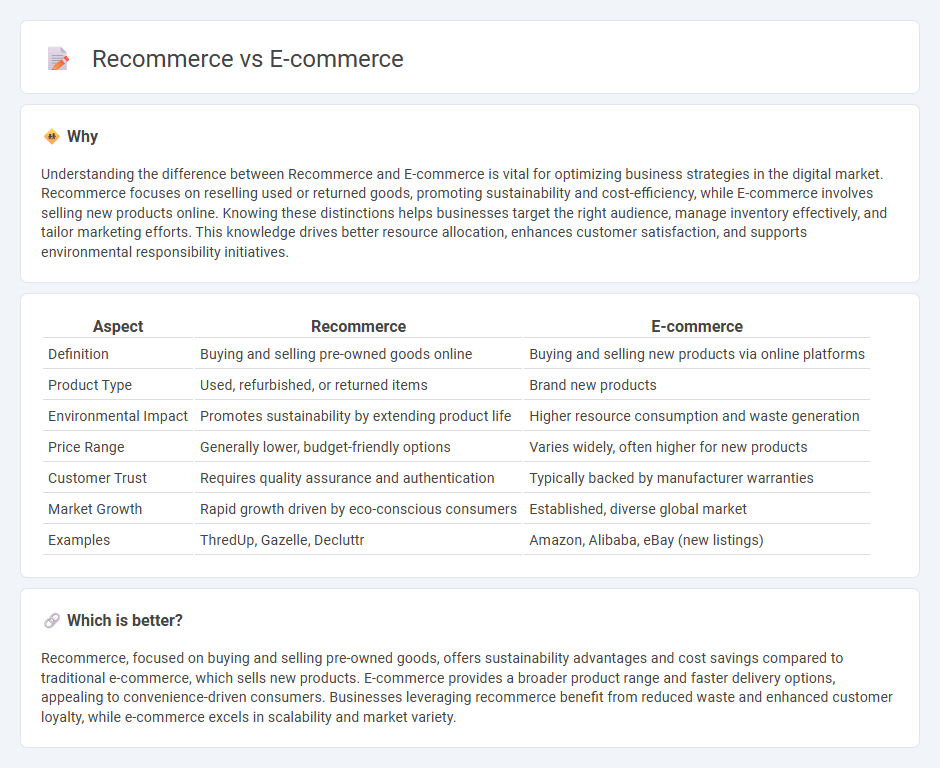
Understanding the difference between Recommerce and E-commerce is vital for optimizing business strategies in the digital market. Recommerce focuses on reselling used or returned goods, promoting sustainability and cost-efficiency, while E-commerce involves selling new products online. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses target the right audience, manage inventory effectively, and tailor marketing efforts. This knowledge drives better resource allocation, enhances customer satisfaction, and supports environmental responsibility initiatives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Recommerce | E-commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying and selling pre-owned goods online | Buying and selling new products via online platforms |
| Product Type | Used, refurbished, or returned items | Brand new products |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes sustainability by extending product life | Higher resource consumption and waste generation |
| Price Range | Generally lower, budget-friendly options | Varies widely, often higher for new products |
| Customer Trust | Requires quality assurance and authentication | Typically backed by manufacturer warranties |
| Market Growth | Rapid growth driven by eco-conscious consumers | Established, diverse global market |
| Examples | ThredUp, Gazelle, Decluttr | Amazon, Alibaba, eBay (new listings) |
Which is better?
Recommerce, focused on buying and selling pre-owned goods, offers sustainability advantages and cost savings compared to traditional e-commerce, which sells new products. E-commerce provides a broader product range and faster delivery options, appealing to convenience-driven consumers. Businesses leveraging recommerce benefit from reduced waste and enhanced customer loyalty, while e-commerce excels in scalability and market variety.
Connection
Recommerce and e-commerce intersect through the digital marketplace enabling both new and pre-owned goods to reach global consumers efficiently. E-commerce platforms provide the infrastructure for recommerce activities, supporting resale, trade-in, and refurbished product transactions that extend product lifecycles. The integration of recommerce within e-commerce drives sustainability, reduces waste, and meets growing consumer demand for affordable, eco-friendly shopping options.
Key Terms
Online Marketplace
E-commerce platforms facilitate the sale of new products directly from manufacturers or retailers to consumers, generating significant market revenue with global sales surpassing $5 trillion in 2023. Recommerce, also known as reverse commerce, emphasizes the resale of pre-owned goods through online marketplaces like eBay, Depop, and ThredUp, contributing to a sustainable economy by reducing waste and extending product life cycles. Explore the evolving dynamics between e-commerce and recommerce and their impact on consumer behavior and environmental sustainability.
Resale Value
E-commerce platforms facilitate the sale of new products, often with fixed pricing, while recommerce focuses on reselling pre-owned goods, emphasizing sustainable consumption and maximizing resale value. Items like electronics, designer apparel, and luxury goods retain significant resale value due to brand demand and product condition in recommerce markets. Explore the evolving dynamics of online resale and its impact on consumer spending by diving deeper into e-commerce versus recommerce trends.
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) transactions in e-commerce facilitate direct sales between individuals, typically through online marketplaces or platforms like eBay and Facebook Marketplace. Recommerce emphasizes the resale, refurbishing, or recycling of pre-owned goods, promoting sustainability and cost savings by extending product lifecycles. Explore the growing impact of C2C models in transforming retail dynamics and fostering circular economy principles.
Source and External Links
What Is Ecommerce? Guide To Selling Online (2025) - Shopify - Ecommerce is the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet, involving transactions such as direct to consumer (DTC), business to business (B2B), and consumer to consumer (C2C), including online shopping, digital downloads, and subscriptions.
Glossary:E-commerce - Statistics Explained - Eurostat - E-commerce broadly refers to the sale or purchase of goods and services electronically via the internet or other online networks, including financial investments, travel reservations, and online auctions, with some exclusions like orders via manually typed emails.
Ecommerce (Learn About the Evolution of Online Shopping) - BigCommerce - Ecommerce business models include B2C (business-to-consumer), B2B (business-to-business), and C2C (consumer-to-consumer), each serving different types of online transactions and audiences, helping businesses scale and optimize operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com