Dark patterns manipulate user behavior through deceptive interfaces, leading to unintended purchases or data sharing, often undermining trust and user autonomy. User-centered design focuses on transparency and usability, prioritizing the user's goals to enhance satisfaction and foster long-term engagement. Explore how ethical design transforms commerce by balancing profitability with user empowerment.
Why it is important
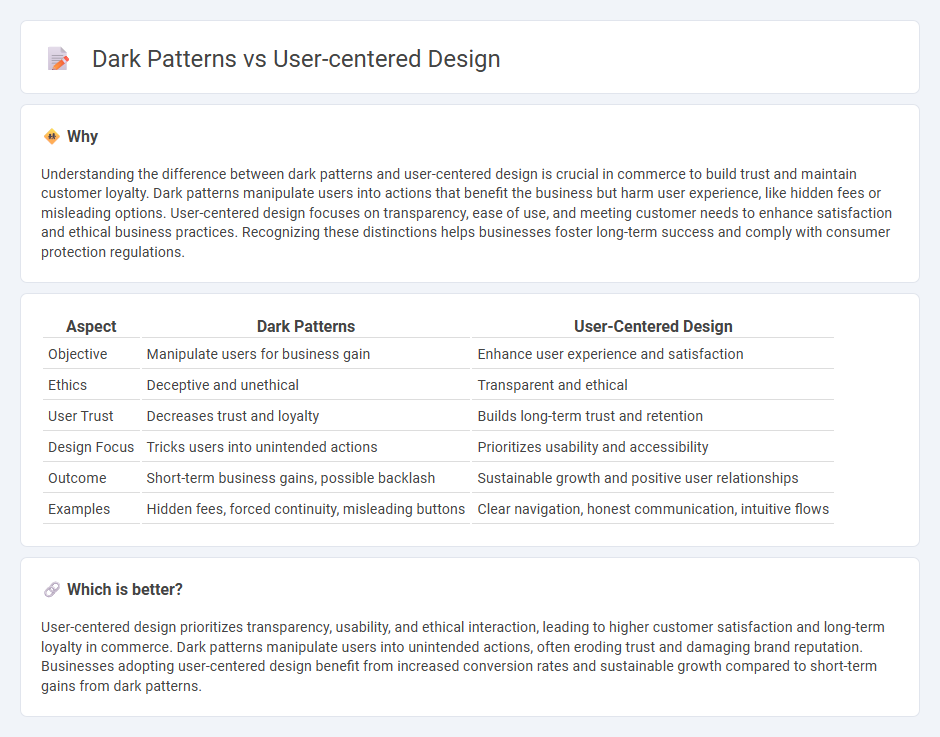
Understanding the difference between dark patterns and user-centered design is crucial in commerce to build trust and maintain customer loyalty. Dark patterns manipulate users into actions that benefit the business but harm user experience, like hidden fees or misleading options. User-centered design focuses on transparency, ease of use, and meeting customer needs to enhance satisfaction and ethical business practices. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses foster long-term success and comply with consumer protection regulations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Patterns | User-Centered Design |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Manipulate users for business gain | Enhance user experience and satisfaction |
| Ethics | Deceptive and unethical | Transparent and ethical |
| User Trust | Decreases trust and loyalty | Builds long-term trust and retention |
| Design Focus | Tricks users into unintended actions | Prioritizes usability and accessibility |
| Outcome | Short-term business gains, possible backlash | Sustainable growth and positive user relationships |
| Examples | Hidden fees, forced continuity, misleading buttons | Clear navigation, honest communication, intuitive flows |
Which is better?
User-centered design prioritizes transparency, usability, and ethical interaction, leading to higher customer satisfaction and long-term loyalty in commerce. Dark patterns manipulate users into unintended actions, often eroding trust and damaging brand reputation. Businesses adopting user-centered design benefit from increased conversion rates and sustainable growth compared to short-term gains from dark patterns.
Connection
Dark patterns exploit cognitive biases to manipulate user behavior in e-commerce, undermining trust and ethical standards. User-centered design prioritizes transparency and usability, fostering positive customer experiences that counteract deceptive tactics. Emphasizing ethical design principles enhances brand loyalty and drives sustainable commercial success.
Key Terms
Usability
User-centered design prioritizes usability by focusing on the needs, behaviors, and preferences of users to create intuitive and efficient interfaces. Dark patterns exploit cognitive biases and deceptive tactics to manipulate user actions, often compromising usability and trust. Explore more about how prioritizing ethical design enhances user satisfaction and engagement.
Manipulation
User-centered design prioritizes transparency and ethical interaction, fostering trust and long-term engagement by aligning interfaces with genuine user needs. Dark patterns exploit psychological manipulation, tricking users into unintended actions such as unwanted subscriptions or privacy compromises. Explore how understanding these differences can enhance ethical digital experiences.
Conversion
User-centered design prioritizes enhancing user experience by creating intuitive interfaces that meet genuine user needs, leading to sustainable conversion rates. Dark patterns manipulate user behavior through deceptive tactics, driving short-term conversions but often damaging brand trust and long-term customer loyalty. Explore the impact of these design approaches on conversion optimization to make informed choices for your product strategy.
Source and External Links
User-Centered Design - Definition, Benefits & Methods - UXCam - User-centered design places the needs and desires of users at the core of the development process, using deep user understanding and research to create products that provide lasting user value.
User-Centered Design: Principles and Examples of UCD - Baymard - User-centered design means designing from the user's perspective by leveraging data on their needs and feedback to build highly usable and accessible digital products.
User-Centered Design: What It Is and How to Do It Right - UCD is an iterative design approach driven by user needs, balancing business goals with empathy, and involving ongoing testing with real users to create products they love.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com