Social shopping leverages interactive platforms where users discover and purchase products through peer recommendations and real-time engagement, enhancing personalized shopping experiences. Dropshipping operates as a retail fulfillment method allowing sellers to offer products without holding inventory, directly shipping items from suppliers to customers with minimal upfront investment. Explore the benefits and challenges of these distinct commerce models to determine the best fit for your business goals.
Why it is important
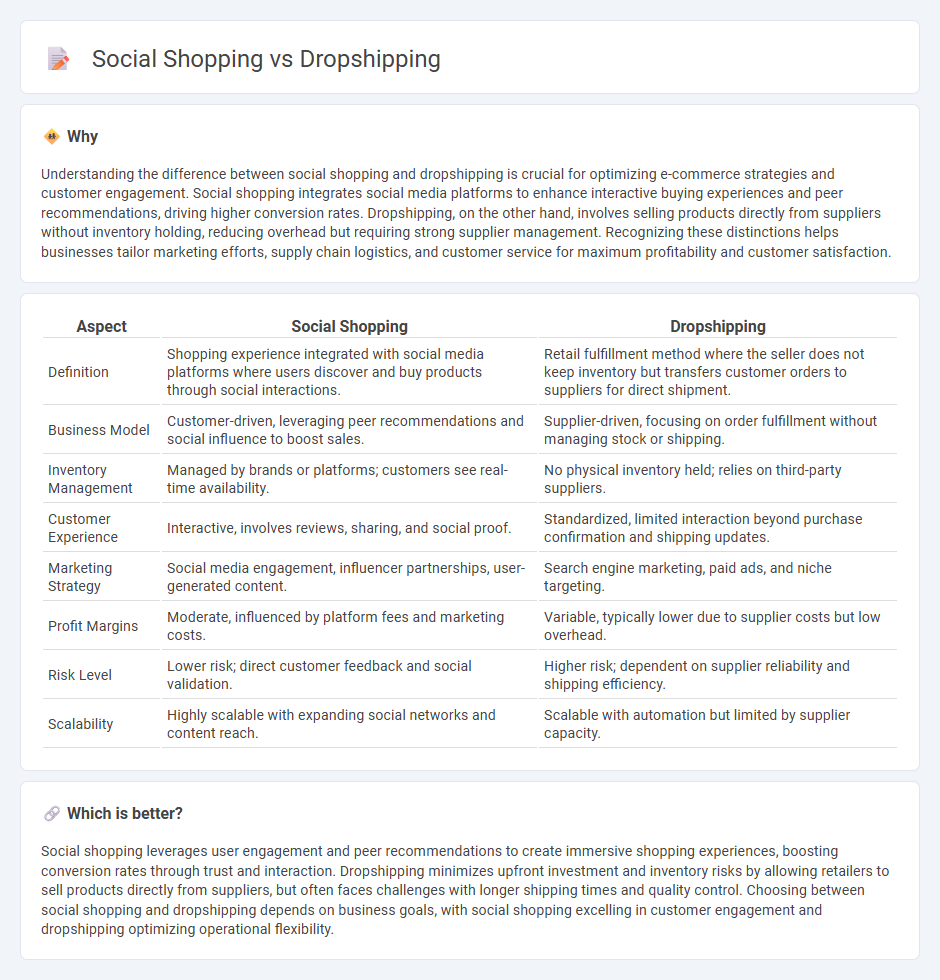
Understanding the difference between social shopping and dropshipping is crucial for optimizing e-commerce strategies and customer engagement. Social shopping integrates social media platforms to enhance interactive buying experiences and peer recommendations, driving higher conversion rates. Dropshipping, on the other hand, involves selling products directly from suppliers without inventory holding, reducing overhead but requiring strong supplier management. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses tailor marketing efforts, supply chain logistics, and customer service for maximum profitability and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Social Shopping | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shopping experience integrated with social media platforms where users discover and buy products through social interactions. | Retail fulfillment method where the seller does not keep inventory but transfers customer orders to suppliers for direct shipment. |
| Business Model | Customer-driven, leveraging peer recommendations and social influence to boost sales. | Supplier-driven, focusing on order fulfillment without managing stock or shipping. |
| Inventory Management | Managed by brands or platforms; customers see real-time availability. | No physical inventory held; relies on third-party suppliers. |
| Customer Experience | Interactive, involves reviews, sharing, and social proof. | Standardized, limited interaction beyond purchase confirmation and shipping updates. |
| Marketing Strategy | Social media engagement, influencer partnerships, user-generated content. | Search engine marketing, paid ads, and niche targeting. |
| Profit Margins | Moderate, influenced by platform fees and marketing costs. | Variable, typically lower due to supplier costs but low overhead. |
| Risk Level | Lower risk; direct customer feedback and social validation. | Higher risk; dependent on supplier reliability and shipping efficiency. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with expanding social networks and content reach. | Scalable with automation but limited by supplier capacity. |
Which is better?
Social shopping leverages user engagement and peer recommendations to create immersive shopping experiences, boosting conversion rates through trust and interaction. Dropshipping minimizes upfront investment and inventory risks by allowing retailers to sell products directly from suppliers, but often faces challenges with longer shipping times and quality control. Choosing between social shopping and dropshipping depends on business goals, with social shopping excelling in customer engagement and dropshipping optimizing operational flexibility.
Connection
Social shopping leverages peer recommendations and real-time interactions on platforms like Instagram and Facebook, driving consumer engagement and purchase intent. Dropshipping enables merchants to offer diverse product selections without inventory, seamlessly integrating with social shopping's dynamic, influencer-driven marketplaces. This synergy accelerates e-commerce scalability by combining personalized social experiences with low-overhead fulfillment models.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory management by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing overhead and storage costs. Social shopping, conversely, often requires managing inventory to display and fulfill products within social platforms, enhancing customer engagement but increasing logistical complexity. Explore how each approach impacts business scalability and operational efficiency for deeper insights.
User Engagement
Dropshipping platforms prioritize streamlined purchasing experiences with minimal interaction, while social shopping emphasizes interactive features such as reviews, live chats, and community sharing to boost user engagement. Social shopping leverages user-generated content and social proof to create a dynamic, participatory environment that increases time spent on site and repeat visits. Discover how these strategies transform ecommerce user engagement and impact sales performance.
Fulfillment Process
Dropshipping involves suppliers directly shipping products to customers, eliminating the need for inventory storage and reducing fulfillment costs. Social shopping blends e-commerce with social media interactions, often relying on integrated platforms that manage order processing and shipping logistics for a seamless customer experience. Explore how these fulfillment models impact efficiency and customer satisfaction in detail.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment business where the seller sets up an online store and markets products, but outsources inventory storage, packaging, and shipping to a third-party supplier who ships directly to customers.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping is a business model where the seller partners with suppliers who manage inventory and shipping, while the seller handles the online store and customer service, with orders forwarded automatically to suppliers for fulfillment.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail method in which the seller takes customer orders without stocking products, transferring order details to suppliers who ship directly to customers, thereby reducing overhead but also limiting control over inventory and shipment quality.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com