Micro fulfillment centers utilize localized, small-scale warehouses to speed up order processing and last-mile delivery in e-commerce, minimizing shipping times and operational costs. The hub-and-spoke model relies on a central hub distributing goods to surrounding spoke locations, optimizing inventory management and transportation efficiency across larger regions. Discover how these fulfillment strategies influence supply chain agility and customer experience.
Why it is important
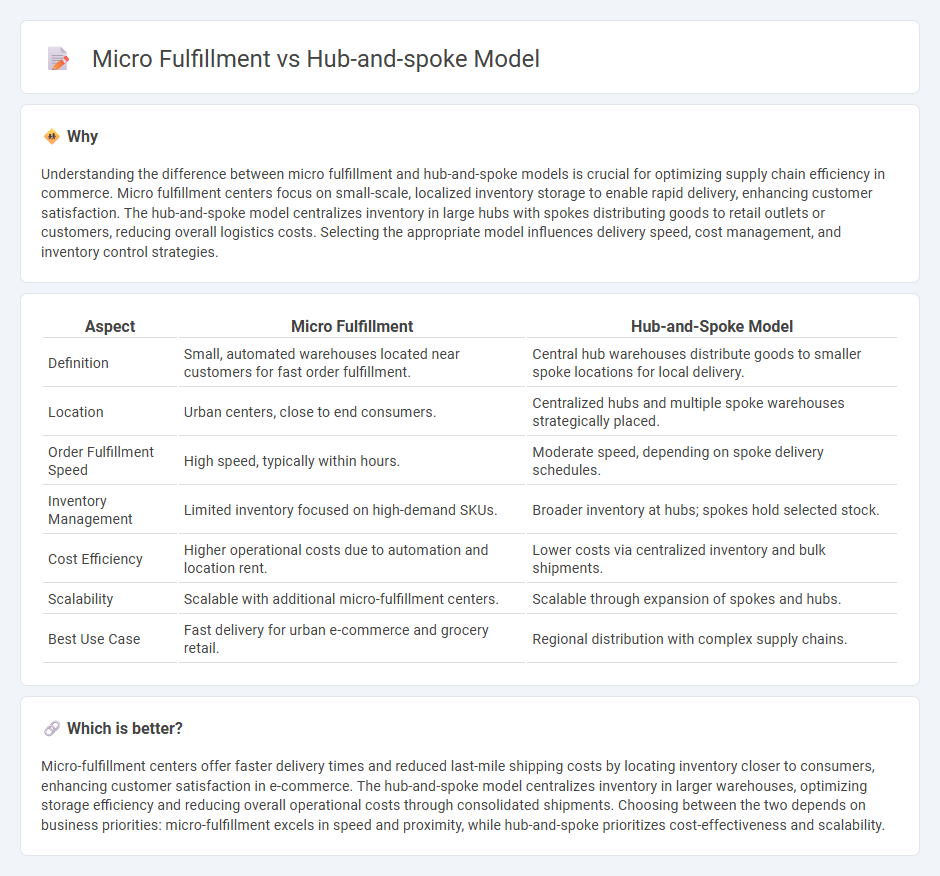
Understanding the difference between micro fulfillment and hub-and-spoke models is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency in commerce. Micro fulfillment centers focus on small-scale, localized inventory storage to enable rapid delivery, enhancing customer satisfaction. The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in large hubs with spokes distributing goods to retail outlets or customers, reducing overall logistics costs. Selecting the appropriate model influences delivery speed, cost management, and inventory control strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Micro Fulfillment | Hub-and-Spoke Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small, automated warehouses located near customers for fast order fulfillment. | Central hub warehouses distribute goods to smaller spoke locations for local delivery. |
| Location | Urban centers, close to end consumers. | Centralized hubs and multiple spoke warehouses strategically placed. |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | High speed, typically within hours. | Moderate speed, depending on spoke delivery schedules. |
| Inventory Management | Limited inventory focused on high-demand SKUs. | Broader inventory at hubs; spokes hold selected stock. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to automation and location rent. | Lower costs via centralized inventory and bulk shipments. |
| Scalability | Scalable with additional micro-fulfillment centers. | Scalable through expansion of spokes and hubs. |
| Best Use Case | Fast delivery for urban e-commerce and grocery retail. | Regional distribution with complex supply chains. |
Which is better?
Micro-fulfillment centers offer faster delivery times and reduced last-mile shipping costs by locating inventory closer to consumers, enhancing customer satisfaction in e-commerce. The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in larger warehouses, optimizing storage efficiency and reducing overall operational costs through consolidated shipments. Choosing between the two depends on business priorities: micro-fulfillment excels in speed and proximity, while hub-and-spoke prioritizes cost-effectiveness and scalability.
Connection
Micro fulfillment centers increase efficiency by acting as localized hubs in the hub-and-spoke distribution model, enabling faster order processing and delivery. This approach reduces last-mile delivery costs and shortens delivery times by positioning inventory closer to consumers. Integration of micro fulfillment centers with hub-and-spoke logistics supports scalability and enhances supply chain responsiveness in commerce.
Key Terms
Centralized Distribution
The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in a main warehouse (hub) with smaller regional warehouses (spokes) for efficient distribution, minimizing overhead and streamlining logistics. Micro fulfillment centers, in contrast, prioritize decentralized, small-scale facilities close to end consumers to accelerate last-mile delivery but require more localized inventory management. Explore how centralization impacts cost-efficiency and delivery speed to determine the best strategy for your supply chain needs.
Last-mile Delivery
The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in key distribution centers, optimizing last-mile delivery by consolidating shipments for efficient dispatch to multiple destinations. Micro-fulfillment strategically places smaller, automated warehouses closer to urban customers to accelerate delivery times and reduce transportation costs. Explore more insights on how these models transform last-mile logistics and customer satisfaction.
Automation
The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in large warehouses (hubs) with smaller local facilities (spokes) facilitating last-mile deliveries, while micro-fulfillment uses automated, compact fulfillment centers near end consumers, optimizing speed and efficiency. Automation in micro-fulfillment employs robotics and AI to streamline order picking and packing, reducing labor costs and enhancing order accuracy compared to traditional hub-and-spoke systems. Discover how leveraging automation in these models can transform supply chain dynamics and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
What is a Hub-and-Spoke Network: 9 Tips, Benefits & Limitations - The hub-and-spoke model features a central hub that coordinates and manages several spoke organizations, centralizing communication and resource allocation while simplifying network interactions.
Spoke-hub distribution paradigm - Wikipedia - This model optimizes transport or communication by connecting outlying points (spokes) to a central hub, pioneered by Delta Air Lines in 1955 and widely adopted in aviation and logistics.
Hub-spoke network topology in Azure - Azure Architecture Center - In cloud networking, the hub-spoke topology connects multiple isolated spoke virtual networks to a central hub network, facilitating controlled shared services and security management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com