Distributed ledger marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to provide transparent, secure, and decentralized trading platforms, enhancing trust and reducing fraud through immutable record-keeping. Hybrid marketplaces combine centralized control with decentralized elements, aiming to offer scalability and flexibility while maintaining a degree of transparency and security. Explore the advantages and challenges of both marketplace models to determine the best fit for modern commercial needs.
Why it is important
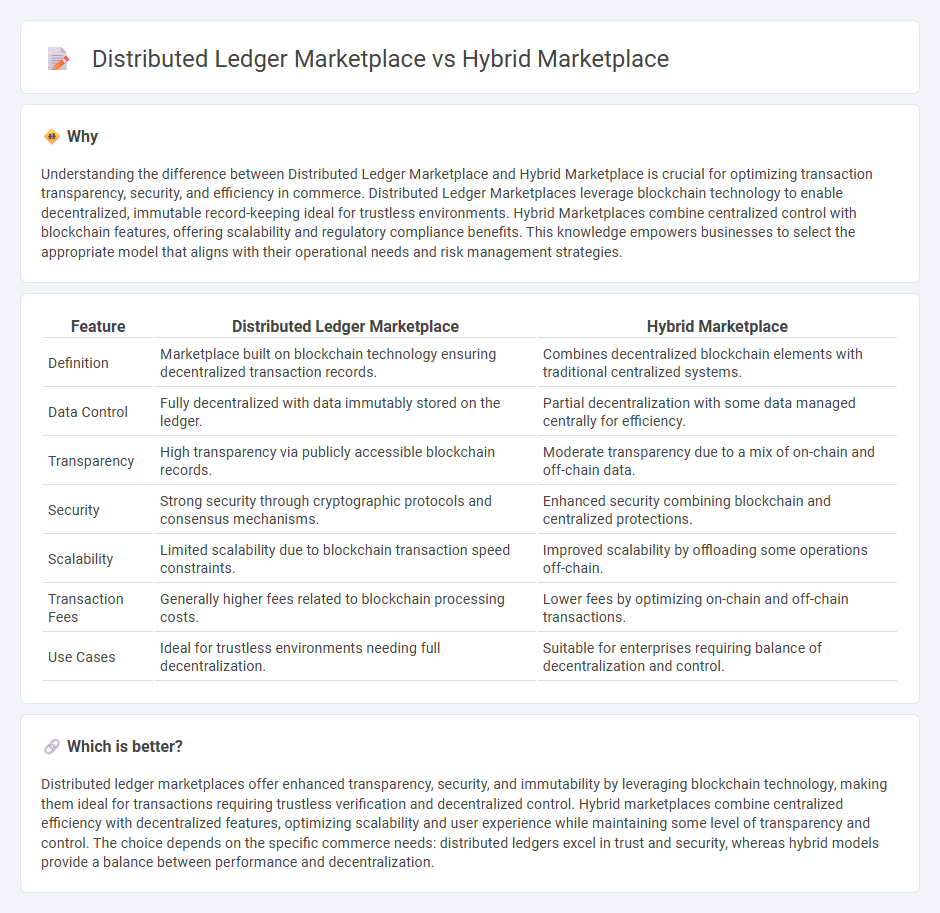
Understanding the difference between Distributed Ledger Marketplace and Hybrid Marketplace is crucial for optimizing transaction transparency, security, and efficiency in commerce. Distributed Ledger Marketplaces leverage blockchain technology to enable decentralized, immutable record-keeping ideal for trustless environments. Hybrid Marketplaces combine centralized control with blockchain features, offering scalability and regulatory compliance benefits. This knowledge empowers businesses to select the appropriate model that aligns with their operational needs and risk management strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Distributed Ledger Marketplace | Hybrid Marketplace |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Marketplace built on blockchain technology ensuring decentralized transaction records. | Combines decentralized blockchain elements with traditional centralized systems. |
| Data Control | Fully decentralized with data immutably stored on the ledger. | Partial decentralization with some data managed centrally for efficiency. |
| Transparency | High transparency via publicly accessible blockchain records. | Moderate transparency due to a mix of on-chain and off-chain data. |
| Security | Strong security through cryptographic protocols and consensus mechanisms. | Enhanced security combining blockchain and centralized protections. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability due to blockchain transaction speed constraints. | Improved scalability by offloading some operations off-chain. |
| Transaction Fees | Generally higher fees related to blockchain processing costs. | Lower fees by optimizing on-chain and off-chain transactions. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for trustless environments needing full decentralization. | Suitable for enterprises requiring balance of decentralization and control. |
Which is better?
Distributed ledger marketplaces offer enhanced transparency, security, and immutability by leveraging blockchain technology, making them ideal for transactions requiring trustless verification and decentralized control. Hybrid marketplaces combine centralized efficiency with decentralized features, optimizing scalability and user experience while maintaining some level of transparency and control. The choice depends on the specific commerce needs: distributed ledgers excel in trust and security, whereas hybrid models provide a balance between performance and decentralization.
Connection
Distributed ledger marketplaces utilize blockchain technology to provide transparent, secure, and decentralized transactions, which enhance trust and reduce fraud in commerce. Hybrid marketplaces combine the benefits of centralized and decentralized systems, incorporating distributed ledger features to optimize efficiency and data integrity while maintaining user control. This connection enables commerce platforms to leverage blockchain's security alongside traditional marketplace scalability and convenience.
Key Terms
Centralized Mediation
Hybrid marketplaces combine centralized mediation with decentralized elements, allowing streamlined dispute resolution and trust management through a central authority. Distributed ledger marketplaces eliminate centralized control, relying on blockchain technology for transparency and consensus, but may face challenges in conflict mediation. Explore how centralized mediation enhances user trust and efficiency in hybrid marketplace models.
Peer-to-Peer Transactions
Hybrid marketplaces combine centralized platforms with decentralized elements, enhancing scalability while maintaining some control over transaction validation. Distributed ledger marketplaces fully leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, secure, and trustless peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Explore further to understand how these models impact transaction efficiency and user autonomy.
Trust Mechanism
Hybrid marketplaces combine centralized control with decentralized elements to enhance transaction efficiency while maintaining some level of user trust through moderated oversight. Distributed ledger marketplaces rely on blockchain technology, offering transparent, tamper-proof trust mechanisms where trust is established via consensus protocols and cryptographic validation. Explore how trust dynamics evolve between these marketplace models and their impact on transactional security and user confidence.
Source and External Links
Hybrid marketplace - Glossary - A hybrid marketplace combines elements of a traditional online store and a marketplace by selling the platform's own inventory alongside offerings from independent third-party sellers; examples include Amazon and JD.com.
On Sellers' Cooperation in Hybrid Marketplaces - Hybrid marketplaces operate by competing with third-party sellers with their own products and setting prices and fees strategically to maximize profits while encouraging competitive pricing among sellers.
Hybrid Marketplaces Buck Conventional Retail Growth ... - The rise of hybrid marketplace models, where platforms like Amazon sell directly and through third-party sellers, is a significant trend driving retail growth strategies in eCommerce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com