Dark stores operate as fulfillment centers designed exclusively for online orders, enabling faster delivery and lower overhead costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar stores that serve in-person shoppers with physical inventory and customer service. Key performance metrics such as order accuracy, delivery speed, and inventory turnover differ significantly between dark stores and physical retail outlets. Explore the advantages and challenges of dark stores versus brick-and-mortar business models to understand their impact on modern commerce.
Why it is important
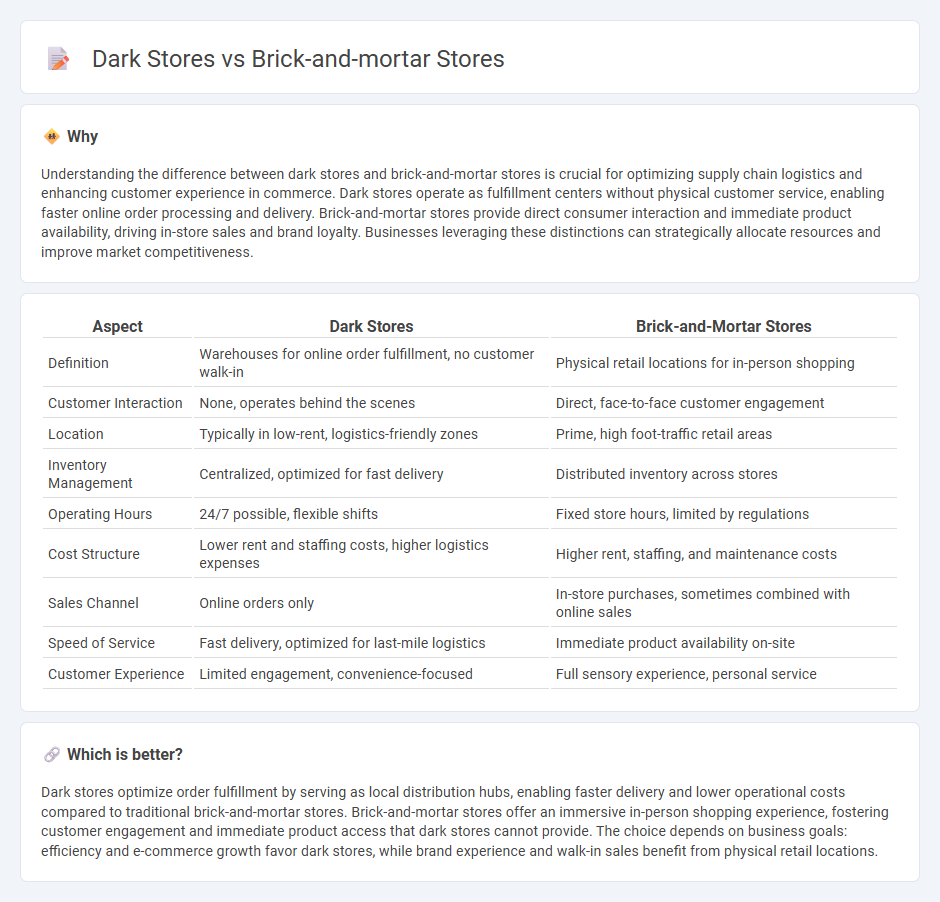
Understanding the difference between dark stores and brick-and-mortar stores is crucial for optimizing supply chain logistics and enhancing customer experience in commerce. Dark stores operate as fulfillment centers without physical customer service, enabling faster online order processing and delivery. Brick-and-mortar stores provide direct consumer interaction and immediate product availability, driving in-store sales and brand loyalty. Businesses leveraging these distinctions can strategically allocate resources and improve market competitiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Stores | Brick-and-Mortar Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Warehouses for online order fulfillment, no customer walk-in | Physical retail locations for in-person shopping |
| Customer Interaction | None, operates behind the scenes | Direct, face-to-face customer engagement |
| Location | Typically in low-rent, logistics-friendly zones | Prime, high foot-traffic retail areas |
| Inventory Management | Centralized, optimized for fast delivery | Distributed inventory across stores |
| Operating Hours | 24/7 possible, flexible shifts | Fixed store hours, limited by regulations |
| Cost Structure | Lower rent and staffing costs, higher logistics expenses | Higher rent, staffing, and maintenance costs |
| Sales Channel | Online orders only | In-store purchases, sometimes combined with online sales |
| Speed of Service | Fast delivery, optimized for last-mile logistics | Immediate product availability on-site |
| Customer Experience | Limited engagement, convenience-focused | Full sensory experience, personal service |
Which is better?
Dark stores optimize order fulfillment by serving as local distribution hubs, enabling faster delivery and lower operational costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar stores. Brick-and-mortar stores offer an immersive in-person shopping experience, fostering customer engagement and immediate product access that dark stores cannot provide. The choice depends on business goals: efficiency and e-commerce growth favor dark stores, while brand experience and walk-in sales benefit from physical retail locations.
Connection
Dark stores serve as localized fulfillment centers that support brick-and-mortar stores by enhancing inventory availability and speeding up delivery for online orders. This integration allows physical stores to cater to e-commerce demand without compromising in-store customer experience, optimizing supply chain efficiency. Leveraging shared inventory and real-time data synchronization between dark stores and traditional retail outlets creates a seamless omnichannel commerce ecosystem.
Key Terms
Physical Retail
Brick-and-mortar stores offer tangible shopping experiences, allowing customers to physically inspect products and enjoy in-person service, which drives foot traffic and builds brand loyalty. Dark stores function as centralized fulfillment centers designed exclusively for online orders, optimizing inventory management and enabling faster delivery without public access. Explore the evolving impact of physical retail and dark stores on consumer behavior and supply chain efficiency.
Online Fulfillment
Brick-and-mortar stores traditionally serve customers through physical shopping experiences, while dark stores operate exclusively for online order fulfillment without in-person sales. Dark stores optimize inventory management and accelerate same-day or next-day delivery by minimizing in-store interruptions and focusing on efficient picking and packing processes. Explore how dark stores are revolutionizing e-commerce logistics and transforming customer satisfaction in online retail.
Last-Mile Delivery
Brick-and-mortar stores serve as physical retail locations offering immediate product availability, while dark stores function solely as fulfillment centers optimized for efficient last-mile delivery without customer foot traffic. Last-mile delivery strategies leverage dark stores to reduce delivery times and improve logistics, enhancing customer satisfaction by enabling faster order processing and localized inventory management. Explore in-depth analysis of how last-mile delivery innovations are reshaping the retail landscape between brick-and-mortar and dark store models.
Source and External Links
Brick and Mortar Stores: Types, Benefits, Examples (2024) - Shopify - Brick-and-mortar stores are physical retail locations where customers can view, try, and purchase products in person, often enhanced by sales staff assistance and omnichannel features like in-store pickup.
What Is a Brick and Mortar Store? Top 10 Retail Examples - These traditional retail businesses operate from physical shops or showrooms, offering hands-on shopping experiences and playing a key role in building local community trust and delivering immediate, personalized service.
Brick and mortar - Wikipedia - "Brick-and-mortar" refers to companies with physical retail or operational facilities, contrasting with online-only businesses by providing face-to-face customer experiences in a physical setting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com