Dropshipping agents coordinate product fulfillment directly from manufacturers to customers, minimizing inventory risks while ensuring faster shipping times. Wholesalers stock bulk products and sell at discounted rates, enabling retailers to purchase large quantities upfront for higher profit margins. Explore the key differences between dropshipping agents and wholesalers to optimize your commerce strategy.
Why it is important
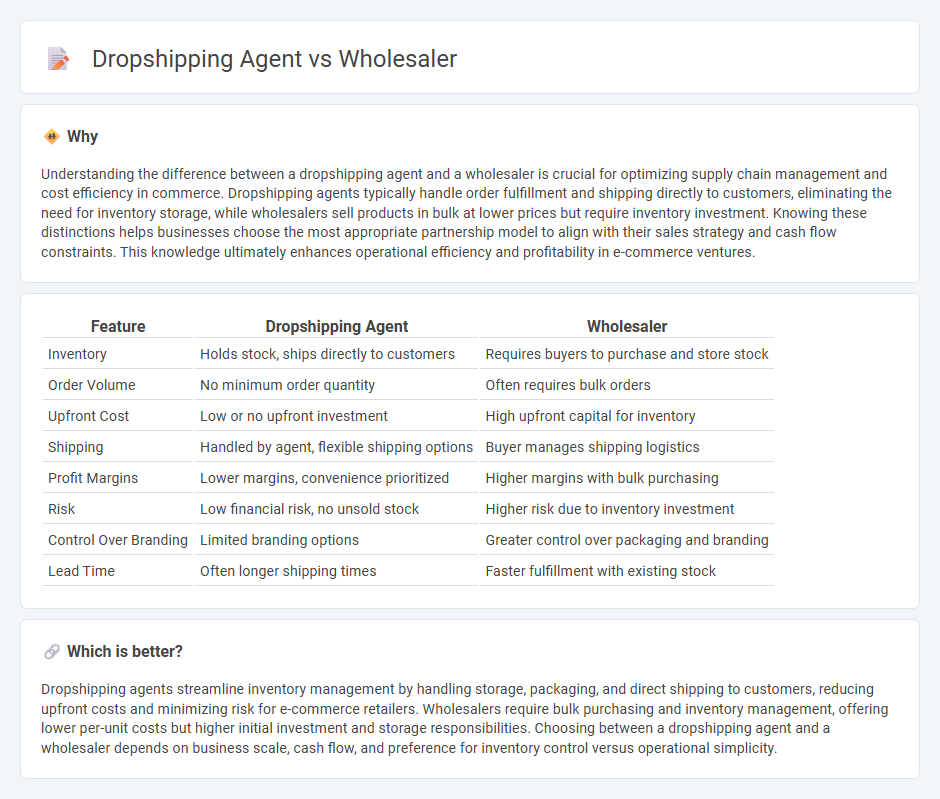
Understanding the difference between a dropshipping agent and a wholesaler is crucial for optimizing supply chain management and cost efficiency in commerce. Dropshipping agents typically handle order fulfillment and shipping directly to customers, eliminating the need for inventory storage, while wholesalers sell products in bulk at lower prices but require inventory investment. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses choose the most appropriate partnership model to align with their sales strategy and cash flow constraints. This knowledge ultimately enhances operational efficiency and profitability in e-commerce ventures.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dropshipping Agent | Wholesaler |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | Holds stock, ships directly to customers | Requires buyers to purchase and store stock |
| Order Volume | No minimum order quantity | Often requires bulk orders |
| Upfront Cost | Low or no upfront investment | High upfront capital for inventory |
| Shipping | Handled by agent, flexible shipping options | Buyer manages shipping logistics |
| Profit Margins | Lower margins, convenience prioritized | Higher margins with bulk purchasing |
| Risk | Low financial risk, no unsold stock | Higher risk due to inventory investment |
| Control Over Branding | Limited branding options | Greater control over packaging and branding |
| Lead Time | Often longer shipping times | Faster fulfillment with existing stock |
Which is better?
Dropshipping agents streamline inventory management by handling storage, packaging, and direct shipping to customers, reducing upfront costs and minimizing risk for e-commerce retailers. Wholesalers require bulk purchasing and inventory management, offering lower per-unit costs but higher initial investment and storage responsibilities. Choosing between a dropshipping agent and a wholesaler depends on business scale, cash flow, and preference for inventory control versus operational simplicity.
Connection
Dropshipping agents act as intermediaries between retailers and wholesalers by managing inventory and shipping logistics, enabling retailers to sell products without holding stock. Wholesalers supply bulk products directly to dropshipping agents, who then fulfill individual customer orders. This connection streamlines supply chain operations, reduces upfront costs, and expands product availability for online businesses.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Wholesalers maintain physical inventory, enabling bulk purchasing and immediate product availability, which ensures consistent stock levels and faster order fulfillment. Dropshipping agents, however, do not hold inventory but instead coordinate order processing directly between the retailer and supplier, reducing overhead costs but potentially increasing delivery times and stockout risks. Explore deeper insights on inventory management strategies to optimize your supply chain efficiency.
Order Fulfillment
Wholesalers typically stock products in bulk and manage their own inventory, enabling faster order fulfillment with direct shipping to retailers. Dropshipping agents act as intermediaries, forwarding customer orders to suppliers who ship directly to end consumers, often resulting in longer delivery times but reduced inventory risks. Explore the differences in order fulfillment processes to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Supply Chain Control
Wholesalers maintain extensive inventory and handle bulk shipping, offering direct control over product quality and fulfillment schedules within the supply chain. Dropshipping agents, however, relay orders to third-party suppliers, reducing inventory management responsibilities but limiting control over stock availability and delivery timelines. Explore further to understand which option suits your supply chain strategy best.
Source and External Links
What is a wholesaler? | BDC.ca - A wholesaler is a company that buys large quantities of goods to sell in volume, acting as an intermediary between manufacturers and retailers, typically specializing by sector and selling mostly B2B, adding value by enabling smaller purchases, coordinating delivery, and widening product access.
Wholesaler vs. Distributor: What's the Difference? | Indeed.com - A wholesaler buys products in bulk, often from distributors or manufacturers, then sells in smaller quantities to retailers or organizations, sometimes across competing brands, helping manufacturers reach various markets by storing and distributing products.
Wholesaling - Wikipedia - Wholesaling is the bulk sale of goods to retailers, business users, or other wholesalers, often involving activities like sorting and repackaging, with wholesalers purchasing directly from manufacturers at discounted rates and retailers then selling to end consumers at higher prices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com