Multi-threading in sales involves managing multiple customer conversations simultaneously to increase efficiency and improve response times. Activity stacking focuses on organizing and prioritizing sales tasks sequentially to maintain clarity and prevent workflow interruptions. Explore these strategies further to optimize your sales performance and boost productivity.
Why it is important
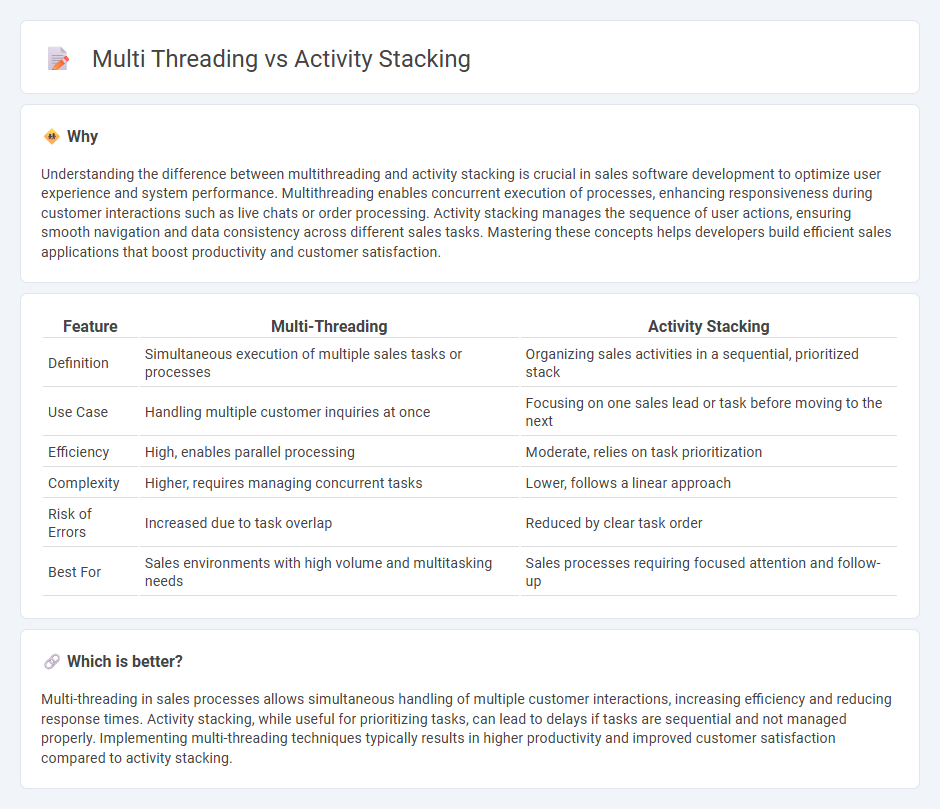
Understanding the difference between multithreading and activity stacking is crucial in sales software development to optimize user experience and system performance. Multithreading enables concurrent execution of processes, enhancing responsiveness during customer interactions such as live chats or order processing. Activity stacking manages the sequence of user actions, ensuring smooth navigation and data consistency across different sales tasks. Mastering these concepts helps developers build efficient sales applications that boost productivity and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Multi-Threading | Activity Stacking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous execution of multiple sales tasks or processes | Organizing sales activities in a sequential, prioritized stack |
| Use Case | Handling multiple customer inquiries at once | Focusing on one sales lead or task before moving to the next |
| Efficiency | High, enables parallel processing | Moderate, relies on task prioritization |
| Complexity | Higher, requires managing concurrent tasks | Lower, follows a linear approach |
| Risk of Errors | Increased due to task overlap | Reduced by clear task order |
| Best For | Sales environments with high volume and multitasking needs | Sales processes requiring focused attention and follow-up |
Which is better?
Multi-threading in sales processes allows simultaneous handling of multiple customer interactions, increasing efficiency and reducing response times. Activity stacking, while useful for prioritizing tasks, can lead to delays if tasks are sequential and not managed properly. Implementing multi-threading techniques typically results in higher productivity and improved customer satisfaction compared to activity stacking.
Connection
Multi-threading in sales involves managing multiple customer interactions simultaneously to maximize engagement and conversion rates. Activity stacking complements this by organizing diverse sales tasks, such as calls, emails, and meetings, in an efficient sequence to optimize productivity. Together, these strategies enhance pipeline management and accelerate deal closures by ensuring continuous momentum across various sales opportunities.
Key Terms
Task Prioritization
Activity stacking allows tasks to be organized in a sequential manner, ensuring that high-priority activities are completed before lower-priority ones, optimizing workflow efficiency. Multi-threading enables concurrent execution of tasks, which can improve responsiveness and resource utilization but requires careful management to prioritize critical threads. Explore more about how task prioritization strategies differ in activity stacking versus multi-threading for optimized performance.
Sequential Execution (Activity Stacking)
Activity stacking refers to the sequential execution of tasks where each activity waits for the previous one to complete before starting, ensuring ordered and predictable outcomes. In contrast, multithreading allows multiple threads to run concurrently within a single process, improving efficiency but introducing complexity in synchronization. Explore deeper to understand how activity stacking ensures controlled flow in sequential processing environments.
Simultaneous Initiatives (Multi-threading)
Simultaneous initiatives, also known as multi-threading, allow multiple threads to execute concurrently within a single application, improving efficiency by utilizing CPU resources optimally and reducing idle time during input/output operations. Activity stacking, in contrast, involves sequential task management where activities are layered over one another without true parallel execution, potentially leading to bottlenecks. Explore the distinctions further to optimize your software's performance and responsiveness.
Source and External Links
Stacking: When do babies start and what are the benefits | Lovevery - Activity stacking involves toddlers placing one object on top of another to build towers, which develops patience, coordination, and problem-solving skills typically starting around 10 to 12 months and advancing by 16 to 18 months with varied sizes and shapes to enhance fine motor precision and language development.
Creative Stacking Activities for Toddlers and Preschoolers - Stacking activities promote fine motor skills, balance, reasoning, and hand-eye coordination with variations such as using tongs or stacking mixed-category items; engagement can be enhanced by narrating the child's stacking process to support cognitive and language development.
Stacking, Sorting, & Matching for Toddlers - Montessori Generation - Stacking is used in Montessori education as a hands-on activity that supports toddlers' natural curiosity by encouraging them to explore, refine fine motor skills, and develop cognitive abilities through playful experimentation with stacking objects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com