Microfulfillment centers optimize urban retail logistics by enabling rapid order fulfillment within smaller spaces, contrasting with traditional warehouses that focus on large-scale storage and bulk shipping. These centers leverage automation and proximity to consumers to reduce delivery times and enhance last-mile efficiency. Explore the advantages and applications of microfulfillment centers compared to traditional warehouses to understand their impact on modern retail.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a microfulfillment center and a traditional warehouse is crucial for optimizing retail supply chain efficiency and reducing last-mile delivery times. Microfulfillment centers use automation and proximity to urban areas to enable faster, cost-effective order fulfillment compared to large, centralized traditional warehouses. Retailers leveraging microfulfillment can significantly improve customer satisfaction through same-day or next-day delivery options. Proper facility selection directly impacts inventory management, operational costs, and overall retail competitiveness.
Comparison Table
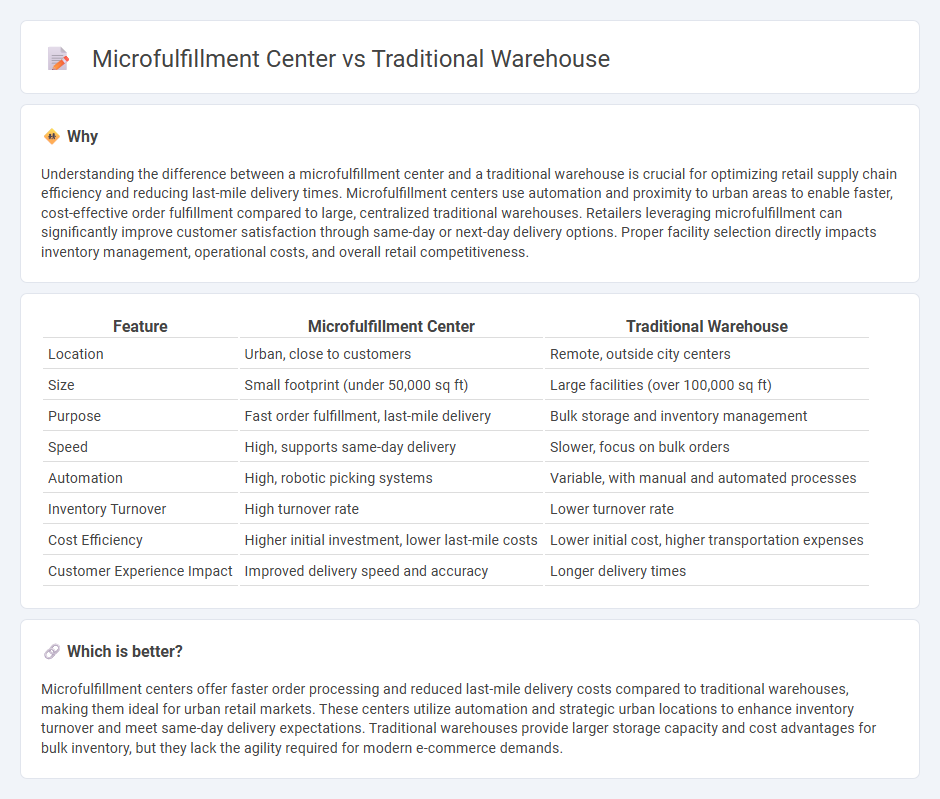
| Feature | Microfulfillment Center | Traditional Warehouse |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Urban, close to customers | Remote, outside city centers |
| Size | Small footprint (under 50,000 sq ft) | Large facilities (over 100,000 sq ft) |
| Purpose | Fast order fulfillment, last-mile delivery | Bulk storage and inventory management |
| Speed | High, supports same-day delivery | Slower, focus on bulk orders |
| Automation | High, robotic picking systems | Variable, with manual and automated processes |
| Inventory Turnover | High turnover rate | Lower turnover rate |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial investment, lower last-mile costs | Lower initial cost, higher transportation expenses |
| Customer Experience Impact | Improved delivery speed and accuracy | Longer delivery times |
Which is better?
Microfulfillment centers offer faster order processing and reduced last-mile delivery costs compared to traditional warehouses, making them ideal for urban retail markets. These centers utilize automation and strategic urban locations to enhance inventory turnover and meet same-day delivery expectations. Traditional warehouses provide larger storage capacity and cost advantages for bulk inventory, but they lack the agility required for modern e-commerce demands.
Connection
Microfulfillment centers complement traditional warehouses by handling rapid order fulfillment close to urban areas, reducing delivery times and last-mile costs. Traditional warehouses store bulk inventory and supply these microfulfillment hubs with products to maintain steady stock levels. This integrated system enhances overall retail efficiency by balancing large-scale storage with agile, localized distribution.
Key Terms
Inventory Storage
Traditional warehouses typically store large quantities of inventory with extensive shelf space organized for bulk storage, supporting long-term stock management and wholesale distribution. Microfulfillment centers prioritize high-density storage solutions and automated retrieval systems to rapidly process small, frequent orders closer to the consumer, optimizing urban space usage and last-mile delivery efficiency. Explore how these inventory storage strategies impact supply chain performance and operational costs.
Order Processing Speed
Traditional warehouses often involve longer order processing times due to larger inventory volumes and manual picking methods, leading to delays in fulfillment. Microfulfillment centers leverage automated technologies and proximity to end consumers, significantly reducing order processing speed and enabling same-day or next-day delivery. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your supply chain efficiency and meet evolving customer demands.
Last-Mile Delivery
Traditional warehouses typically store large volumes of inventory in centralized locations, leading to longer shipping times and higher last-mile delivery costs. Microfulfillment centers, strategically located near urban areas, enable rapid order processing and faster delivery by utilizing automation and minimizing travel distances. Discover how microfulfillment centers are revolutionizing last-mile delivery efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Source and External Links
What Is Traditional Warehousing- Concept, Benefits & Operation - Traditional warehousing refers to storing products in a permanent building designed for long-term storage, using systematic methods such as palletized storage and shelving to organize goods efficiently while relying on manual or basic barcode inventory tracking and centralized logistics coordination.
Smart Warehouse vs. Traditional Warehouse - Portable Intelligence - Traditional warehouses typically involve rigid layouts and labor-intensive, manual processes that can lead to inefficiencies and inventory inaccuracies, with limited real-time inventory visibility and challenges in optimizing order fulfillment.
Flexible Warehousing Vs Traditional Warehousing - Traditional warehousing is characterized by fixed, long-term storage capacity with stable costs and guaranteed space but lacks flexibility to scale quickly or adapt to fluctuating inventory demands, potentially causing inefficiencies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com