Circular retail emphasizes sustainable product lifecycle management through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to minimize waste, contrasting with linear retail's traditional model of produce, consume, and dispose. By integrating circular economy principles, retailers can reduce environmental impact and foster long-term resource efficiency. Discover how circular retail is transforming industry sustainability and consumer practices.
Why it is important
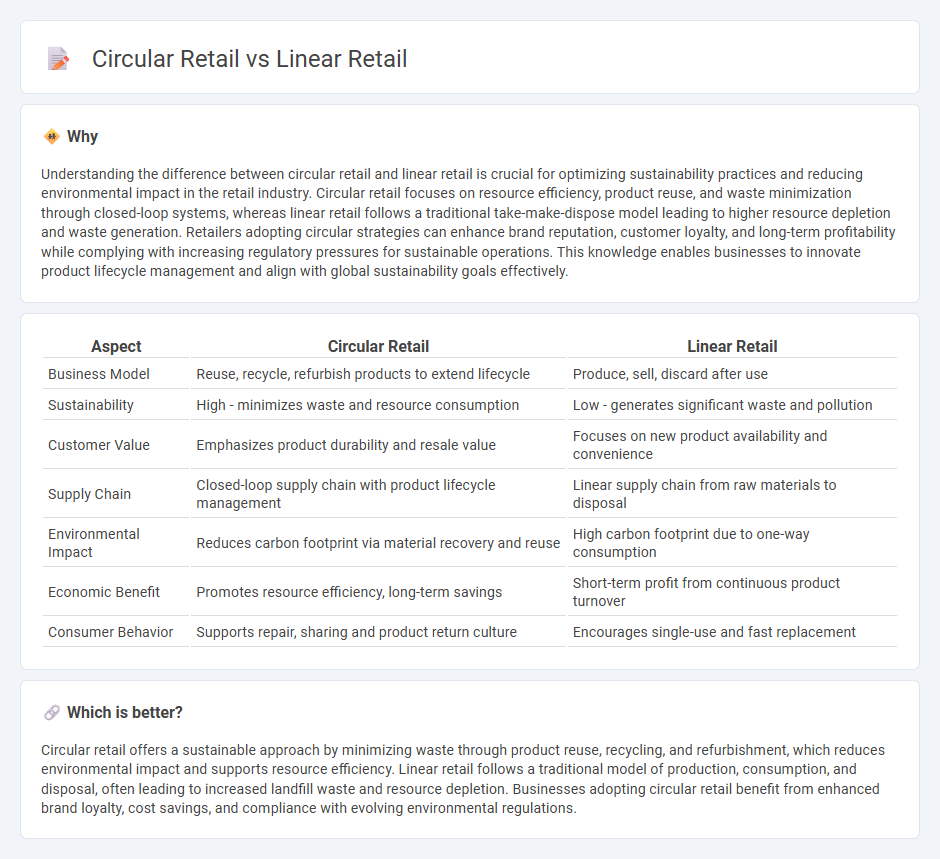
Understanding the difference between circular retail and linear retail is crucial for optimizing sustainability practices and reducing environmental impact in the retail industry. Circular retail focuses on resource efficiency, product reuse, and waste minimization through closed-loop systems, whereas linear retail follows a traditional take-make-dispose model leading to higher resource depletion and waste generation. Retailers adopting circular strategies can enhance brand reputation, customer loyalty, and long-term profitability while complying with increasing regulatory pressures for sustainable operations. This knowledge enables businesses to innovate product lifecycle management and align with global sustainability goals effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Circular Retail | Linear Retail |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Reuse, recycle, refurbish products to extend lifecycle | Produce, sell, discard after use |
| Sustainability | High - minimizes waste and resource consumption | Low - generates significant waste and pollution |
| Customer Value | Emphasizes product durability and resale value | Focuses on new product availability and convenience |
| Supply Chain | Closed-loop supply chain with product lifecycle management | Linear supply chain from raw materials to disposal |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces carbon footprint via material recovery and reuse | High carbon footprint due to one-way consumption |
| Economic Benefit | Promotes resource efficiency, long-term savings | Short-term profit from continuous product turnover |
| Consumer Behavior | Supports repair, sharing and product return culture | Encourages single-use and fast replacement |
Which is better?
Circular retail offers a sustainable approach by minimizing waste through product reuse, recycling, and refurbishment, which reduces environmental impact and supports resource efficiency. Linear retail follows a traditional model of production, consumption, and disposal, often leading to increased landfill waste and resource depletion. Businesses adopting circular retail benefit from enhanced brand loyalty, cost savings, and compliance with evolving environmental regulations.
Connection
Circular retail and linear retail are interconnected through their supply chain dynamics, where linear retail follows a traditional take-make-dispose model, and circular retail emphasizes reuse, refurbishment, and recycling to minimize waste. Retailers adopting circular strategies integrate product life cycle extension, enabling the recovery of value from returned or end-of-life products, thus reducing reliance on new raw materials. This connection drives sustainability goals and innovation in inventory management, ultimately reshaping consumer behavior and operational models in the retail sector.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Linear retail supply chains prioritize one-way product flow from raw material extraction to disposal, resulting in significant resource depletion and waste generation. Circular retail supply chains emphasize closed-loop systems, incorporating product reuse, recycling, and efficient resource management to minimize environmental impact and enhance sustainability. Explore how adopting circular supply chains can transform retail operations and drive long-term profitability.
Resource Utilization
Linear retail follows a take-make-dispose model, leading to significant resource depletion and waste generation, whereas circular retail emphasizes resource efficiency through reuse, recycling, and sustainable product lifecycle management. Circular retail leverages closed-loop systems, reducing raw material consumption by extending product lifespan and promoting refurbishing, which supports environmental sustainability and cost savings. Discover more about how circular retail transforms resource utilization for a greener economy.
Product Lifecycle
Linear retail follows a traditional product lifecycle of extraction, manufacturing, consumption, and disposal, creating significant waste and environmental impact. Circular retail emphasizes product longevity through design for reuse, repair, and recycling, aiming to close the loop and reduce resource depletion. Explore how businesses implement circular strategies to enhance sustainability and profitability in retail models.
Source and External Links
Linear Retail | Convenience-Driven Retail Real Estate - Linear Retail is a New England based retail real estate landlord focused on convenience-driven retail properties in Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Southern New England, owning over 79 properties and hosting 400+ tenants.
Linear Retail Properties - Based in Burlington, MA, Linear Retail is a leading acquirer, owner, developer, and operator of retail properties, particularly convenience-oriented strip shopping centers and specialty storefronts across New England.
Linear Retail Properties Financing - Linear Retail Properties, LLC focuses on acquiring and managing convenience-oriented retail properties in Greater Boston and surrounding areas, supported by financing solutions like a $50 million revolving line of credit to enable rapid acquisition.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com