Microfulfillment centers streamline retail inventory management by utilizing automated systems to rapidly fulfill online orders close to urban areas, reducing delivery times and costs. Last-mile delivery hubs focus on the efficient distribution of packages by acting as localized transfer points, enhancing delivery speed and customer satisfaction in densely populated regions. Explore how integrating these strategies can revolutionize your retail logistics and boost operational efficiency.
Why it is important
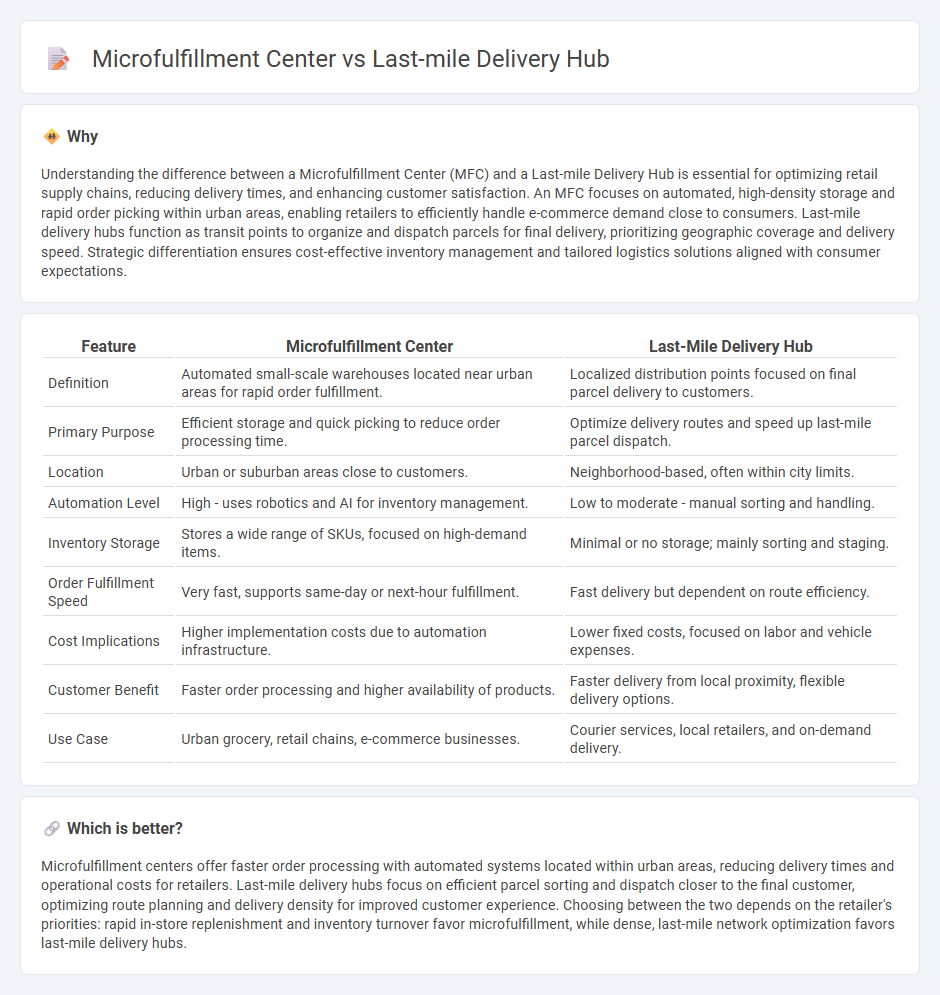
Understanding the difference between a Microfulfillment Center (MFC) and a Last-mile Delivery Hub is essential for optimizing retail supply chains, reducing delivery times, and enhancing customer satisfaction. An MFC focuses on automated, high-density storage and rapid order picking within urban areas, enabling retailers to efficiently handle e-commerce demand close to consumers. Last-mile delivery hubs function as transit points to organize and dispatch parcels for final delivery, prioritizing geographic coverage and delivery speed. Strategic differentiation ensures cost-effective inventory management and tailored logistics solutions aligned with consumer expectations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Microfulfillment Center | Last-Mile Delivery Hub |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated small-scale warehouses located near urban areas for rapid order fulfillment. | Localized distribution points focused on final parcel delivery to customers. |
| Primary Purpose | Efficient storage and quick picking to reduce order processing time. | Optimize delivery routes and speed up last-mile parcel dispatch. |
| Location | Urban or suburban areas close to customers. | Neighborhood-based, often within city limits. |
| Automation Level | High - uses robotics and AI for inventory management. | Low to moderate - manual sorting and handling. |
| Inventory Storage | Stores a wide range of SKUs, focused on high-demand items. | Minimal or no storage; mainly sorting and staging. |
| Order Fulfillment Speed | Very fast, supports same-day or next-hour fulfillment. | Fast delivery but dependent on route efficiency. |
| Cost Implications | Higher implementation costs due to automation infrastructure. | Lower fixed costs, focused on labor and vehicle expenses. |
| Customer Benefit | Faster order processing and higher availability of products. | Faster delivery from local proximity, flexible delivery options. |
| Use Case | Urban grocery, retail chains, e-commerce businesses. | Courier services, local retailers, and on-demand delivery. |
Which is better?
Microfulfillment centers offer faster order processing with automated systems located within urban areas, reducing delivery times and operational costs for retailers. Last-mile delivery hubs focus on efficient parcel sorting and dispatch closer to the final customer, optimizing route planning and delivery density for improved customer experience. Choosing between the two depends on the retailer's priorities: rapid in-store replenishment and inventory turnover favor microfulfillment, while dense, last-mile network optimization favors last-mile delivery hubs.
Connection
Microfulfillment centers and last-mile delivery hubs are interconnected nodes within the retail supply chain that enhance order fulfillment speed and efficiency. Microfulfillment centers, strategically located near urban areas, use automation to rapidly process online orders, while last-mile delivery hubs serve as distribution points to expedite the final delivery to customers. The synergy between these facilities reduces delivery times, lowers costs, and improves customer satisfaction by streamlining inventory management and minimizing transit distances.
Key Terms
Proximity
Last-mile delivery hubs are strategically located close to urban centers to ensure rapid final delivery to customers, often handling small parcels and leveraging local courier services. Microfulfillment centers, typically integrated within or near retail stores, utilize high-density automation to efficiently process and pack orders, minimizing delivery distances to boost speed and reduce costs. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which model better suits specific logistics and retail needs.
Inventory Management
Last-mile delivery hubs prioritize quick sorting and dispatching of packages close to the end consumer, optimizing for speed rather than extensive inventory storage. Microfulfillment centers hold a more diverse and substantial inventory on-site, using automated systems to efficiently manage stock and fulfill orders rapidly within urban areas. Explore the key differences in inventory management strategies to determine the best solution for your logistics needs.
Automation
Last-mile delivery hubs prioritize rapid parcel sorting and dispatch using automated conveyor systems and robotic arms to expedite urban deliveries. Microfulfillment centers employ advanced automation like autonomous mobile robots and AI-driven inventory management to maximize storage density and order accuracy in compact warehouse spaces. Explore the latest innovations in automation transforming last-mile logistics and microfulfillment efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is a Last-Mile Delivery Station? - Wise Systems - A last-mile delivery hub or station is a local facility that receives packages from larger distribution centers, sorts them, and dispatches them for final delivery, enabling faster delivery times, improved accuracy, and better customer experience by being closer to end consumers.
Central Hub and Last Mile Depot Solutions - FORTNA - A last-mile delivery hub refers to the last stage depot where parcels are delivered to consumers after being sorted and distributed in a centralized hub facility.
Last Mile Delivery Solutions | Ryder Final Mile Logistics - Last-mile delivery hubs are part of a network of multi-client hubs that help companies achieve broad geographic coverage and flexible delivery options, facilitating the final segment of parcel delivery directly to customers with technology-driven logistics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com