Microfulfillment centers utilize automated systems to rapidly process and fulfill online orders within urban areas, reducing delivery times and operational costs. Dark stores function as localized warehouses that cater exclusively to online shopping, optimizing inventory management and improving order accuracy without traditional retail customer traffic. Explore how these innovative retail solutions transform e-commerce logistics and customer experience.
Why it is important
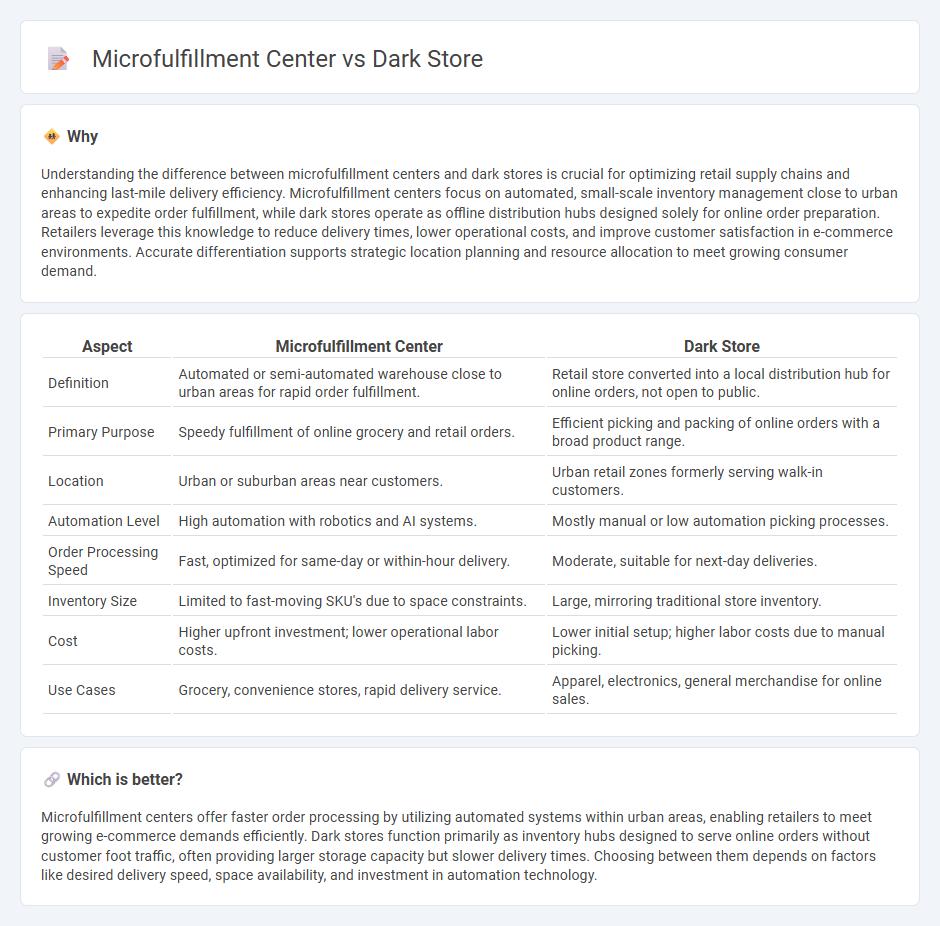
Understanding the difference between microfulfillment centers and dark stores is crucial for optimizing retail supply chains and enhancing last-mile delivery efficiency. Microfulfillment centers focus on automated, small-scale inventory management close to urban areas to expedite order fulfillment, while dark stores operate as offline distribution hubs designed solely for online order preparation. Retailers leverage this knowledge to reduce delivery times, lower operational costs, and improve customer satisfaction in e-commerce environments. Accurate differentiation supports strategic location planning and resource allocation to meet growing consumer demand.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microfulfillment Center | Dark Store |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated or semi-automated warehouse close to urban areas for rapid order fulfillment. | Retail store converted into a local distribution hub for online orders, not open to public. |
| Primary Purpose | Speedy fulfillment of online grocery and retail orders. | Efficient picking and packing of online orders with a broad product range. |
| Location | Urban or suburban areas near customers. | Urban retail zones formerly serving walk-in customers. |
| Automation Level | High automation with robotics and AI systems. | Mostly manual or low automation picking processes. |
| Order Processing Speed | Fast, optimized for same-day or within-hour delivery. | Moderate, suitable for next-day deliveries. |
| Inventory Size | Limited to fast-moving SKU's due to space constraints. | Large, mirroring traditional store inventory. |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment; lower operational labor costs. | Lower initial setup; higher labor costs due to manual picking. |
| Use Cases | Grocery, convenience stores, rapid delivery service. | Apparel, electronics, general merchandise for online sales. |
Which is better?
Microfulfillment centers offer faster order processing by utilizing automated systems within urban areas, enabling retailers to meet growing e-commerce demands efficiently. Dark stores function primarily as inventory hubs designed to serve online orders without customer foot traffic, often providing larger storage capacity but slower delivery times. Choosing between them depends on factors like desired delivery speed, space availability, and investment in automation technology.
Connection
Microfulfillment centers and dark stores are interconnected retail strategies designed to enhance e-commerce efficiency and speed. Microfulfillment centers focus on automated, compact storage solutions near urban areas to enable rapid order fulfillment, while dark stores function as inventory-only retail locations optimized for online order picking without serving walk-in customers. Both concepts leverage technology and strategic placement to reduce delivery times and meet rising consumer demand for same-day or next-day delivery.
Key Terms
Order Fulfillment
Dark stores optimize order fulfillment by functioning solely as local distribution hubs for online grocery orders, enabling faster delivery times and higher picking accuracy. Microfulfillment centers integrate advanced robotics within smaller urban spaces to increase inventory density and speed up sorting and packing processes, reducing last-mile delivery costs. Explore the key differences in scalability, technology, and operational efficiency to enhance your fulfillment strategy.
Inventory Management
Dark stores optimize inventory management by operating as dedicated fulfillment hubs, enabling real-time stock updates and efficient order picking without customer foot traffic interference. Microfulfillment centers leverage advanced automation and compact layouts to streamline inventory storage and accelerate last-mile delivery in urban areas. Explore how these approaches transform inventory strategies for enhanced retail operations.
Last-Mile Delivery
Dark stores and microfulfillment centers both optimize last-mile delivery by enhancing speed and reducing fulfillment costs, but they differ in scale and technology; dark stores operate as localized warehouses tailored for rapid order picking, while microfulfillment centers utilize automated systems within urban spaces for higher efficiency. Dark stores prioritize flexibility and proximity to customers, enabling quicker delivery windows, whereas microfulfillment centers focus on automation to handle higher order volumes seamlessly. Explore how these fulfillment models transform the logistics landscape and improve customer satisfaction in urban last-mile delivery.
Source and External Links
What is a Dark Store? How to Make it Work for You - Vaimo - A dark store is a brick-and-mortar location closed to the public and converted into a fulfillment center to handle online orders efficiently, enabling options like same-day delivery or in-store pickup.
Dark store - Wikipedia - A dark store is a retail outlet or distribution center that exists exclusively for online shopping, often functioning as warehouses for order fulfillment or click-and-collect services.
What Is a Dark Store? - NetSuite - Dark stores are repurposed brick-and-mortar stores serving as mini fulfillment depots that enable rapid online order fulfillment through home delivery, curbside, or pickup, especially accelerated by the pandemic shift to online shopping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com