Modular home construction involves factory-built sections transported and assembled on-site, offering faster build times and reduced waste compared to traditional stick-built homes, which are constructed entirely on-site using lumber framing. Modular homes often provide consistent quality control and can be more cost-effective, while stick-built homes allow for greater customization and design flexibility. Discover the advantages and considerations of each method to choose the best option for your real estate investment.
Why it is important
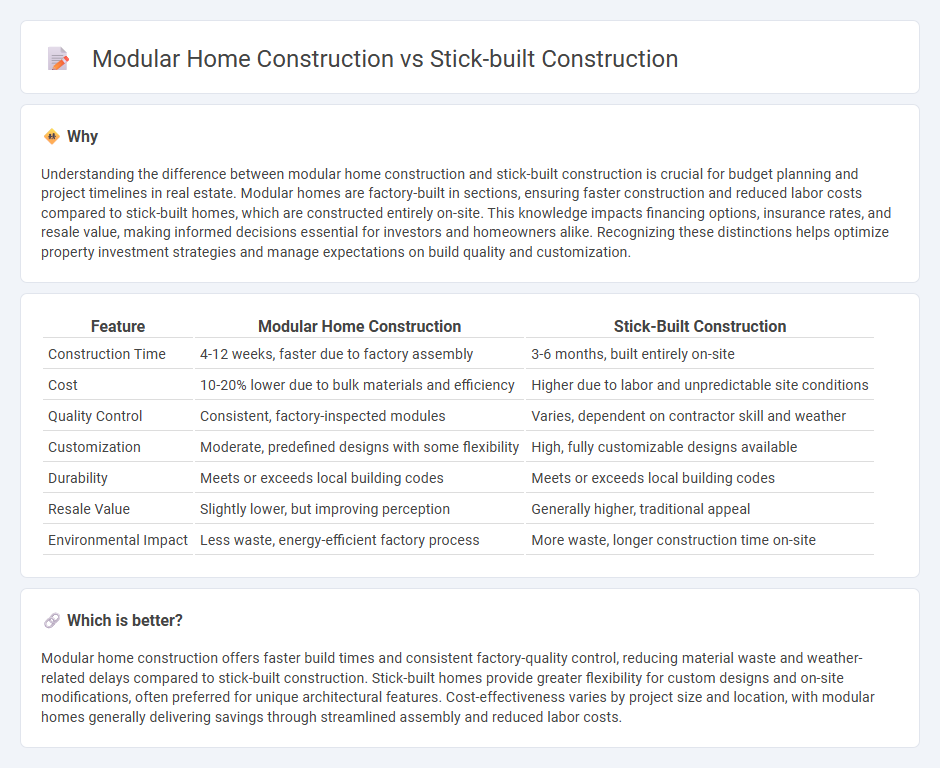
Understanding the difference between modular home construction and stick-built construction is crucial for budget planning and project timelines in real estate. Modular homes are factory-built in sections, ensuring faster construction and reduced labor costs compared to stick-built homes, which are constructed entirely on-site. This knowledge impacts financing options, insurance rates, and resale value, making informed decisions essential for investors and homeowners alike. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize property investment strategies and manage expectations on build quality and customization.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Home Construction | Stick-Built Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Time | 4-12 weeks, faster due to factory assembly | 3-6 months, built entirely on-site |
| Cost | 10-20% lower due to bulk materials and efficiency | Higher due to labor and unpredictable site conditions |
| Quality Control | Consistent, factory-inspected modules | Varies, dependent on contractor skill and weather |
| Customization | Moderate, predefined designs with some flexibility | High, fully customizable designs available |
| Durability | Meets or exceeds local building codes | Meets or exceeds local building codes |
| Resale Value | Slightly lower, but improving perception | Generally higher, traditional appeal |
| Environmental Impact | Less waste, energy-efficient factory process | More waste, longer construction time on-site |
Which is better?
Modular home construction offers faster build times and consistent factory-quality control, reducing material waste and weather-related delays compared to stick-built construction. Stick-built homes provide greater flexibility for custom designs and on-site modifications, often preferred for unique architectural features. Cost-effectiveness varies by project size and location, with modular homes generally delivering savings through streamlined assembly and reduced labor costs.
Connection
Modular home construction and stick-built construction both use traditional building materials like wood and drywall, but modular homes are prefabricated in factory-controlled environments before being transported to the site for assembly. This connection allows modular construction to offer faster build times and consistent quality control while still adhering to local building codes and design flexibility similar to stick-built homes. The integration of modular techniques with conventional stick-built methods enhances efficiency in residential real estate development.
Key Terms
On-site Construction
Stick-built construction involves assembling a home entirely on-site, offering customization but often resulting in longer build times due to weather and labor variability. Modular home construction significantly reduces on-site work as sections are pre-fabricated in factory-controlled environments, enhancing quality control and speeding up installation. Explore the detailed benefits and considerations of on-site construction methods to determine the best approach for your project.
Prefabrication
Prefabrication in modular home construction involves factory-built components assembled on-site, ensuring consistent quality and faster completion compared to traditional stick-built construction, where framing is constructed entirely on-site. Modular homes benefit from controlled environments during the manufacturing process, reducing delays caused by weather and improving material efficiency. Explore the advantages of prefabrication to understand how it transforms residential building efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Building Codes
Stick-built construction strictly adheres to local building codes throughout the entire construction process, ensuring each phase meets or exceeds safety and quality regulations. Modular home construction must also comply with the same building codes, but factory-built modules are inspected before shipment, often accelerating approval and reducing on-site inspections. Explore how building code compliance affects project timelines and cost-efficiency in both construction methods.
Source and External Links
What Does 'Stick Built' Mean and Why Does it Matter? - Stick-built construction refers to building a house on-site using individual pieces of lumber, a traditional method that allows for high customization and is often perceived as higher quality by builders and clients.
Stick-built construction - Wikipedia - Stick-built homes are constructed entirely or mostly on-site from wood, in contrast to manufactured or modular homes that are built in factories and shipped to the site.
Oasis Stick Built Homes - Stick-built construction involves assembling the house piece-by-piece at the location where it will be occupied, offering greater flexibility and customization compared to modular building methods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com