Nature-inclusive design integrates natural elements and ecosystems into real estate projects to enhance biodiversity, improve air quality, and create healthier living environments. Passive house design focuses on energy efficiency through airtight construction, high insulation, and heat recovery systems, significantly reducing the building's carbon footprint. Discover how these innovative approaches redefine sustainable living and elevate property value.
Why it is important
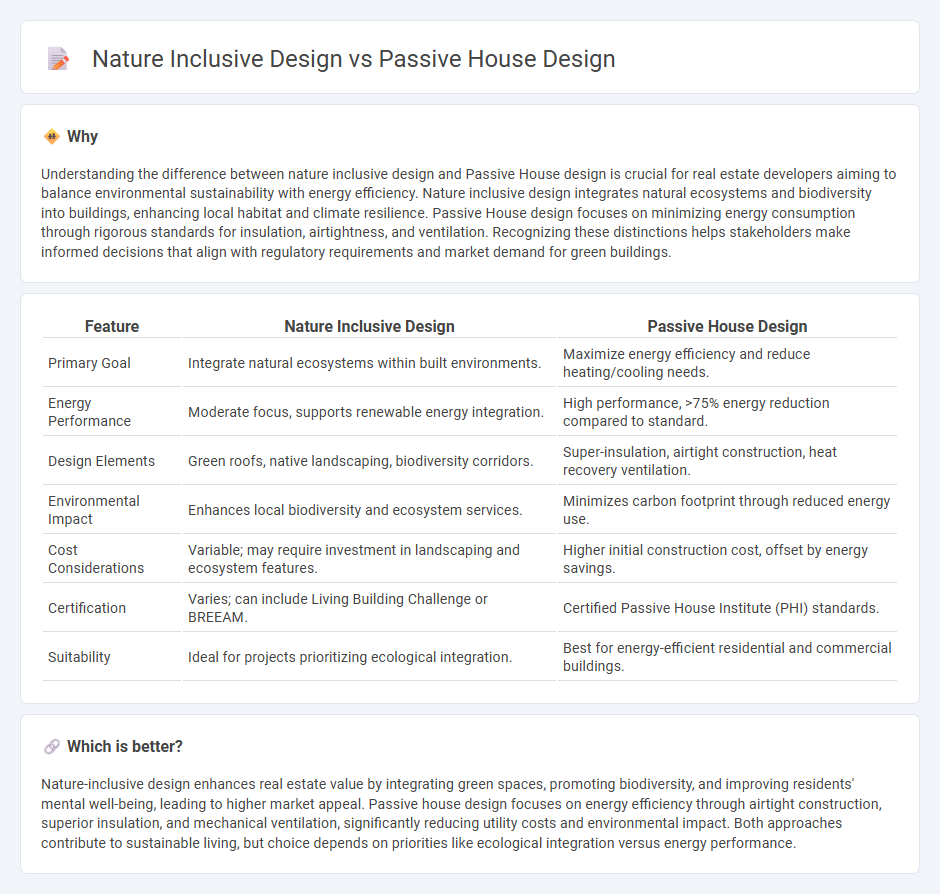
Understanding the difference between nature inclusive design and Passive House design is crucial for real estate developers aiming to balance environmental sustainability with energy efficiency. Nature inclusive design integrates natural ecosystems and biodiversity into buildings, enhancing local habitat and climate resilience. Passive House design focuses on minimizing energy consumption through rigorous standards for insulation, airtightness, and ventilation. Recognizing these distinctions helps stakeholders make informed decisions that align with regulatory requirements and market demand for green buildings.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Nature Inclusive Design | Passive House Design |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Integrate natural ecosystems within built environments. | Maximize energy efficiency and reduce heating/cooling needs. |
| Energy Performance | Moderate focus, supports renewable energy integration. | High performance, >75% energy reduction compared to standard. |
| Design Elements | Green roofs, native landscaping, biodiversity corridors. | Super-insulation, airtight construction, heat recovery ventilation. |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances local biodiversity and ecosystem services. | Minimizes carbon footprint through reduced energy use. |
| Cost Considerations | Variable; may require investment in landscaping and ecosystem features. | Higher initial construction cost, offset by energy savings. |
| Certification | Varies; can include Living Building Challenge or BREEAM. | Certified Passive House Institute (PHI) standards. |
| Suitability | Ideal for projects prioritizing ecological integration. | Best for energy-efficient residential and commercial buildings. |
Which is better?
Nature-inclusive design enhances real estate value by integrating green spaces, promoting biodiversity, and improving residents' mental well-being, leading to higher market appeal. Passive house design focuses on energy efficiency through airtight construction, superior insulation, and mechanical ventilation, significantly reducing utility costs and environmental impact. Both approaches contribute to sustainable living, but choice depends on priorities like ecological integration versus energy performance.
Connection
Nature-inclusive design and Passive House design both focus on enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability in real estate by integrating natural elements and optimizing building performance. Passive House design minimizes energy consumption through airtight construction, superior insulation, and heat recovery ventilation, while nature-inclusive design promotes biodiversity and ecological balance by incorporating green spaces, natural materials, and habitat-friendly landscaping. Together, these approaches create environmentally responsible buildings that improve occupant comfort and reduce the real estate sector's carbon footprint.
Key Terms
Thermal Insulation
Passive house design emphasizes superior thermal insulation through airtight building envelopes and high-performance windows, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling by up to 90%. Nature inclusive design integrates thermal insulation with natural materials and vegetation to enhance microclimates and biodiversity, promoting sustainable comfort. Explore the benefits of both approaches to optimize your building's thermal performance.
Biodiversity
Passive house design emphasizes energy efficiency and airtight construction aimed at reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. Nature inclusive design prioritizes biodiversity by integrating habitats and natural systems into urban planning, promoting ecosystem health and species variety. Explore how combining these approaches can create sustainable and biodiversity-rich living environments.
Airtightness
Passive house design prioritizes high levels of airtightness to minimize heat loss, ensuring energy efficiency and consistent indoor temperatures by preventing air leakage. In contrast, nature inclusive design balances airtightness with natural ventilation strategies to support biodiversity and maintain ecological connectivity within building environments. Explore deeper insights into how airtightness impacts both sustainable architectural approaches.
Source and External Links
What's a Passive House - RPA | Richard Pedranti Architect - This webpage explains the principles of Passive House design, emphasizing energy efficiency, superior sound insulation, durability, and low maintenance.
What is Passive House? - Passive House Massachusetts - This webpage describes Passive House as a performance-based building certification that dramatically reduces energy use for space heating and cooling, providing healthier and more comfortable spaces.
Passive house - Wikipedia - This article provides an overview of Passive House design, highlighting its focus on energy efficiency through techniques like passive solar design and superinsulation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com