Green hushing refers to companies deliberately downplaying or hiding their environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny or backlash, while cause-related marketing involves brands actively promoting social or environmental causes to connect with consumers and build goodwill. Effective cause-related marketing can enhance brand reputation and consumer loyalty by aligning business practices with societal values. Explore the differences between green hushing and cause-related marketing strategies to leverage authentic brand communication.
Why it is important
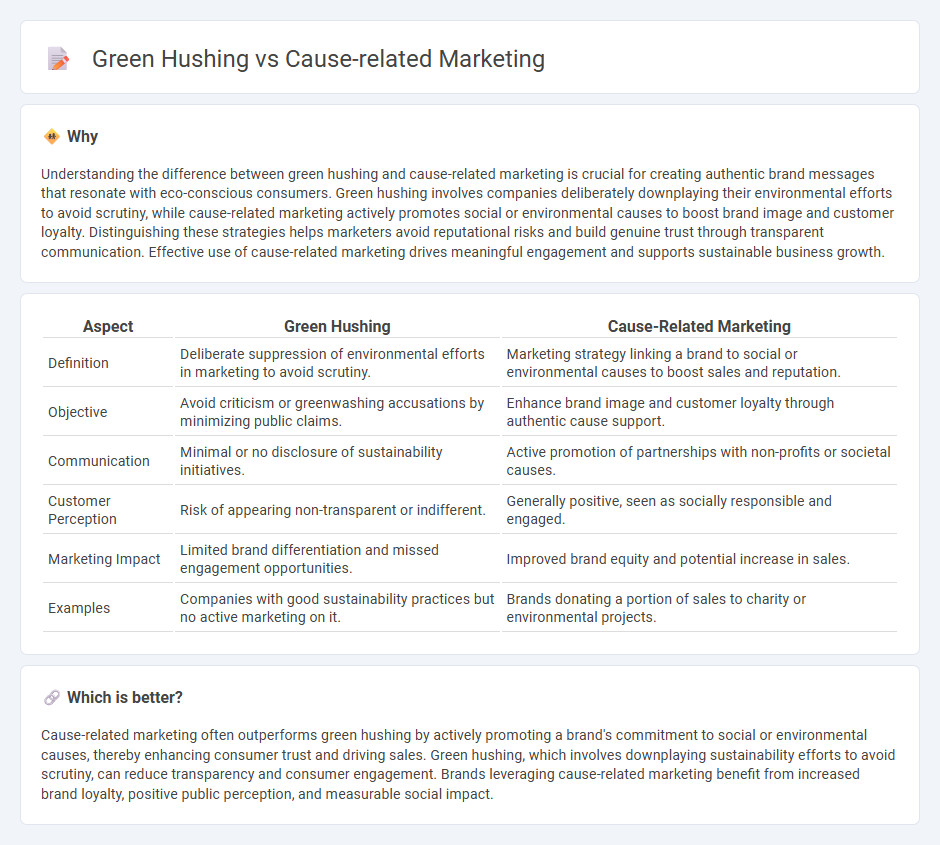
Understanding the difference between green hushing and cause-related marketing is crucial for creating authentic brand messages that resonate with eco-conscious consumers. Green hushing involves companies deliberately downplaying their environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny, while cause-related marketing actively promotes social or environmental causes to boost brand image and customer loyalty. Distinguishing these strategies helps marketers avoid reputational risks and build genuine trust through transparent communication. Effective use of cause-related marketing drives meaningful engagement and supports sustainable business growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Hushing | Cause-Related Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate suppression of environmental efforts in marketing to avoid scrutiny. | Marketing strategy linking a brand to social or environmental causes to boost sales and reputation. |
| Objective | Avoid criticism or greenwashing accusations by minimizing public claims. | Enhance brand image and customer loyalty through authentic cause support. |
| Communication | Minimal or no disclosure of sustainability initiatives. | Active promotion of partnerships with non-profits or societal causes. |
| Customer Perception | Risk of appearing non-transparent or indifferent. | Generally positive, seen as socially responsible and engaged. |
| Marketing Impact | Limited brand differentiation and missed engagement opportunities. | Improved brand equity and potential increase in sales. |
| Examples | Companies with good sustainability practices but no active marketing on it. | Brands donating a portion of sales to charity or environmental projects. |
Which is better?
Cause-related marketing often outperforms green hushing by actively promoting a brand's commitment to social or environmental causes, thereby enhancing consumer trust and driving sales. Green hushing, which involves downplaying sustainability efforts to avoid scrutiny, can reduce transparency and consumer engagement. Brands leveraging cause-related marketing benefit from increased brand loyalty, positive public perception, and measurable social impact.
Connection
Green hushing occurs when companies downplay their environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny, while cause-related marketing leverages social or environmental causes to enhance brand image and consumer loyalty. Both strategies affect corporate communication by influencing how sustainability messages are shared or withheld, impacting consumer trust and brand authenticity. Integrating transparent cause-related marketing can counteract green hushing by openly showcasing genuine commitment to environmental and social issues.
Key Terms
**Cause-Related Marketing:**
Cause-related marketing aligns brands with social or environmental causes to enhance reputation and consumer loyalty by demonstrating corporate social responsibility. Campaigns often feature partnerships with nonprofits, driving both sales and positive social impact through targeted messaging and cause engagement. Explore deeper insights into how cause-related marketing strategies effectively build brand equity and consumer trust.
Social cause partnership
Cause-related marketing aligns brands with social causes to build consumer trust and drive engagement, emphasizing transparency and authentic partnership. Green hushing occurs when companies minimize public communication about their sustainability or social responsibility efforts to avoid scrutiny or criticism. Explore deeper insights into how social cause partnerships can balance effective marketing with genuine impact.
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Cause-related marketing leverages brand partnerships with social causes to enhance corporate reputation and drive customer engagement through visible CSR initiatives, while green hushing involves companies deliberately minimizing publicity around their environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny or backlash. Both strategies impact corporate social responsibility communication but differ in transparency; cause-related marketing promotes active stakeholder involvement, whereas green hushing prioritizes risk management and discretion. Explore how these contrasting approaches shape CSR effectiveness and consumer trust in today's corporate landscape.
Source and External Links
What is Cause Marketing? - This article explains cause marketing as a strategic collaboration between businesses and nonprofits to benefit both parties while enhancing brand awareness and social responsibility.
What is Cause Marketing? - This resource describes cause marketing as a partnership between for-profit businesses and nonprofits to achieve mutual benefits, emphasizing corporate social responsibility.
Cause Marketing - Wikipedia defines cause marketing as a strategy where for-profit businesses collaborate with nonprofits to increase profits while contributing positively to society.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com