The post-purchase journey focuses on enhancing customer satisfaction and building brand loyalty after the initial sale through personalized follow-ups and support. Cross-selling aims to increase revenue by recommending complementary products or services that match the customer's purchase history and preferences. Discover how integrating both strategies can maximize customer lifetime value and boost sales.
Why it is important
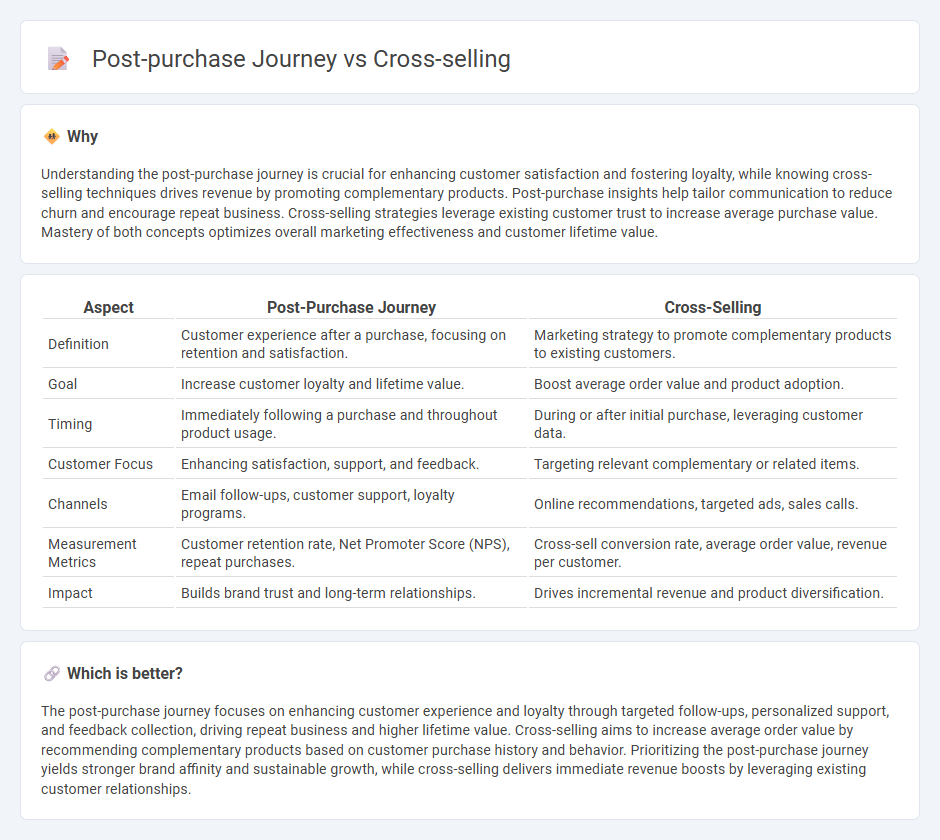
Understanding the post-purchase journey is crucial for enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering loyalty, while knowing cross-selling techniques drives revenue by promoting complementary products. Post-purchase insights help tailor communication to reduce churn and encourage repeat business. Cross-selling strategies leverage existing customer trust to increase average purchase value. Mastery of both concepts optimizes overall marketing effectiveness and customer lifetime value.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Post-Purchase Journey | Cross-Selling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Customer experience after a purchase, focusing on retention and satisfaction. | Marketing strategy to promote complementary products to existing customers. |
| Goal | Increase customer loyalty and lifetime value. | Boost average order value and product adoption. |
| Timing | Immediately following a purchase and throughout product usage. | During or after initial purchase, leveraging customer data. |
| Customer Focus | Enhancing satisfaction, support, and feedback. | Targeting relevant complementary or related items. |
| Channels | Email follow-ups, customer support, loyalty programs. | Online recommendations, targeted ads, sales calls. |
| Measurement Metrics | Customer retention rate, Net Promoter Score (NPS), repeat purchases. | Cross-sell conversion rate, average order value, revenue per customer. |
| Impact | Builds brand trust and long-term relationships. | Drives incremental revenue and product diversification. |
Which is better?
The post-purchase journey focuses on enhancing customer experience and loyalty through targeted follow-ups, personalized support, and feedback collection, driving repeat business and higher lifetime value. Cross-selling aims to increase average order value by recommending complementary products based on customer purchase history and behavior. Prioritizing the post-purchase journey yields stronger brand affinity and sustainable growth, while cross-selling delivers immediate revenue boosts by leveraging existing customer relationships.
Connection
Post-purchase journey optimization enhances customer satisfaction by providing timely support and personalized recommendations, which boosts opportunities for effective cross-selling. Analyzing purchase behavior and feedback during this stage enables marketers to identify relevant complementary products, increasing average order value and customer lifetime value. Seamless integration of cross-selling strategies into the post-purchase experience nurtures brand loyalty and drives repeat sales.
Key Terms
Upsell
Cross-selling targets complementary products during the purchase process, while the post-purchase journey emphasizes upselling by encouraging customers to upgrade or buy premium versions after initial acquisition. Upsell strategies in the post-purchase phase enhance customer lifetime value through personalized recommendations and timely engagement. Discover effective upsell techniques to maximize revenue and deepen customer loyalty.
Customer Retention
Cross-selling leverages existing customer data to introduce complementary products that enhance the buyer's original purchase, boosting revenue and customer engagement. The post-purchase journey emphasizes follow-up interactions, satisfaction monitoring, and personalized support to strengthen brand loyalty and reduce churn. Discover effective strategies to integrate cross-selling techniques within the post-purchase experience to maximize customer retention.
Customer Lifetime Value
Cross-selling strategies aim to maximize Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) by introducing complementary products or services during the initial purchase phase. The post-purchase journey enhances CLV by fostering customer loyalty, satisfaction, and repeat purchases through personalized follow-ups and support. Discover how optimizing both approaches can significantly boost long-term profitability and customer engagement.
Source and External Links
What Is Cross-Selling? Intro, Steps, and Pro Tips [+Data] - Cross-selling is the practice of offering customers additional products or services that complement their original purchase, such as suggesting fries and a drink when a customer orders a burger, aimed at increasing sales by meeting related needs.
What is Cross-selling - Definition by Insider - Cross-selling is a marketing technique to boost revenue by recommending supplementary products alongside the main product, often using AI-driven personalized suggestions to improve average order value and customer engagement.
Cross-Sell - Overview, How It Works, and Examples - Cross-selling involves selling an additional, related product or service to an existing customer to enhance their primary purchase, which can strengthen customer relationships and increase revenue across various industries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com