Leadership shadow reflects the influence leaders have on organizational culture through their behaviors and values, shaping employee motivation and ethical standards. Transactional leadership focuses on structured tasks, utilizing rewards and penalties to achieve performance goals and maintain order. Explore the differences between these leadership styles to understand their impact on team dynamics and organizational success.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between leadership shadow and transactional leadership is crucial for effective management because the leadership shadow reflects the lasting impact of a leader's values and behaviors on organizational culture, while transactional leadership focuses on short-term goals through rewards and punishments. Recognizing these distinctions helps managers foster a positive work environment, drive employee motivation, and align team actions with long-term strategic objectives. Differentiating the two allows leaders to balance immediate performance with sustainable influence on organizational success. Knowledge of these concepts enhances decision-making and leadership development within enterprises.
Comparison Table
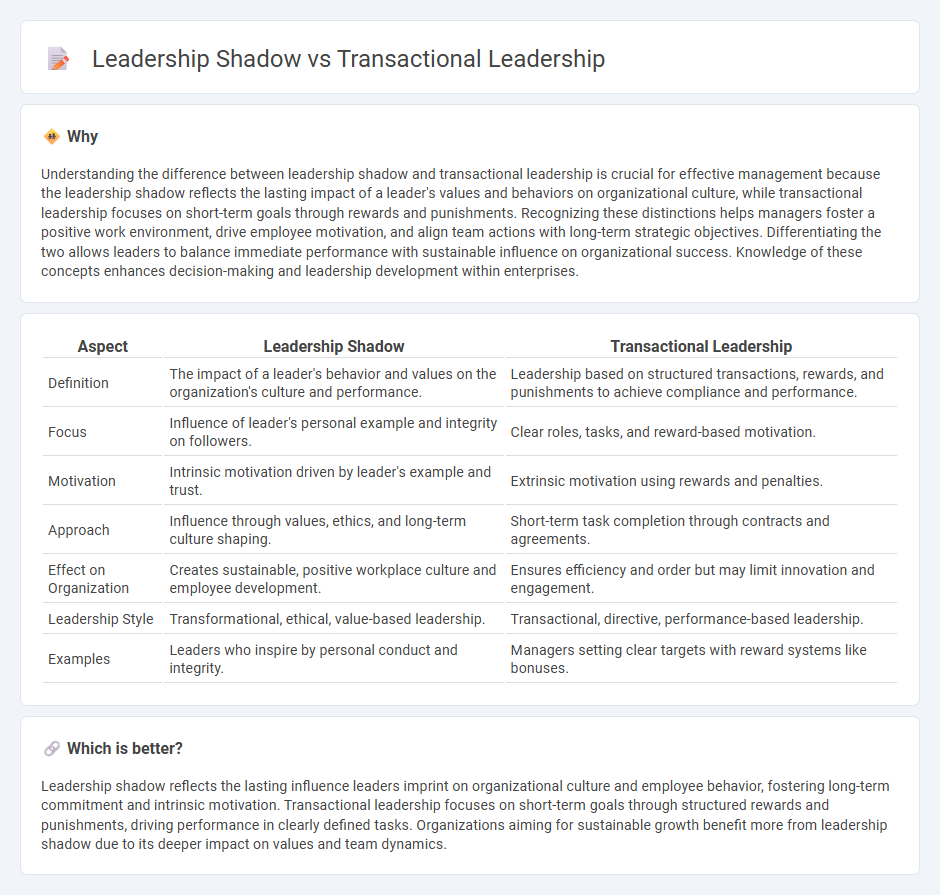
| Aspect | Leadership Shadow | Transactional Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The impact of a leader's behavior and values on the organization's culture and performance. | Leadership based on structured transactions, rewards, and punishments to achieve compliance and performance. |
| Focus | Influence of leader's personal example and integrity on followers. | Clear roles, tasks, and reward-based motivation. |
| Motivation | Intrinsic motivation driven by leader's example and trust. | Extrinsic motivation using rewards and penalties. |
| Approach | Influence through values, ethics, and long-term culture shaping. | Short-term task completion through contracts and agreements. |
| Effect on Organization | Creates sustainable, positive workplace culture and employee development. | Ensures efficiency and order but may limit innovation and engagement. |
| Leadership Style | Transformational, ethical, value-based leadership. | Transactional, directive, performance-based leadership. |
| Examples | Leaders who inspire by personal conduct and integrity. | Managers setting clear targets with reward systems like bonuses. |
Which is better?
Leadership shadow reflects the lasting influence leaders imprint on organizational culture and employee behavior, fostering long-term commitment and intrinsic motivation. Transactional leadership focuses on short-term goals through structured rewards and punishments, driving performance in clearly defined tasks. Organizations aiming for sustainable growth benefit more from leadership shadow due to its deeper impact on values and team dynamics.
Connection
Leadership shadow reflects the influence leaders have on organizational culture through their behaviors and values, which directly impacts the effectiveness of transactional leadership. Transactional leadership relies on clear structures, rewards, and penalties, and the leader's shadow shapes how these elements are perceived and executed by employees. Organizations with a positive leadership shadow enhance transactional leadership outcomes by fostering trust and consistency in performance management.
Key Terms
Rewards and Penalties
Transactional leadership emphasizes a structured system of rewards and penalties to motivate performance, relying on clear expectations and consequences to drive results. In contrast, the leadership shadow reflects the unintended impact of a leader's behavior and values on organizational culture and employee morale, beyond formal reward systems. Explore how recognizing the leadership shadow can enhance traditional transactional strategies.
Role Modeling
Transactional leadership emphasizes clear structure, rewards, and punishments to achieve compliance and performance. Leadership shadow, by contrast, centers on role modeling where leaders' behaviors, values, and attitudes indirectly shape organizational culture and employee conduct. Discover how mastering role modeling can enhance leadership impact and organizational success.
Influence
Transactional leadership emphasizes structured exchanges between leaders and followers, relying heavily on rewards and penalties to influence behavior. The leadership shadow concept explores how a leader's unconscious traits, beliefs, and actions impact organizational culture and influence beyond formal authority. Discover more about the nuanced dynamics of influence in leadership by exploring the leadership shadow framework.
Source and External Links
What is transactional leadership? - Definition from WhatIs.com - Transactional leadership is a style where leaders use rewards and punishments to motivate employees, focusing on clear goals, close supervision, and maintaining established processes within structured environments.
Defining Transactional Leadership - This management approach emphasizes strict adherence to company guidelines, rewards for meeting goals, reprimands for failures, and works best in organizations that value structure and consistency over creativity.
Transactional leadership - Transactional leadership centers on short-term exchanges between leaders and followers, using contingent rewards and management-by-exception to achieve specific, measurable outcomes without fostering deeper, lasting relationships.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com