Proximity bias occurs when managers favor employees who are physically closer, impacting fair evaluations and decision-making in workplace management. The halo effect influences judgments by allowing one positive trait to overshadow other attributes, leading to skewed performance assessments. Explore these cognitive biases to enhance equitable leadership and employee appraisal strategies.
Why it is important
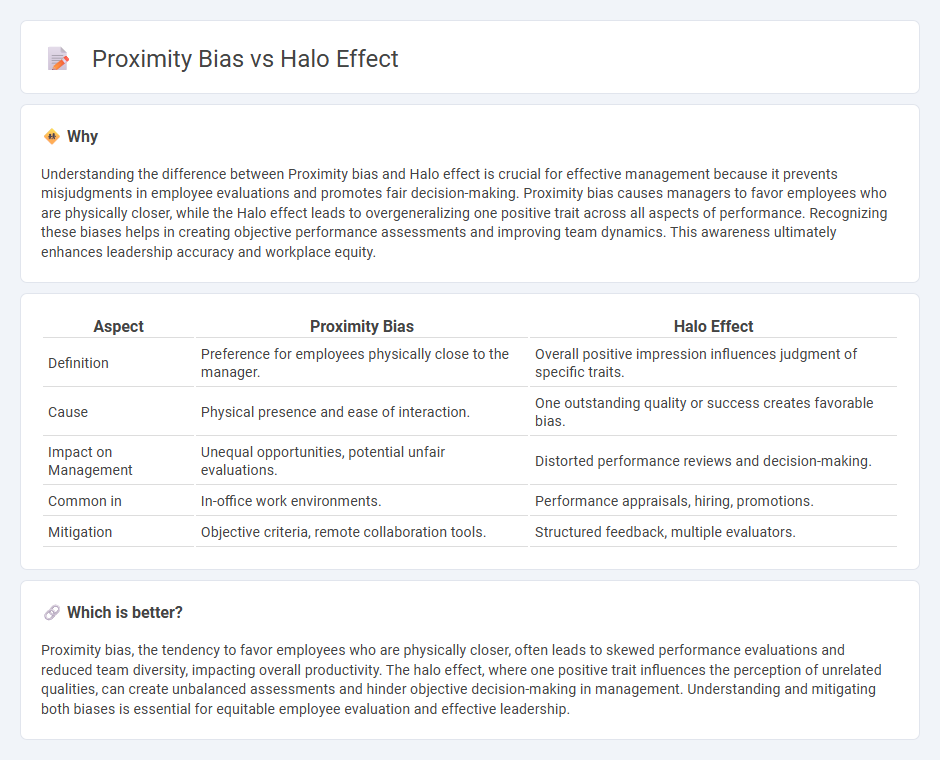
Understanding the difference between Proximity bias and Halo effect is crucial for effective management because it prevents misjudgments in employee evaluations and promotes fair decision-making. Proximity bias causes managers to favor employees who are physically closer, while the Halo effect leads to overgeneralizing one positive trait across all aspects of performance. Recognizing these biases helps in creating objective performance assessments and improving team dynamics. This awareness ultimately enhances leadership accuracy and workplace equity.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Proximity Bias | Halo Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Preference for employees physically close to the manager. | Overall positive impression influences judgment of specific traits. |
| Cause | Physical presence and ease of interaction. | One outstanding quality or success creates favorable bias. |
| Impact on Management | Unequal opportunities, potential unfair evaluations. | Distorted performance reviews and decision-making. |
| Common in | In-office work environments. | Performance appraisals, hiring, promotions. |
| Mitigation | Objective criteria, remote collaboration tools. | Structured feedback, multiple evaluators. |
Which is better?
Proximity bias, the tendency to favor employees who are physically closer, often leads to skewed performance evaluations and reduced team diversity, impacting overall productivity. The halo effect, where one positive trait influences the perception of unrelated qualities, can create unbalanced assessments and hinder objective decision-making in management. Understanding and mitigating both biases is essential for equitable employee evaluation and effective leadership.
Connection
Proximity bias occurs when managers favor employees who are physically closer, impacting performance evaluations through limited observation. The halo effect amplifies this bias by causing managers to let one positive trait or action of nearby employees skew overall judgment. Together, these cognitive biases distort fair management decisions, reducing objectivity in employee assessment and development.
Key Terms
Perception
The halo effect influences perception by causing individuals to generalize one positive trait across an entire person, enhancing overall attractiveness or competence unfairly. Proximity bias shapes perception through a preference for those physically or digitally closer, often leading to skewed evaluations in professional or social settings. Explore more to understand how these cognitive biases impact decision-making and interpersonal relationships.
Evaluation
Halo effect causes evaluators to let one positive trait overshadow other aspects, leading to an overall inflated evaluation of an individual. Proximity bias influences assessment by favoring individuals who are physically or socially closer, potentially skewing objective judgment based on access or familiarity. Explore more about how these cognitive biases impact performance reviews and decision-making processes.
Workplace fairness
The halo effect in workplace fairness occurs when an employee's positive trait unduly influences the overall perception of their performance, overshadowing objective evaluations. Proximity bias refers to favoring employees who are physically closer to managers, often leading to unequal opportunities for remote or distant workers. Explore how mitigating these biases enhances equitable treatment and decision-making within organizations.
Source and External Links
Halo effect - Wikipedia - The halo effect is a cognitive bias where positive impressions of a person, product, or brand in one area influence opinions positively in other areas, often preventing objective evaluation of all traits.
Halo effect - The Decision Lab - This cognitive bias causes people to generalize from a single positive trait to assume other positive qualities, leading to distorted evaluations of people, brands, or products even without evidence supporting these traits.
Halo Effect Bias In Psychology: Definition & Examples - The halo effect involves attributing positive overall judgments based on one trait, such as attractiveness or warmth, often leading to biased perceptions of personality or abilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com