Reverse mentorship fosters knowledge exchange by pairing younger employees with seasoned leaders, enhancing digital skills and fresh perspectives, whereas traditional mentorship emphasizes experience and hierarchical guidance. Both approaches cultivate professional growth, but reverse mentorship accelerates innovation and inclusivity within organizations. Explore further to understand which mentorship model best fits your leadership development strategy.
Why it is important
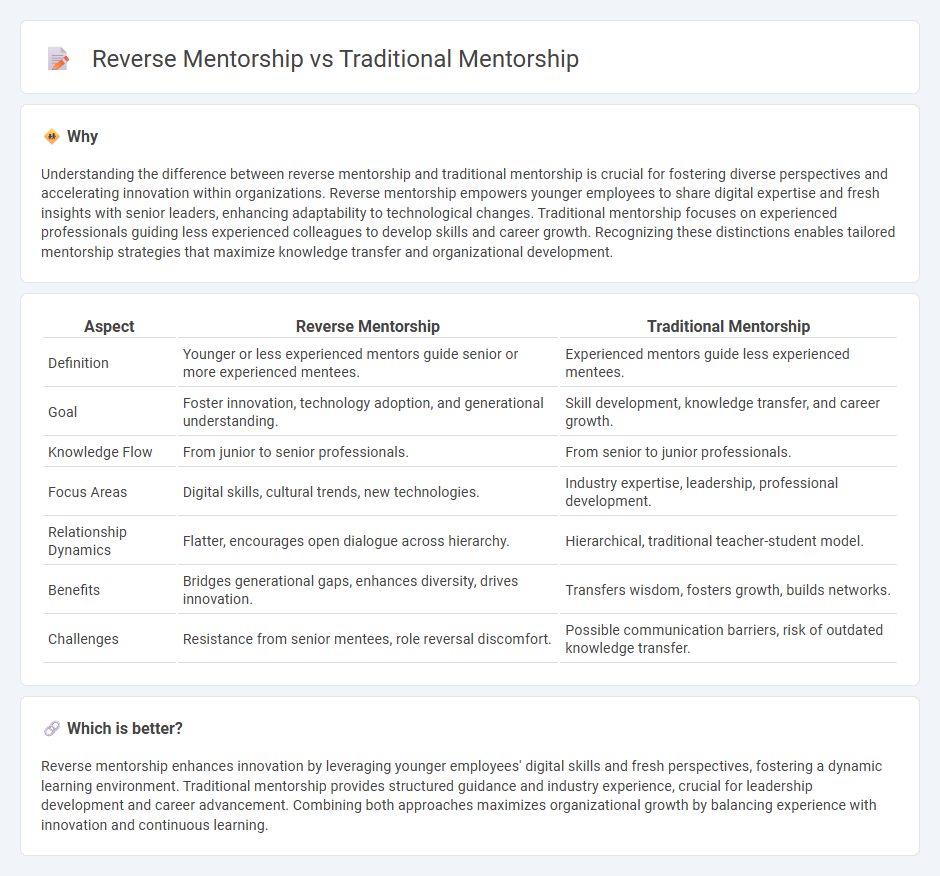
Understanding the difference between reverse mentorship and traditional mentorship is crucial for fostering diverse perspectives and accelerating innovation within organizations. Reverse mentorship empowers younger employees to share digital expertise and fresh insights with senior leaders, enhancing adaptability to technological changes. Traditional mentorship focuses on experienced professionals guiding less experienced colleagues to develop skills and career growth. Recognizing these distinctions enables tailored mentorship strategies that maximize knowledge transfer and organizational development.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Mentorship | Traditional Mentorship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Younger or less experienced mentors guide senior or more experienced mentees. | Experienced mentors guide less experienced mentees. |
| Goal | Foster innovation, technology adoption, and generational understanding. | Skill development, knowledge transfer, and career growth. |
| Knowledge Flow | From junior to senior professionals. | From senior to junior professionals. |
| Focus Areas | Digital skills, cultural trends, new technologies. | Industry expertise, leadership, professional development. |
| Relationship Dynamics | Flatter, encourages open dialogue across hierarchy. | Hierarchical, traditional teacher-student model. |
| Benefits | Bridges generational gaps, enhances diversity, drives innovation. | Transfers wisdom, fosters growth, builds networks. |
| Challenges | Resistance from senior mentees, role reversal discomfort. | Possible communication barriers, risk of outdated knowledge transfer. |
Which is better?
Reverse mentorship enhances innovation by leveraging younger employees' digital skills and fresh perspectives, fostering a dynamic learning environment. Traditional mentorship provides structured guidance and industry experience, crucial for leadership development and career advancement. Combining both approaches maximizes organizational growth by balancing experience with innovation and continuous learning.
Connection
Reverse mentorship and traditional mentorship are interconnected through their shared goal of knowledge exchange between different experience levels within an organization. While traditional mentorship involves experienced professionals guiding less experienced individuals, reverse mentorship reverses this dynamic, allowing younger or less experienced employees to impart insights, particularly in areas like technology and social trends. This reciprocal relationship enhances organizational learning, fosters innovation, and bridges generational gaps in management practices.
Key Terms
Hierarchical Structure
Traditional mentorship typically emphasizes a clear hierarchical structure where experienced senior employees guide juniors, fostering knowledge transfer from top to bottom. Reverse mentorship inverts this dynamic, with younger or less experienced employees providing insights on technology, trends, and new perspectives to senior leaders, promoting a more collaborative and flexible hierarchy. Explore how these distinct mentorship models influence organizational learning and leadership development.
Knowledge Transfer
Traditional mentorship facilitates knowledge transfer by enabling experienced professionals to share industry insights, skills, and organizational wisdom with less experienced mentees, fostering career development and expertise growth. Reverse mentorship reverses this dynamic, where younger employees impart digital skills, contemporary trends, and innovative perspectives to senior leaders, enhancing adaptability and strategic decision-making. Explore more about optimizing knowledge transfer through blended mentorship models.
Generational Learning
Traditional mentorship typically involves experienced senior professionals guiding younger employees, emphasizing knowledge transfer and career development. Reverse mentorship flips this dynamic, enabling younger generations to share digital literacy, social trends, and fresh perspectives with senior leaders, fostering mutual growth and organizational adaptability. Explore deeper insights into how generational learning transforms workplace mentorship models.
Source and External Links
Mentoring Styles | EDUCAUSE - Traditional mentoring is a supportive learning relationship where a mentor shares knowledge and experience with a mentee to enrich their professional journey through just-in-time help and expertise sharing.
Traditional Mentoring vs Modern Mentoring - Insala - Traditional mentoring involves one-on-one, uninterrupted attention from the mentor, allowing for a personal connection and guidance tailored to broader long-term goals.
Types of Mentoring - UC Davis Human Resources - Traditional one-on-one mentoring pairs a mentor and mentee either through a program or independently, with structure and timeframes set by the participants or the formal program.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com