The deskless workforce comprises employees performing tasks outside traditional office settings, often in retail, manufacturing, or field services, requiring mobile communication tools and real-time data access. In contrast, the distributed workforce operates remotely across diverse locations, leveraging cloud-based collaboration platforms to maintain productivity and connectivity. Explore strategies to effectively manage these evolving workforce models and enhance operational efficiency.
Why it is important
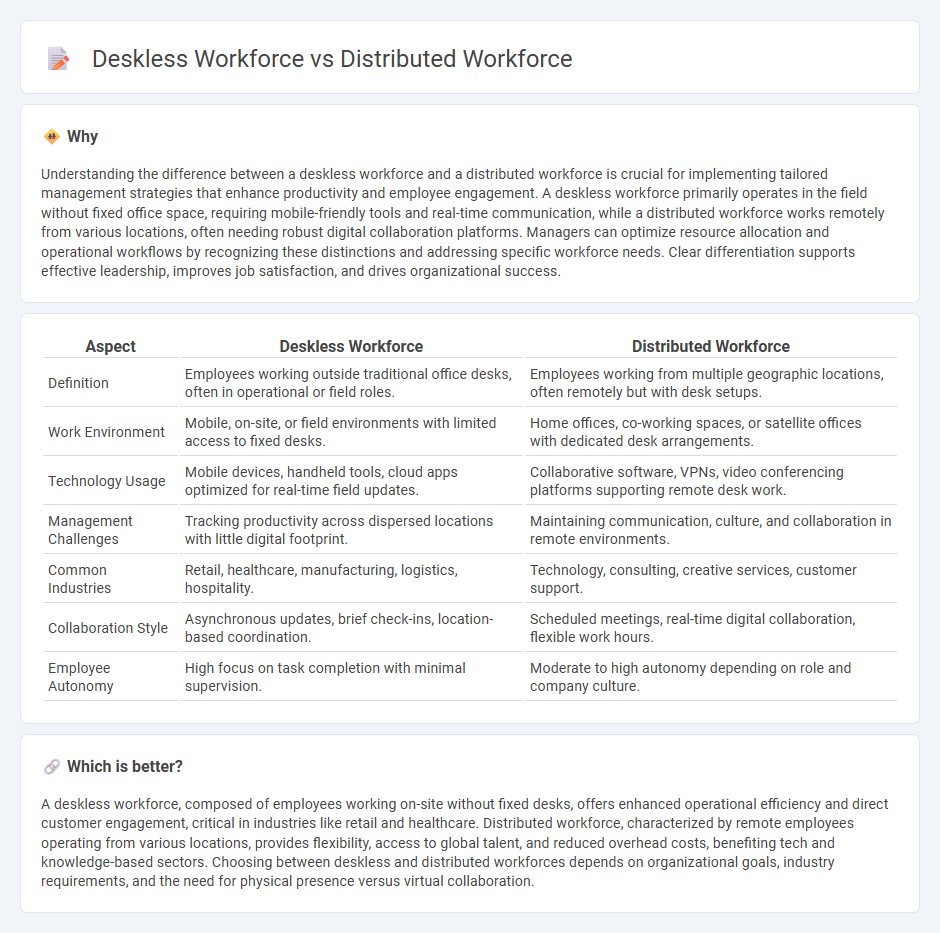
Understanding the difference between a deskless workforce and a distributed workforce is crucial for implementing tailored management strategies that enhance productivity and employee engagement. A deskless workforce primarily operates in the field without fixed office space, requiring mobile-friendly tools and real-time communication, while a distributed workforce works remotely from various locations, often needing robust digital collaboration platforms. Managers can optimize resource allocation and operational workflows by recognizing these distinctions and addressing specific workforce needs. Clear differentiation supports effective leadership, improves job satisfaction, and drives organizational success.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deskless Workforce | Distributed Workforce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees working outside traditional office desks, often in operational or field roles. | Employees working from multiple geographic locations, often remotely but with desk setups. |
| Work Environment | Mobile, on-site, or field environments with limited access to fixed desks. | Home offices, co-working spaces, or satellite offices with dedicated desk arrangements. |
| Technology Usage | Mobile devices, handheld tools, cloud apps optimized for real-time field updates. | Collaborative software, VPNs, video conferencing platforms supporting remote desk work. |
| Management Challenges | Tracking productivity across dispersed locations with little digital footprint. | Maintaining communication, culture, and collaboration in remote environments. |
| Common Industries | Retail, healthcare, manufacturing, logistics, hospitality. | Technology, consulting, creative services, customer support. |
| Collaboration Style | Asynchronous updates, brief check-ins, location-based coordination. | Scheduled meetings, real-time digital collaboration, flexible work hours. |
| Employee Autonomy | High focus on task completion with minimal supervision. | Moderate to high autonomy depending on role and company culture. |
Which is better?
A deskless workforce, composed of employees working on-site without fixed desks, offers enhanced operational efficiency and direct customer engagement, critical in industries like retail and healthcare. Distributed workforce, characterized by remote employees operating from various locations, provides flexibility, access to global talent, and reduced overhead costs, benefiting tech and knowledge-based sectors. Choosing between deskless and distributed workforces depends on organizational goals, industry requirements, and the need for physical presence versus virtual collaboration.
Connection
The deskless workforce primarily operates outside traditional office environments, relying heavily on mobile technology and remote communication tools that also support distributed workforces. Both workforce models emphasize flexibility, real-time data access, and decentralized decision-making to enhance productivity across diverse locations. Effective management integrates digital platforms to synchronize tasks, streamline processes, and maintain consistent collaboration among deskless and distributed employees.
Key Terms
Remote Collaboration
A distributed workforce consists of employees working from various geographical locations, often remotely, leveraging digital tools for seamless collaboration. In contrast, a deskless workforce operates primarily in the field or on the move without fixed workstations, relying on mobile technology for communication and task management. Explore how these workforce models optimize remote collaboration to enhance productivity and connectivity.
Mobility
The distributed workforce relies on employees working remotely from various locations, leveraging advanced communication technologies to maintain productivity and collaboration. The deskless workforce, often comprising frontline and field workers, prioritizes mobility with tools like mobile devices and cloud-based applications to perform tasks outside traditional office settings. Explore how mobility solutions enhance both workforce models for greater efficiency and flexibility.
Autonomy
A distributed workforce operates remotely across various locations, leveraging technology to maintain autonomy in decision-making and task execution. In contrast, a deskless workforce, often mobile and on-site, experiences autonomy through real-time, field-based problem-solving and direct adaptability to immediate work environments. Explore how autonomy shapes productivity in both workforce models for innovative management strategies.
Source and External Links
10 Tips on How to Effectively Engage a Diverse, Distributed Workforce - This article provides strategies for engaging a diverse and distributed workforce, leveraging technology to enhance collaboration and productivity.
What is a Distributed Workforce and How to Manage it? - This resource explains what a distributed workforce is and offers insights on managing it, highlighting the use of digital tools for seamless collaboration.
What is a Distributed Workforce: Benefits, Best Practices, and Examples - This page discusses the benefits and best practices of a distributed workforce, including increased access to diverse talent and improved work-life balance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com