Employee ghosting occurs when workers abruptly stop communicating and fail to show up for their job without notice, causing disruption to team productivity and workflow. Silent quitting involves employees doing the bare minimum required, disengaging from extra responsibilities and limiting their effort, which impacts overall organizational performance and morale. Discover more about how these behaviors affect workplace management and strategies to address them.
Why it is important
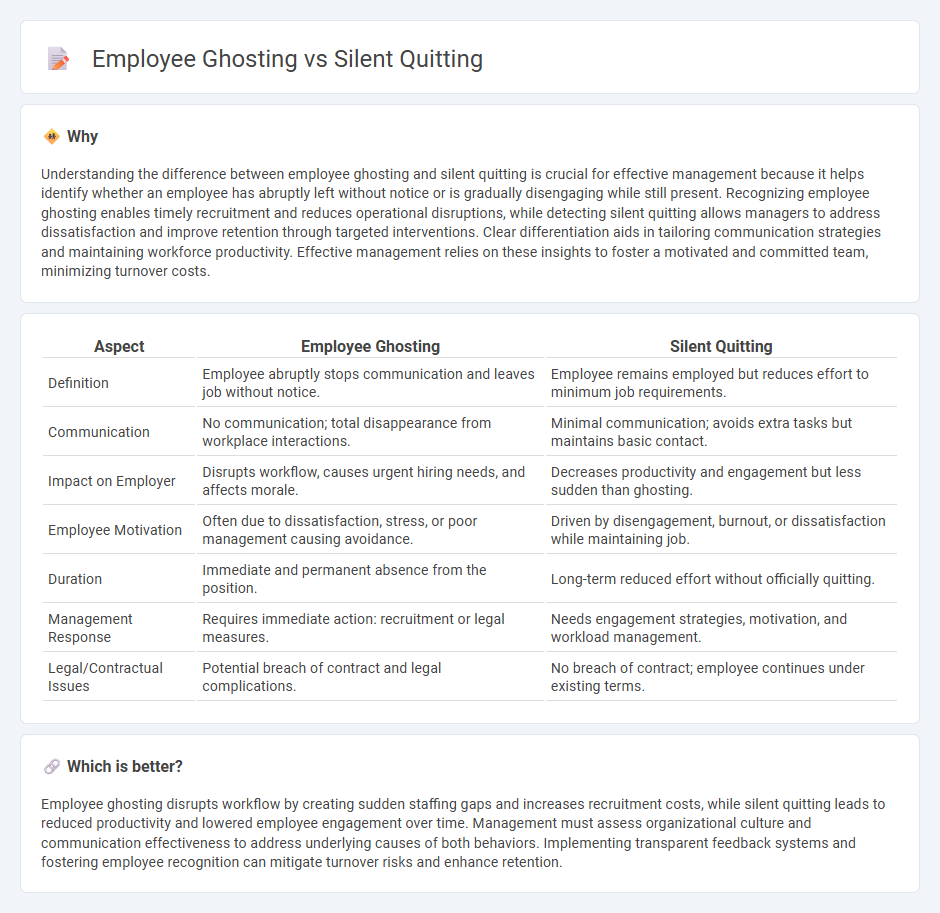
Understanding the difference between employee ghosting and silent quitting is crucial for effective management because it helps identify whether an employee has abruptly left without notice or is gradually disengaging while still present. Recognizing employee ghosting enables timely recruitment and reduces operational disruptions, while detecting silent quitting allows managers to address dissatisfaction and improve retention through targeted interventions. Clear differentiation aids in tailoring communication strategies and maintaining workforce productivity. Effective management relies on these insights to foster a motivated and committed team, minimizing turnover costs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Employee Ghosting | Silent Quitting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee abruptly stops communication and leaves job without notice. | Employee remains employed but reduces effort to minimum job requirements. |
| Communication | No communication; total disappearance from workplace interactions. | Minimal communication; avoids extra tasks but maintains basic contact. |
| Impact on Employer | Disrupts workflow, causes urgent hiring needs, and affects morale. | Decreases productivity and engagement but less sudden than ghosting. |
| Employee Motivation | Often due to dissatisfaction, stress, or poor management causing avoidance. | Driven by disengagement, burnout, or dissatisfaction while maintaining job. |
| Duration | Immediate and permanent absence from the position. | Long-term reduced effort without officially quitting. |
| Management Response | Requires immediate action: recruitment or legal measures. | Needs engagement strategies, motivation, and workload management. |
| Legal/Contractual Issues | Potential breach of contract and legal complications. | No breach of contract; employee continues under existing terms. |
Which is better?
Employee ghosting disrupts workflow by creating sudden staffing gaps and increases recruitment costs, while silent quitting leads to reduced productivity and lowered employee engagement over time. Management must assess organizational culture and communication effectiveness to address underlying causes of both behaviors. Implementing transparent feedback systems and fostering employee recognition can mitigate turnover risks and enhance retention.
Connection
Employee ghosting and silent quitting both reflect disengagement and breakdowns in workplace communication, where workers withdraw commitment without explicit notice. Ghosting involves abruptly cutting off contact during recruitment or employment, while silent quitting entails employees doing the bare minimum to avoid burnout without formally resigning. Both trends negatively impact management effectiveness by increasing turnover risks and reducing productivity, underscoring the importance of fostering transparent dialogue and employee well-being strategies.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Silent quitting and employee ghosting both significantly impact employee engagement and organizational productivity. Silent quitting occurs when employees emotionally disengage and reduce effort without officially resigning, while employee ghosting involves abruptly leaving without notice during or after the hiring process. Explore these phenomena further to understand their effects on workplace dynamics and retention strategies.
Workplace Communication
Silent quitting involves employees disengaging from tasks without formally resigning, while employee ghosting refers to abruptly ceasing all communication and leaving the job unexpectedly. Both phenomena disrupt workplace communication and productivity, prompting organizations to enhance engagement strategies and clear dialogue channels. Explore effective communication techniques to mitigate silent quitting and ghosting in professional settings.
Retention Strategies
Silent quitting involves employees disengaging from discretionary tasks while maintaining basic job responsibilities, whereas employee ghosting occurs when employees abruptly stop communicating or showing up without notice. Retention strategies should target enhancing employee engagement, clear communication channels, and proactive feedback systems to address both behaviors effectively. Explore comprehensive retention tactics to mitigate silent quitting and ghosting in your workforce.
Source and External Links
What Is Quiet Quitting and Can It Be Prevented? - This article explains quiet quitting, where employees disengage gradually before leaving, and discusses its distinction from quiet firing.
Gen Z is Quiet Quitting: Are You Listening? - This piece explores quiet quitting among Gen Z workers, highlighting it as a response to unrealistic expectations and toxic work cultures.
Is Quiet Quitting Real? - Gallup's article discusses the prevalence of quiet quitting, noting that at least half of the U.S. workforce is disengaged and doing the minimum required at work.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com