Servant leadership focuses on prioritizing the needs and growth of team members by fostering a supportive and empathetic environment, while situational leadership adapts leadership styles based on the team's maturity and specific circumstances to maximize effectiveness. Both models emphasize flexibility and human-centric approaches but differ in their core focus--servant leadership concentrates on serving others, whereas situational leadership adjusts directives and support according to situational demands. Explore the nuances of these leadership styles to determine which approach best fits your organizational goals.
Why it is important
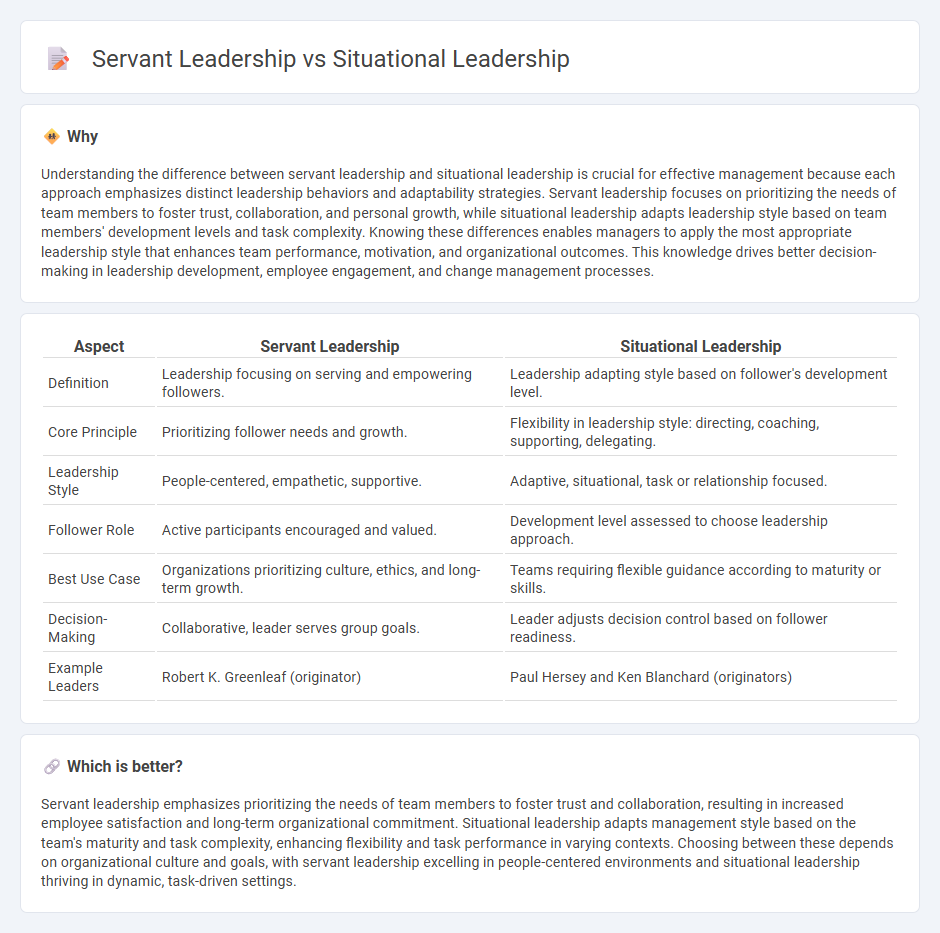
Understanding the difference between servant leadership and situational leadership is crucial for effective management because each approach emphasizes distinct leadership behaviors and adaptability strategies. Servant leadership focuses on prioritizing the needs of team members to foster trust, collaboration, and personal growth, while situational leadership adapts leadership style based on team members' development levels and task complexity. Knowing these differences enables managers to apply the most appropriate leadership style that enhances team performance, motivation, and organizational outcomes. This knowledge drives better decision-making in leadership development, employee engagement, and change management processes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Servant Leadership | Situational Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Leadership focusing on serving and empowering followers. | Leadership adapting style based on follower's development level. |
| Core Principle | Prioritizing follower needs and growth. | Flexibility in leadership style: directing, coaching, supporting, delegating. |
| Leadership Style | People-centered, empathetic, supportive. | Adaptive, situational, task or relationship focused. |
| Follower Role | Active participants encouraged and valued. | Development level assessed to choose leadership approach. |
| Best Use Case | Organizations prioritizing culture, ethics, and long-term growth. | Teams requiring flexible guidance according to maturity or skills. |
| Decision-Making | Collaborative, leader serves group goals. | Leader adjusts decision control based on follower readiness. |
| Example Leaders | Robert K. Greenleaf (originator) | Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard (originators) |
Which is better?
Servant leadership emphasizes prioritizing the needs of team members to foster trust and collaboration, resulting in increased employee satisfaction and long-term organizational commitment. Situational leadership adapts management style based on the team's maturity and task complexity, enhancing flexibility and task performance in varying contexts. Choosing between these depends on organizational culture and goals, with servant leadership excelling in people-centered environments and situational leadership thriving in dynamic, task-driven settings.
Connection
Servant leadership and situational leadership both emphasize flexibility and the leader's role in addressing the needs of their team, fostering an environment centered on support and development. Servant leadership prioritizes serving others and empowering employees, while situational leadership adjusts leadership style based on employees' readiness and task complexity. Their connection lies in the adaptive mindset and focus on facilitating team growth, enhancing overall management effectiveness.
Key Terms
Adaptability (Situational Leadership)
Situational leadership emphasizes adaptability by encouraging leaders to adjust their style based on team members' development levels and task complexity, promoting effective performance in dynamic environments. This model contrasts with servant leadership, which centers on prioritizing followers' needs and fostering a supportive community rather than flexibility in leadership approach. Discover how choosing the right leadership style can enhance organizational success and employee engagement.
Empowerment (Servant Leadership)
Servant leadership prioritizes empowerment by actively supporting team members' growth, fostering collaboration, and addressing individual needs to build trust and enhance morale. Situational leadership adapts leadership style based on team maturity and task complexity but may not consistently emphasize empowerment as a core value. Explore how servant leadership's commitment to empowerment drives transformational workplace culture and sustained performance.
Decision-making Authority
Situational leadership adapts decision-making authority based on the followers' competence and commitment levels, allowing leaders to shift between directing, coaching, supporting, and delegating roles for optimal team performance. Servant leadership, however, prioritizes empowering team members by distributing decision-making authority and focusing on their growth and well-being, fostering a collaborative environment. Explore further to understand how these leadership styles impact organizational dynamics and employee engagement.
Source and External Links
What is Situational Leadership? (4 Styles and Examples) - Situational leadership involves adapting the leadership style to suit the current work environment and team needs, incorporating elements like direction, flexibility, and delegation.
The Four Leadership Styles of Situational Leadership - Situational leaders use four styles--Telling, Selling, Participating, and Delegating--each tailored to the follower's ability and willingness to perform tasks.
Situational Leadership - This framework helps leaders tailor their approach based on the work to be accomplished, the follower's ability and willingness, and the leader's style.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com